Removal of solvent-based ink from printed surface of HDPE bottles ...
Removal of solvent-based ink from printed surface of HDPE bottles ...
Removal of solvent-based ink from printed surface of HDPE bottles ...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
986<br />
<strong>surface</strong> to become more positive. The <strong>of</strong>fered explanation<br />
agreed well with the point <strong>of</strong> charge reversal (PZC)<br />
observed in Fig. 7 (i.e., blown-up plots <strong>from</strong> Fig. 5a shown<br />
with the linear scale on the x-axis). With increasing alkyl<br />
chain length <strong>of</strong> the CnTAB molecules, the PZC was<br />
observed at about 0.17 mM for DTAB, 0.07 mM for TTAB,<br />
and 0.03 mM for CTAB. Therefore, charge reversal <strong>of</strong> the<br />
<strong>ink</strong> occurs at a lower concentration as the alkyl chain length<br />
<strong>of</strong> the surfactant increases. The results are consistent with<br />
the observed increase in the wettability with increasing<br />
alkyl chain length <strong>of</strong> the CnTAB molecules in the framework<br />
<strong>of</strong> increasing surfactant adsorption with increasing<br />
alkyl chain length and increasing surfactant concentration.<br />
Solubilization<br />
Solubilization <strong>of</strong> <strong>ink</strong> binder in surfactant micelles is a very<br />
important step for the de<strong>ink</strong>ing process. <strong>Removal</strong> <strong>of</strong> the<br />
binder <strong>from</strong> the <strong>surface</strong> is necessary to permit removal <strong>of</strong><br />
the colored pigment particles (de<strong>ink</strong>ing). It has been<br />
hypothesized in a previous work that it is the negative<br />
charge on the binder (carboxylate groups) which is the<br />
cause <strong>of</strong> the effectiveness <strong>of</strong> cationic surfactants relative to<br />
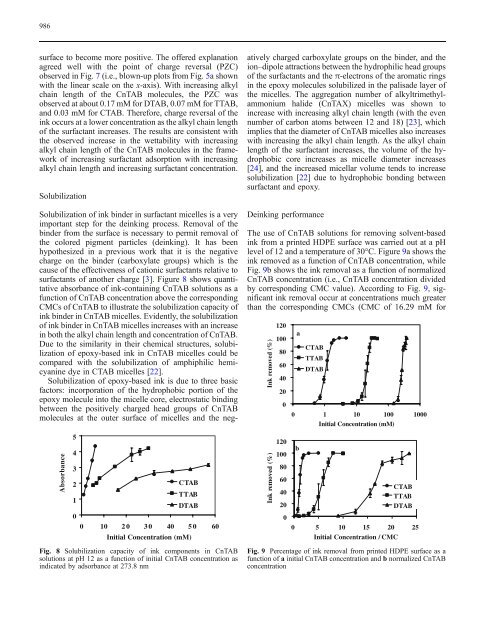
surfactants <strong>of</strong> another charge [3]. Figure 8 shows quantitative<br />
absorbance <strong>of</strong> <strong>ink</strong>-containing CnTAB solutions as a<br />
function <strong>of</strong> CnTAB concentration above the corresponding<br />
CMCs <strong>of</strong> CnTAB to illustrate the solubilization capacity <strong>of</strong><br />
<strong>ink</strong> binder in CnTAB micelles. Evidently, the solubilization<br />
<strong>of</strong> <strong>ink</strong> binder in CnTAB micelles increases with an increase<br />
in both the alkyl chain length and concentration <strong>of</strong> CnTAB.<br />
Due to the similarity in their chemical structures, solubilization<br />
<strong>of</strong> epoxy-<strong>based</strong> <strong>ink</strong> in CnTAB micelles could be<br />
compared with the solubilization <strong>of</strong> amphiphilic hemicyanine<br />
dye in CTAB micelles [22].<br />
Solubilization <strong>of</strong> epoxy-<strong>based</strong> <strong>ink</strong> is due to three basic<br />
factors: incorporation <strong>of</strong> the hydrophobic portion <strong>of</strong> the<br />
epoxy molecule into the micelle core, electrostatic binding<br />
between the positively charged head groups <strong>of</strong> CnTAB<br />
molecules at the outer <strong>surface</strong> <strong>of</strong> micelles and the neg-<br />
Absorbance<br />
5<br />
4<br />
3<br />
2<br />
CTAB<br />
1<br />
0<br />
TTAB<br />
DTAB<br />
0 10 20 30 40 50 60<br />
Initial Concentration (mM)<br />
Fig. 8 Solubilization capacity <strong>of</strong> <strong>ink</strong> components in CnTAB<br />
solutions at pH 12 as a function <strong>of</strong> initial CnTAB concentration as<br />
indicated by adsorbance at 273.8 nm<br />
atively charged carboxylate groups on the binder, and the<br />
ion–dipole attractions between the hydrophilic head groups<br />
<strong>of</strong> the surfactants and the π-electrons <strong>of</strong> the aromatic rings<br />
in the epoxy molecules solubilized in the palisade layer <strong>of</strong><br />
the micelles. The aggregation number <strong>of</strong> alkyltrimethylammonium<br />
halide (CnTAX) micelles was shown to<br />
increase with increasing alkyl chain length (with the even<br />
number <strong>of</strong> carbon atoms between 12 and 18) [23], which<br />
implies that the diameter <strong>of</strong> CnTAB micelles also increases<br />
with increasing the alkyl chain length. As the alkyl chain<br />
length <strong>of</strong> the surfactant increases, the volume <strong>of</strong> the hydrophobic<br />
core increases as micelle diameter increases<br />
[24], and the increased micellar volume tends to increase<br />
solubilization [22] due to hydrophobic bonding between<br />
surfactant and epoxy.<br />
De<strong>ink</strong>ing performance<br />
The use <strong>of</strong> CnTAB solutions for removing <strong>solvent</strong>-<strong>based</strong><br />
<strong>ink</strong> <strong>from</strong> a <strong>printed</strong> <strong>HDPE</strong> <strong>surface</strong> was carried out at a pH<br />
level <strong>of</strong> 12 and a temperature <strong>of</strong> 30°C. Figure 9a shows the<br />
<strong>ink</strong> removed as a function <strong>of</strong> CnTAB concentration, while<br />
Fig. 9b shows the <strong>ink</strong> removal as a function <strong>of</strong> normalized<br />
CnTAB concentration (i.e., CnTAB concentration divided<br />
by corresponding CMC value). According to Fig. 9, significant<br />
<strong>ink</strong> removal occur at concentrations much greater<br />
than the corresponding CMCs (CMC <strong>of</strong> 16.29 mM for<br />
Ink removed (%)<br />
Ink removed (%)<br />
120<br />
100<br />
80<br />
60<br />
40<br />
20<br />
0<br />
120<br />
100<br />
80<br />
60<br />
40<br />
20<br />
0<br />
a<br />
CTAB<br />
TTAB<br />
DTAB<br />
0 1 10 100 1000<br />
Initial Concentration (mM)<br />
b<br />
CTAB<br />
TTAB<br />
DTAB<br />
0 5 10 15 20 25<br />
Initial Concentration / CMC<br />
Fig. 9 Percentage <strong>of</strong> <strong>ink</strong> removal <strong>from</strong> <strong>printed</strong> <strong>HDPE</strong> <strong>surface</strong> as a<br />
function <strong>of</strong> a initial CnTAB concentration and b normalized CnTAB<br />
concentration