You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
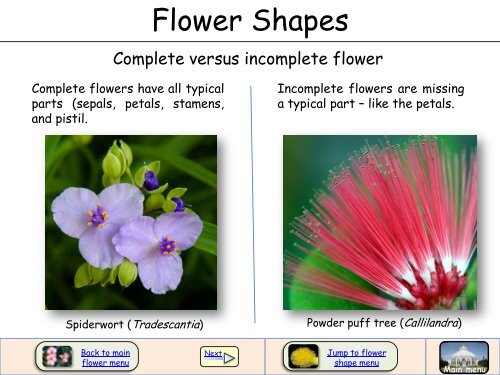
<strong>Flower</strong> <strong>Shapes</strong><br />
Complete versus incomplete flower<br />
Complete flowers have all typical<br />
parts (sepals, petals, stamens,<br />
and pistil.<br />
Spiderwort (Tradescantia)<br />
Back to main<br />
flower menu<br />
Incomplete flowers are missing<br />
a typical part – like the petals.<br />
Powder puff tree (Callilandra)<br />
Next Jump to flower<br />
shape menu<br />
Main menu
Perfect versus imperfect flowers<br />
Perfect flowers are bisexual<br />
with functioning male and female<br />
parts in the same flower.<br />
Ardisia (Ardisia)<br />
Back to main<br />
flower menu<br />
<strong>Flower</strong> <strong>Shapes</strong><br />
Back<br />
Next<br />
Imperfect flowers are unisexual<br />
with only male or female parts in<br />
a single flower.<br />
Hazelnut (Corylus) female flower<br />
Jump to flower<br />
shape menu<br />
Main menu
Dioecious versus monecious plants<br />
Dioecious plants have imperfect<br />
flowers and male and female flowers<br />
reside on separate plants.<br />
Holly (Ilex)<br />
female flower male flower<br />
<strong>Flower</strong> <strong>Shapes</strong><br />
Monecious plants contain imperfect<br />
flowers and the male and female<br />
flowers are on the same plant but in<br />
different locations.<br />
female flower<br />
Chestnut (Castanea)<br />
male flowers<br />
There are examples where monecious and dioecious plants can produce some perfect<br />
flowers. When they appear on the same plant it is called polygamo-monecious. When it<br />
occurs on plants with unisexual flowers on different plants it is polygamo-dioecious.<br />
Back to main<br />
flower menu<br />
Back Next<br />
Jump to flower<br />
shape menu<br />
Main menu
<strong>Flower</strong> <strong>Shapes</strong><br />
Monecious plants<br />
Begonia produces male and female flowers in different flowers in the cyme<br />
and they open at different times to reduce self pollination.<br />
female flower male flower<br />
Back to main<br />
flower menu<br />
Begonia (Begonia)<br />
female flowers<br />
Back Next<br />
Jump to flower<br />
shape menu<br />
male flowers<br />
Main menu
<strong>Flower</strong> <strong>Shapes</strong><br />
Monecious plants<br />
Pecan is a good example of a wind pollinated tree that produces male and<br />
female flowers on different flowers on the same tree.<br />
Female flower<br />
female flower male flower<br />
Back to main<br />
flower menu<br />
Pecan (Carya)<br />
Male flower<br />
Back Next<br />
Jump to flower<br />
shape menu<br />
Main menu
<strong>Flower</strong> <strong>Shapes</strong><br />
<strong>Flower</strong>s without petals (apetalous)<br />
It is generally accepted that showy or fragrant petals function to<br />
interact with insect or mammal pollinators. Their job is to signal the<br />
pollinator of a potential flower find and in the process facilitate pollen<br />
transfer within or between flowers.<br />
<strong>Flower</strong>s that are wind pollinated tend to have reduced or no petals and<br />
therefore no obstructions between flying pollen and the stigma.<br />
Date palm (Phoenix) Barley (Hordeum) Maple (Acer) Oak (Quercus)<br />
Back to main<br />
flower menu<br />
Back Next<br />
Jump to flower<br />
shape menu<br />
Main menu
<strong>Flower</strong> <strong>Shapes</strong><br />
Actinimorphic versus Zyomorphic flowers<br />
Actinimorphic flowers have a radial<br />
symmetry where the flower can be<br />
divided equally on two or more planes.<br />
Zygomorphic flowers have bilateral<br />
symmetry where the flower can be<br />
divided equally on only one plane.<br />
