Tamara Zulim_diplomski rad - Sveučilišni odjel za forenzične ...
Tamara Zulim_diplomski rad - Sveučilišni odjel za forenzične ...
Tamara Zulim_diplomski rad - Sveučilišni odjel za forenzične ...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
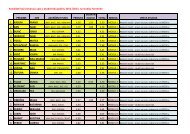
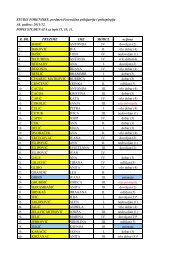
ZULIM, T.: Application of physico-chemical analyses in optimi<strong>za</strong>tion of bone samplesnumber for DNA analysis. G<strong>rad</strong>uate thesisAbstractIn cases where it is necessary to determine the identity of a large number of skeletal remainsusing DNA typing techniques, due to the high cost of the analysis as well as the possibility offailure because of contamination and deg<strong>rad</strong>ation of DNA, prior proceedings and analysis arerequired to optimize the number of bone samples for DNA analysis. The aim of this studywas to verify the usability and features offered by physico-chemical analyses, asrepresentatives of "classical" methods, in the process of matching fragments of left and rightfemurs belonging to skeletal remains exhumed in September 2009. from two mass graves onthe island Daksa near Dubrovnik. At the same time the performance of these analyses wasverified by the results of previously conducted DNA analysis of bone fragments thereof as aninevitable confirmation/denial of pairing results obtained by physico-chemical analyses.Physico-chemical analyses of 94 bone fragments included; measurement of the outer diameterof bone fragments; densitometry of the fragments; measurement of mass and volume offragments; determination of average bone density on the basis of measured values of the massand volume. The results of fragment matching by physico-chemical analyses were comparedwith the pairing results obtained by previously conducted DNA analysis. A deviation inmeasured values from matching bone fragments that make a pair was calculated for allsuccessfully matched fragments.36 pairs of femurs were successfully matched by DNA analysis. 29 pairs of femurs weresuccessfully matched based on the results of physico-chemical analyses. Success of theanalyses was expressed as a percentage with a value of 75.86%. The largest proportion ofmatched femur fragments were matched according to the measured values of theseparameters; femur lengths (25.9%) and diameter of femur heads (51.7%).Optimi<strong>za</strong>tion of the number of bone fragment samples by physico-chemical analyses used inthe procedure of matching left and right femur fragments and thereby reducing the number ofsamples for DNA analysis that follows, was not proven fully successful.Keywords: identification, skeletal remains, DNA analysis, physico-chemical analyses, thethigh bone (lat. femur)32