A Patient's Guide to Prostate Cancer - Prostate Cancer Centre
A Patient's Guide to Prostate Cancer - Prostate Cancer Centre
A Patient's Guide to Prostate Cancer - Prostate Cancer Centre
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
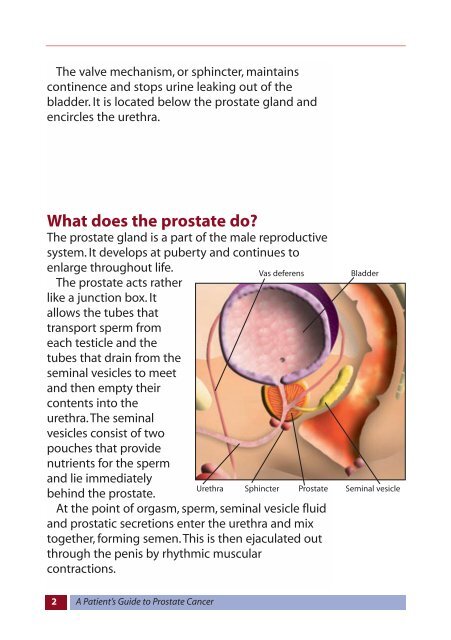
The valve mechanism, or sphincter, maintains<br />
continence and s<strong>to</strong>ps urine leaking out of the<br />
bladder. It is located below the prostate gland and<br />
encircles the urethra.<br />
What does the prostate do?<br />
The prostate gland is a part of the male reproductive<br />
system. It develops at puberty and continues <strong>to</strong><br />
enlarge throughout life.<br />
The prostate acts rather<br />
like a junction box. It<br />
allows the tubes that<br />
transport sperm from<br />
each testicle and the<br />
tubes that drain from the<br />
seminal vesicles <strong>to</strong> meet<br />
and then empty their<br />
contents in<strong>to</strong> the<br />
urethra. The seminal<br />
vesicles consist of two<br />
pouches that provide<br />
nutrients for the sperm<br />
and lie immediately<br />
behind the prostate.<br />
At the point of orgasm, sperm, seminal vesicle fluid<br />
and prostatic secretions enter the urethra and mix<br />
<strong>to</strong>gether, forming semen. This is then ejaculated out<br />
through the penis by rhythmic muscular<br />
contractions.<br />
2<br />
A Patient’s <strong>Guide</strong> <strong>to</strong> <strong>Prostate</strong> <strong>Cancer</strong><br />
Vas deferens<br />
Bladder<br />
Urethra Sphincter <strong>Prostate</strong> Seminal vesicle