Spaghetti in PTFE
Spaghetti in PTFE
Spaghetti in PTFE
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
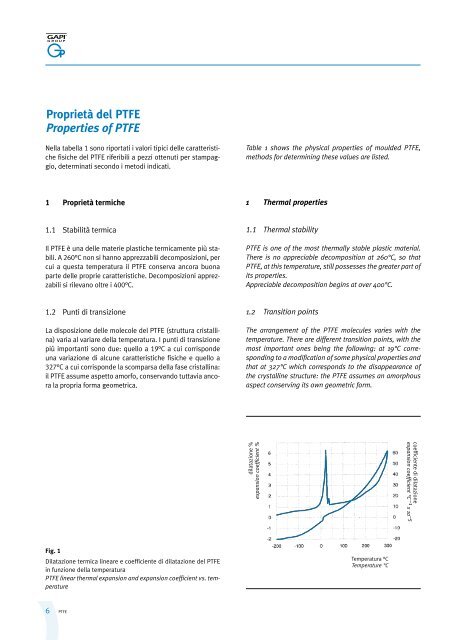
Proprietà del <strong>PTFE</strong>Properties of <strong>PTFE</strong>Nella tabella 1 sono riportati i valori tipici delle caratteristichefisiche del <strong>PTFE</strong> riferibili a pezzi ottenuti per stampaggio,determ<strong>in</strong>ati secondo i metodi <strong>in</strong>dicati.Table 1 shows the physical properties of moulded <strong>PTFE</strong>,methods for determ<strong>in</strong><strong>in</strong>g these values are listed.1 Proprietà termiche1 Thermal properties1.1 Stabilità termicaIl <strong>PTFE</strong> è una delle materie plastiche termicamente più stabili.A 260°C non si hanno apprezzabili decomposizioni, percui a questa temperatura il <strong>PTFE</strong> conserva ancora buonaparte delle proprie caratteristiche. Decomposizioni apprezzabilisi rilevano oltre i 400°C.1.1 Thermal stability<strong>PTFE</strong> is one of the most thermally stable plastic material.There is no appreciable decomposition at 260°C, so that<strong>PTFE</strong>, at this temperature, still possesses the greater part ofits properties.Appreciable decomposition beg<strong>in</strong>s at over 400°C.1.2 Punti di transizioneLa disposizione delle molecole del <strong>PTFE</strong> (struttura cristall<strong>in</strong>a)varia al variare della temperatura. I punti di transizionepiù importanti sono due: quello a 19°C a cui corrispondeuna variazione di alcune caratteristiche fisiche e quello a327°C a cui corrisponde la scomparsa della fase cristall<strong>in</strong>a:il <strong>PTFE</strong> assume aspetto amorfo, conservando tuttavia ancorala propria forma geometrica.1.2 Transition po<strong>in</strong>tsThe arrangement of the <strong>PTFE</strong> molecules varies with thetemperature. There are different transition po<strong>in</strong>ts, with themost important ones be<strong>in</strong>g the follow<strong>in</strong>g: at 19°C correspond<strong>in</strong>gto a modification of some physical properties andthat at 327°C which corresponds to the disappearance ofthe crystall<strong>in</strong>e structure: the <strong>PTFE</strong> assumes an amorphousaspect conserv<strong>in</strong>g its own geometric form.dilatazione %expansion coefficient %coefficiente di dilatazioneexpansion coefficient °C –1 x 10 –5Fig. 1Dilatazione termica l<strong>in</strong>eare e coefficiente di dilatazione del <strong>PTFE</strong><strong>in</strong> funzione della temperatura<strong>PTFE</strong> l<strong>in</strong>ear thermal expansion and expansion coefficient vs. temperatureTemperatura °CTemperature °C6<strong>PTFE</strong>