Tema 9. Productos derivados de los hidrocarburos aromáticos
Tema 9. Productos derivados de los hidrocarburos aromáticos
Tema 9. Productos derivados de los hidrocarburos aromáticos
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
<strong>Tema</strong> <strong>9.</strong> <strong>Productos</strong> <strong><strong>de</strong>rivados</strong> <strong>de</strong> <strong>los</strong> <strong>hidrocarburos</strong> <strong>aromáticos</strong> 1<br />
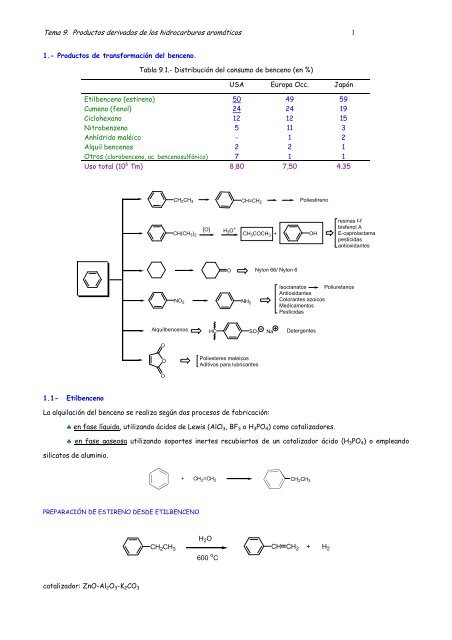
1.- <strong>Productos</strong> <strong>de</strong> transformación <strong>de</strong>l benceno.<br />
1.1- Etilbenceno<br />
Tabla <strong>9.</strong>1.- Distribución <strong>de</strong>l consumo <strong>de</strong> benceno (en %)<br />
USA Europa Occ. Japón<br />
Etilbenceno (estireno) 50 49 59<br />
Cumeno (fenol) 24 24 19<br />
Ciclohexano 12 12 15<br />
Nitrobenzeno 5 11 3<br />
Anhídrido maléico - 1 2<br />
Alquil bencenos 2 2 1<br />
Otros (clorobenceno, ac. bencenosulfónico) 7 1 1<br />
Uso total (10 6 Tm) 8,80 7,50 4.35<br />
CH 2CH 3 CH=CH2 Poliestireno<br />
CH(CH 3) 2<br />
NO 2<br />
[O] H 3O +<br />
O<br />
CH 3COCH 3 +<br />
NH2<br />
Nylon 66/ Nylon 6<br />
OH<br />
Isocianatos Poliuretanos<br />
Antioxidantes<br />
Colorantes azoicos<br />
Medicamentos<br />
Pesticidas<br />
Alquilbencenos HC<br />
SO3 Na Detergentes<br />
O<br />
O<br />
O<br />
Poliesteres maleicos<br />
Aditivos para lubricantes<br />
La alquilación <strong>de</strong>l benceno se realiza según dos procesos <strong>de</strong> fabricación:<br />
♣ en fase líquida, utilizando ácidos <strong>de</strong> Lewis (AlCl 3, BF 3 o H 3PO 4) como catalizadores.<br />
resinas f-f<br />
bisfenol A<br />
E-caprolactama<br />
pesticidas<br />
antioxidantes<br />
♣ en fase gaseosa utilizando soportes inertes recubiertos <strong>de</strong> un catalizador ácido (H 3PO 4) o empleando<br />
silicatos <strong>de</strong> aluminio.<br />
PREPARACIÓN DE ESTIRENO DESDE ETILBENCENO<br />
catalizador: ZnO-Al2O 3-K 2CO 3<br />
CH 2CH 3<br />
+ CH 2=CH 2 CH2CH 3<br />
H 2O<br />
600 o C<br />
CH CH 2 + H 2
<strong>Tema</strong> <strong>9.</strong> <strong>Productos</strong> <strong><strong>de</strong>rivados</strong> <strong>de</strong> <strong>los</strong> <strong>hidrocarburos</strong> <strong>aromáticos</strong> 2<br />
Tabla <strong>9.</strong>2.- Uso <strong>de</strong> estireno (en %)<br />
Mundo USA Europa Occ. Japón<br />
Pliestireno 63 66 66 54<br />
SBR 11 12 13 9<br />
ABS 12 7 8 14<br />
SAN 1 1 4<br />
Resinas poliester 4 7 6 5<br />
Otros 9 8 6 14<br />
SBR: estireno-butadieno rubber; ABS: acrilonitrilo-butadieno-estireno; SAN: estireno-acrilonitrilo<br />
1.2.1- Cumeno.<br />
El proceso <strong>de</strong> fabricación se realiza en fase líquida, (AlCl 3) o en en fase gaseosa (H 3PO 4/SiO 2)<br />
+ CH 2=CHCH 3<br />
PREPARACIÓN DE FENOL DESDE CUMENO<br />
CH(CH 3) 2<br />
O 2<br />
cat.<br />
CH3 C O-OH<br />
CH3 H 3O<br />
CH(CH 3) 2<br />
OH + CH 3COCH 3<br />
Tb = 153 o C Tb = 182 o C Tb = 56 o C<br />
Diagrama <strong>de</strong> la fabricación <strong>de</strong> fenol y acetona <strong>de</strong>s<strong>de</strong> benceno
<strong>Tema</strong> <strong>9.</strong> <strong>Productos</strong> <strong><strong>de</strong>rivados</strong> <strong>de</strong> <strong>los</strong> <strong>hidrocarburos</strong> <strong>aromáticos</strong> 3<br />
BISFENOL A:<br />
ALQUILFENOLES:<br />
Tabla <strong>9.</strong>3. Aplicaciones <strong>de</strong>l fenol (en %)<br />