Primrose (Primula) Pansy (Viola)<br />
Back to main<br />
flower menu<br />
Back Next<br />
Jump to flower<br />
shape menu<br />
Main menu
Campanulate<br />
Coroniform<br />
Cruciform<br />
Cupuliform<br />
<strong>Flower</strong> <strong>Shapes</strong><br />
Some characteristic flower shapes<br />
Bellshaped<br />
Crownshaped<br />
Crossshaped<br />
Cupshaped<br />
Funnelform<br />
Inflated<br />
Labiate<br />
Funnelshaped<br />
bladdershaped<br />
Lip-like<br />
petals<br />
Cucullate Hooded Ligulate Strap-like<br />
Double<br />
With extra<br />
petals<br />
Back to main<br />
flower menu<br />
Papillionoid<br />
Reflexed<br />
Butterflyshaped<br />
Petals bent<br />
back<br />
Back Jump to flower<br />
shape menu<br />
Saccate<br />
Salverform<br />
Spurred<br />
Stellate<br />
Tubular<br />
Urceolate<br />
Slipper<br />
orchids<br />
Tube with<br />
flat lobes<br />
With a<br />
spur<br />
Starshaped<br />
Tubeshaped<br />
Urnshaped<br />
Main menu
Asia bell (Condonopsis)<br />
Back to main<br />
flower menu<br />
<strong>Flower</strong> <strong>Shapes</strong><br />
Campanulate<br />
Bell-shaped flowers formed by fused petals.<br />
Bell flower (Campanula)<br />
Back to flower<br />
shapes menu<br />
Redveined enkianthus<br />
(Enkianthus)<br />
Main menu
Daffodil (Narcissus)<br />
Coroniform<br />
<strong>Flower</strong>s with a corona (crown). A corona is a group of petal-like organs between<br />
the petals and stamens.<br />
Back to main<br />
flower menu<br />
<strong>Flower</strong> <strong>Shapes</strong><br />
Back to flower<br />
shapes menu<br />
Passion flower<br />
(Passiflora)<br />
Main menu
Mustard<br />
(Brassica nigra)<br />
Back to main<br />
flower menu<br />
<strong>Flower</strong> <strong>Shapes</strong><br />
Wallflower<br />
(Erysimum)<br />
Cruciform<br />
<strong>Flower</strong>s are cross-shaped with four petals.<br />
Phlox<br />
(Phlox)<br />
Back to flower<br />
shapes menu<br />
Bluets<br />
(Hedyotis)<br />
Main menu
Culcullate<br />
<strong>Flower</strong>s that are hooded by modified fused petals.<br />
Back to main<br />
flower menu<br />
<strong>Flower</strong> <strong>Shapes</strong><br />
Monk’s hood (Aconitum)<br />
Back to flower<br />
shapes menu<br />
Main menu
Cupuliform<br />
A cylindrical tube-like flower that does not have spreading petal tips.<br />
Tulip (Tulipa)<br />
Back to main<br />
flower menu<br />
<strong>Flower</strong> <strong>Shapes</strong><br />
Cup vine (Solandra)<br />
Back to flower<br />
shapes menu<br />
Main menu
A semi-double rose (Rosa).<br />
Double<br />
Double flowers have additional floral organs compared to the usual sets of four,<br />
five or six found in most plants. The extra organs are usually petals that have<br />
replaced stamens. A semi-double flower has additional petals but stamens still<br />
remain. A fully double flower has lost most or all stamens to petals.<br />
Back to main<br />
flower menu<br />
<strong>Flower</strong> <strong>Shapes</strong><br />
A fully double amaryllis (Hippeastrum).<br />
Back to flower<br />
shapes menu<br />
Main menu
<strong>Flower</strong> <strong>Shapes</strong><br />
Funnelform<br />
A funnel shaped flower that widens from the base to the top.<br />
Wild petunia (Ruellia) Gentian (Gentiana) Virginia blue bells<br />
(Mertensia)<br />
Back to main<br />
flower menu<br />
Back to flower<br />
shapes menu<br />
Main menu
<strong>Flower</strong> <strong>Shapes</strong><br />
Inflated<br />
Floral parts are swollen to form a bladder-like flower.<br />
Soapwort (Sapanaria) Bladdernut (Staphylea)<br />
Back to main<br />
flower menu<br />
Back to flower<br />
shapes menu<br />
Main menu
<strong>Flower</strong> <strong>Shapes</strong><br />
Labiate<br />
