Veenstra 170 - Anxiety Disorders Association of America
Veenstra 170 - Anxiety Disorders Association of America
Veenstra 170 - Anxiety Disorders Association of America
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
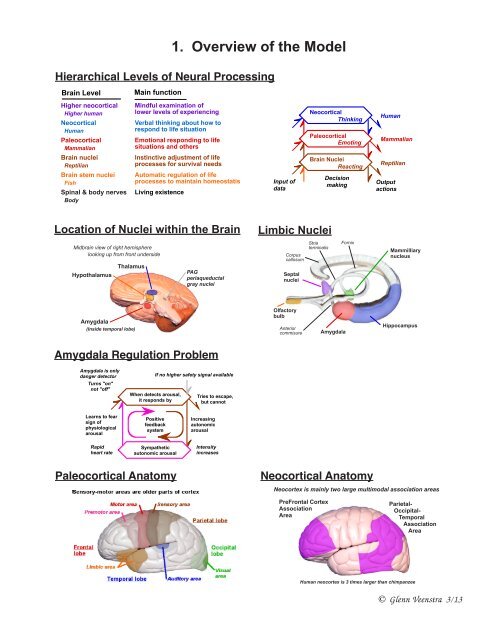
1. Overview <strong>of</strong> the Model<br />
Hierarchical Levels <strong>of</strong> Neural Processing<br />
Brain Level<br />
Higher neocortical<br />
Higher human<br />
Neocortical<br />
Human<br />
Paleocortical<br />
Mammalian<br />
Brain nuclei<br />
Reptilian<br />
Brain stem nuclei<br />
Fish<br />
Spinal & body nerves<br />
Body<br />
Main function<br />
Mindful examination <strong>of</strong><br />
lower levels <strong>of</strong> experiencing<br />
Verbal thinking about how to<br />
respond to life situation<br />
Emotional responding to life<br />
situations and others<br />
Instinctive adjustment <strong>of</strong> life<br />
processes for survival needs<br />
Automatic regulation <strong>of</strong> life<br />
processes to maintain homeostatis<br />
Living existence<br />
Location <strong>of</strong> Nuclei within the Brain<br />
Midbrain view <strong>of</strong> right hemisphere<br />
looking up from front underside<br />
Hypothalamus<br />
Thalamus<br />
Amygdala<br />
(Inside temporal lobe)<br />
PAG<br />
periaqueductal<br />
gray nuclei<br />
Amygdala Regulation Problem<br />
Amygdala is only<br />
danger detector<br />
Turns "on"<br />
not "<strong>of</strong>f"<br />
Learns to fear<br />
sign <strong>of</strong><br />
physiological<br />
arousal<br />
Rapid<br />
heart rate<br />
When detects arousal,<br />
it responds by<br />
Positive<br />
feedback<br />
system<br />
Sympathetic<br />
autonomic arousal<br />
Paleocortical Anatomy<br />
If no higher safety signal available<br />
Tries to escape,<br />
but cannot<br />
Increasing<br />
autonomic<br />
arousal<br />
Intensity<br />
increases<br />
Input <strong>of</strong><br />
data<br />
Limbic Nuclei<br />
Stria<br />
terminalis<br />
Corpus<br />
callosum<br />
Septal<br />
nuclei<br />
Olfactory<br />
bulb<br />
Anterior<br />
commisure<br />
Neocortical<br />
Thinking<br />
Paleocortical<br />
Emoting<br />
Brain Nuclei<br />
Reacting<br />
Decision<br />
making<br />
Amygdala<br />
Fornix<br />
Neocortical Anatomy<br />
PreFrontal Cortex<br />
<strong>Association</strong><br />
Area<br />
Human<br />
Mammalian<br />
Reptilian<br />
Output<br />
actions<br />
Mammilliary<br />
nucleus<br />
Hippocampus<br />
Neocortex is mainly two large multimodal association areas<br />
Parietal-<br />
Occipital-<br />
Temporal<br />
<strong>Association</strong><br />
Area<br />
Human neocortex is 3 times larger than chimpanzee<br />
© Glenn <strong>Veenstra</strong> 3/13