Mundo USA Japón Europa Occ.<br />
Resinas fenólicas 37 34 30 27<br />
ε-caprolactama 15 15 - 21<br />
Bisfenol A 32 37 42 28<br />
Ác. adípico 2 1 - 2<br />
Alquilfenoles 2 4 4 5<br />
Otros* 12 9 24 17<br />
Uso total (en 10 6 Tm) 6,1 2,15 0,61 1,65<br />
* anilina, clorofenol, plastificantes, antioxidantes<br />
HO (CH 2) 8-CH 3<br />
OH + CH 3COCH 3<br />
H 3C OH<br />
H 3O<br />
antioxidante para caucho intermedio para plaguicidas,<br />
colorantes y medicamentos<br />
1.3- Ciclohexano<br />
+ H 2<br />
R<br />
R<br />
200 o C/30 atm<br />
Ni<br />
HO<br />
OH<br />
CH3 C<br />
CH3 Cl<br />
Cl<br />
OH<br />
Cl<br />
Cl Cl<br />
OH<br />
fungicida <strong>de</strong>sinfectante para ma<strong>de</strong>ras<br />
El ciclohexano obtenido se transforma en ciclohexanona que es un producto intermedio para acce<strong>de</strong>r a <strong>los</strong><br />
precursores <strong>de</strong>l Nylon 6 y 66: ácido adípico, hexametiléndiamina y ε-caprolactama.<br />
1.4- Nitrobenceno.<br />
O<br />
aire<br />
H<br />
o<br />
HOOC-(CH 2) 4-COOH<br />
+<br />
HNO 3<br />
1. 2 NH 3<br />
H 2SO 4/H 2O<br />
HOOC(CH 2) 4COOH<br />
NH 2(CH 2) 6NH 2<br />
O<br />
NH<br />
Nylon 6<br />
Nylon 66<br />
2. <strong>de</strong>shidr. NC-(CH 2) 4-CN H 2N-(CH 2) 6-NH 2<br />
H 2<br />
NO2 + H3O H-O-NO 2 + H 2SO 4 H-O-NO 2<br />
H<br />
H-O-NO 2<br />
H<br />
+ HSO 4<br />
NO 2 + H 2O<br />
electrófilo<br />
+ HSO 4
<strong>Tema</strong> <strong>9.</strong> <strong>Productos</strong> <strong><strong>de</strong>rivados</strong> <strong>de</strong> <strong>los</strong> <strong>hidrocarburos</strong> <strong>aromáticos</strong> 4<br />
1.5- Alquilbencenos.<br />
1.6- Anhídrido maleico<br />
parafinas<br />
+ 4,5 O 2<br />
AlCl 3<br />
1. SO 3/aire<br />
2. NaOH/agua<br />
O<br />
O<br />
O<br />
SO 3<br />
Na<br />
+ 2 CO 2 + 2 H 2O<br />
Diagrama <strong>de</strong> la fabricación <strong>de</strong>l anhídrido maleico
<strong>Tema</strong> <strong>9.</strong> <strong>Productos</strong> <strong><strong>de</strong>rivados</strong> <strong>de</strong> <strong>los</strong> <strong>hidrocarburos</strong> <strong>aromáticos</strong> 5<br />
2.-<br />
<strong>Productos</strong> <strong>de</strong> transformación <strong>de</strong>l tolueno.<br />
CH 3<br />
50%<br />
10%<br />
30%<br />
10%<br />
O 2N<br />
CH 3<br />
NO 2<br />
+ CH 4<br />
CH 3<br />
NO 2<br />
NO 2<br />
NO2 H2 fase liq.<br />
Disolvente<br />
Aditivo para gasolina<br />
3.- <strong>Productos</strong> <strong>de</strong> transformación <strong>de</strong> <strong>los</strong> xilenos.<br />
3.1.-<br />
<strong>Productos</strong> <strong>de</strong> transformación <strong>de</strong>l o-xileno<br />
CH 3<br />
CH 3<br />
3.2.-<br />
<strong>Productos</strong> <strong>de</strong> transformación <strong>de</strong>l p-xileno<br />
CH 3<br />
CH 3<br />
3.3.- <strong>Productos</strong> <strong>de</strong> transformación <strong>de</strong>l m-xileno<br />
O<br />
O<br />
O<br />
Exp<strong>los</strong>ivo<br />
COOMe<br />
COOMe<br />
pureza > 99,99%<br />
CH 3<br />
NO 2<br />
R-OH<br />
NH 2<br />
- Disolvente<br />
- Aditivo para aumentar el índice <strong>de</strong> octanos <strong>de</strong> las gasolinas<br />
Cl 2CO<br />
COOR<br />
COOR<br />
CH 3<br />
N=C=O<br />
N=C=O<br />
Plastificantes<br />
R= n-alcoholes (4-11) y 2-etilhexanol<br />
Resinas alquídicas<br />
(poliesteres con glicerina, propilenglicol y otros)<br />
Fibras y películas <strong>de</strong> poliester<br />
Poliuretanos