3 Fourier Series Representation of Periodic Signals
3 Fourier Series Representation of Periodic Signals
3 Fourier Series Representation of Periodic Signals
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
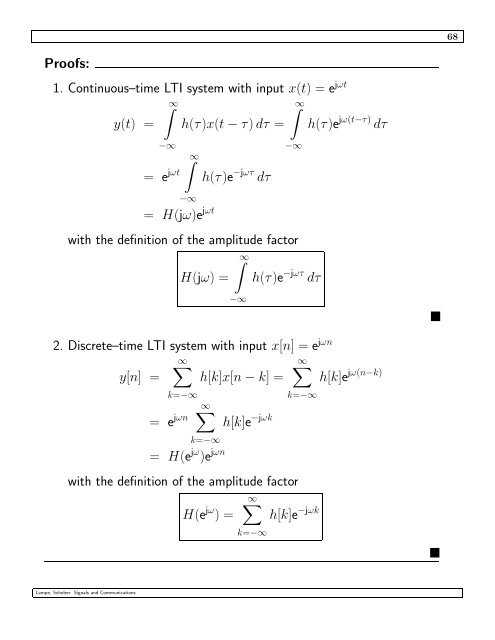
Pro<strong>of</strong>s:<br />
1. Continuous–time LTI system with input x(t) = ejωt ∞<br />
∞<br />
y(t) = h(τ)x(t − τ) dτ = h(τ)e jω(t−τ) dτ<br />
−∞<br />
= e jωt<br />
∞<br />
−∞<br />
= H(jω)e jωt<br />
h(τ)e −jωτ dτ<br />
−∞<br />
with the definition <strong>of</strong> the amplitude factor<br />
∞<br />
H(jω) = h(τ)e −jωτ dτ<br />
−∞<br />
2. Discrete–time LTI system with input x[n] = ejωn y[n] =<br />
∞<br />
h[k]x[n − k] =<br />
∞<br />
k=−∞<br />
= e jωn<br />
∞<br />
k=−∞<br />
= H(e jω )e jωn<br />
h[k]e −jωk<br />
with the definition <strong>of</strong> the amplitude factor<br />
H(e jω ∞<br />
) =<br />
Lampe, Schober: <strong>Signals</strong> and Communications<br />
k=−∞<br />
k=−∞<br />
h[k]e −jωk<br />
h[k]e jω(n−k)<br />
<br />
<br />
68