<strong>Flower</strong>s with lip-like petals. Those with distinctly two lips are called bilabiate.<br />
Those like turtlehead are also galeate meaning helmet shaped. Those like blue<br />
sage are ringent meaning gaping because of the distance between the two lips.<br />
Blue sage (Salvia) Bugleflower (Ajuga) Turtlehead (Chelone)<br />
Back to main<br />
flower menu<br />
Back to flower<br />
shapes menu<br />
Main menu
Ligulate<br />
<strong>Flower</strong>s with a strap-like petiole especially those in composite flowers.<br />
Back to main<br />
flower menu<br />
<strong>Flower</strong> <strong>Shapes</strong><br />
Zinnia (Zinnia)<br />
Back to flower<br />
shapes menu<br />
Main menu
<strong>Flower</strong> <strong>Shapes</strong><br />
Papillionoid<br />
Butterfly shaped flowers typical of some legumes. <strong>Flower</strong>s have petals modified<br />
into a large upper banner, two side wings, and two fused petals that form the lower<br />
keel that encloses the stamens.<br />
Yellowwood (Cladrastis) False indigo (Baptisia) Lupine (Lupinus)<br />
Back to main<br />
flower menu<br />
Back to flower<br />
shapes menu<br />
Main menu
Shooting star (Dodecatheron)<br />
petals are reflexed.<br />
<strong>Flower</strong> <strong>Shapes</strong><br />
Reflexed<br />
Some flowers have petals that bend backwards. Petals that are fully bent are<br />
called reflexed, while those partially bent are called recurved.<br />
Back to main<br />
flower menu<br />
Lily (Lillium) petals are<br />
recurved.<br />
Back to flower<br />
shapes menu<br />
Main menu
Saccate<br />
A flower with petals shaped like a sac as occurs in slipper orchids.<br />
South American slipper orchid<br />
(Phragmipedium)<br />
Back to main<br />
flower menu<br />
<strong>Flower</strong> <strong>Shapes</strong><br />
Slipper orchid<br />
(Paphiopedilum)<br />
Back to flower<br />
shapes menu<br />
Kentucky lady slipper<br />
(Cypripedium kentuckiense)<br />
Main menu
<strong>Flower</strong> <strong>Shapes</strong><br />
Salverform<br />
Tubular flowers that become spreading at the top.<br />
Primrose (Primula) Rhododendron (Rhododendron)<br />
Back to main<br />
flower menu<br />
Back to flower<br />
shapes menu<br />
Main menu
Spurred<br />
Spurred flowers have a petal(s) modified into a spur. The spur is usually nectar<br />
containing to attract pollinators.<br />
Back to main<br />
flower menu<br />
<strong>Flower</strong> <strong>Shapes</strong><br />
Delphinium (Delphinium)<br />
Back to flower<br />
shapes menu<br />
Main menu
Columbine (Aquilegia)<br />
<strong>Flower</strong> <strong>Shapes</strong><br />
Spurred<br />
Spurred flowers have a petal(s) modified into a spur. The spur is usually nectar<br />
containing to attract pollinators.<br />
Back to main<br />
flower menu<br />
Nasturtium (Tropaeolum) Jewelweed (Impatiens)<br />
Back to flower<br />
shapes menu<br />
Main menu
<strong>Flower</strong> <strong>Shapes</strong><br />
Stellate<br />
Stellate flowers are star-shaped often with five petals.<br />
Jasmine (Jasminum) Fire pink (Silene) Pink (Dianthus)<br />
Back to main<br />
flower menu<br />
Back to flower<br />
shapes menu<br />
Main menu
<strong>Flower</strong> <strong>Shapes</strong><br />
Tubular<br />
A cylindrical tube-like flower that does not have spreading petal tips.<br />
Fuschia (Fuschia) Iochroma (Iochroma)<br />
Back to main<br />
flower menu<br />
Back to flower<br />
shapes menu<br />
Pinkroot (Spigelia)<br />
Main menu
Back to main<br />
flower menu<br />
<strong>Flower</strong> <strong>Shapes</strong><br />
Grape hyacinth<br />
(Muscari)<br />
Urceolate<br />
These flowers are urn or pitcher-like in shape.<br />
Andromeda<br />
(Pieris)<br />
Back to flower<br />
shapes menu<br />
Main menu