who guideline on quality risk management - World Health ...
who guideline on quality risk management - World Health ...
who guideline on quality risk management - World Health ...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
Working document QAS/10.376<br />
page 20<br />
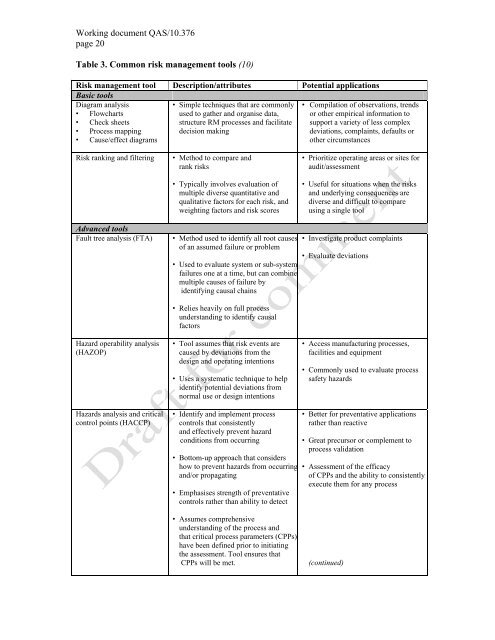
Table 3. Comm<strong>on</strong> <strong>risk</strong> <strong>management</strong> tools (10)<br />
Risk <strong>management</strong> tool Descripti<strong>on</strong>/attributes Potential applicati<strong>on</strong>s<br />
Basic tools<br />
Diagram analysis<br />
• Flowcharts<br />
• Check sheets<br />
• Process mapping<br />
• Cause/effect diagrams<br />
• Simple techniques that are comm<strong>on</strong>ly<br />
used to gather and organise data,<br />
structure RM processes and facilitate<br />
decisi<strong>on</strong> making<br />
Risk ranking and filtering • Method to compare and<br />
rank <strong>risk</strong>s<br />
• Typically involves evaluati<strong>on</strong> of<br />
multiple diverse quantitative and<br />
qualitative factors for each <strong>risk</strong>, and<br />
weighting factors and <strong>risk</strong> scores<br />
Advanced tools<br />
Fault tree analysis (FTA) • Method used to identify all root causes<br />
of an assumed failure or problem<br />
Hazard operability analysis<br />
(HAZOP)<br />
Hazards analysis and critical<br />
c<strong>on</strong>trol points (HACCP)<br />
• Used to evaluate system or sub-system<br />
failures <strong>on</strong>e at a time, but can combine<br />
multiple causes of failure by<br />
identifying causal chains<br />
• Relies heavily <strong>on</strong> full process<br />
understanding to identify causal<br />
factors<br />
• Tool assumes that <strong>risk</strong> events are<br />
caused by deviati<strong>on</strong>s from the<br />
design and operating intenti<strong>on</strong>s<br />
• Uses a systematic technique to help<br />
identify potential deviati<strong>on</strong>s from<br />
normal use or design intenti<strong>on</strong>s<br />
• Identify and implement process<br />
c<strong>on</strong>trols that c<strong>on</strong>sistently<br />
and effectively prevent hazard<br />
c<strong>on</strong>diti<strong>on</strong>s from occurring<br />
• Bottom-up approach that c<strong>on</strong>siders<br />
how to prevent hazards from occurring<br />
and/or propagating<br />
• Emphasises strength of preventative<br />
c<strong>on</strong>trols rather than ability to detect<br />
• Assumes comprehensive<br />
understanding of the process and<br />
that critical process parameters (CPPs)<br />
have been defined prior to initiating<br />
the assessment. Tool ensures that<br />
CPPs will be met.<br />
• Compilati<strong>on</strong> of observati<strong>on</strong>s, trends<br />
or other empirical informati<strong>on</strong> to<br />
support a variety of less complex<br />
deviati<strong>on</strong>s, complaints, defaults or<br />
other circumstances<br />
• Prioritize operating areas or sites for<br />
audit/assessment<br />
• Useful for situati<strong>on</strong>s when the <strong>risk</strong>s<br />
and underlying c<strong>on</strong>sequences are<br />
diverse and difficult to compare<br />
using a single tool<br />
• Investigate product complaints<br />
• Evaluate deviati<strong>on</strong>s<br />
• Access manufacturing processes,<br />
facilities and equipment<br />
• Comm<strong>on</strong>ly used to evaluate process<br />
safety hazards<br />
• Better for preventative applicati<strong>on</strong>s<br />
rather than reactive<br />
• Great precursor or complement to<br />
process validati<strong>on</strong><br />
• Assessment of the efficacy<br />
of CPPs and the ability to c<strong>on</strong>sistently<br />
execute them for any process<br />
(c<strong>on</strong>tinued)