Removal of solvent-based ink from printed surface - The Petroleum ...
Removal of solvent-based ink from printed surface - The Petroleum ...
Removal of solvent-based ink from printed surface - The Petroleum ...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
168 A. Chotipong et al. / Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochem. Eng. Aspects 297 (2007) 163–171<br />
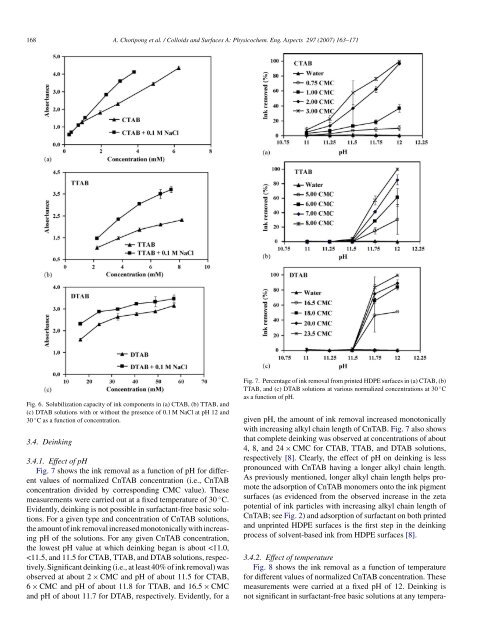
Fig. 6. Solubilization capacity <strong>of</strong> <strong>ink</strong> components in (a) CTAB, (b) TTAB, and<br />
(c) DTAB solutions with or without the presence <strong>of</strong> 0.1 M NaCl at pH 12 and<br />
30 ◦ C as a function <strong>of</strong> concentration.<br />
3.4. De<strong>ink</strong>ing<br />
3.4.1. Effect <strong>of</strong> pH<br />
Fig. 7 shows the <strong>ink</strong> removal as a function <strong>of</strong> pH for different<br />
values <strong>of</strong> normalized CnTAB concentration (i.e., CnTAB<br />
concentration divided by corresponding CMC value). <strong>The</strong>se<br />
measurements were carried out at a fixed temperature <strong>of</strong> 30 ◦ C.<br />
Evidently, de<strong>ink</strong>ing is not possible in surfactant-free basic solutions.<br />
For a given type and concentration <strong>of</strong> CnTAB solutions,<br />
the amount <strong>of</strong> <strong>ink</strong> removal increased monotonically with increasing<br />
pH <strong>of</strong> the solutions. For any given CnTAB concentration,<br />
the lowest pH value at which de<strong>ink</strong>ing began is about