Ch05 Molecular Structure and Orbitals.pdf - finedrafts
Ch05 Molecular Structure and Orbitals.pdf - finedrafts
Ch05 Molecular Structure and Orbitals.pdf - finedrafts
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
V<br />
V<br />
V<br />
V<br />
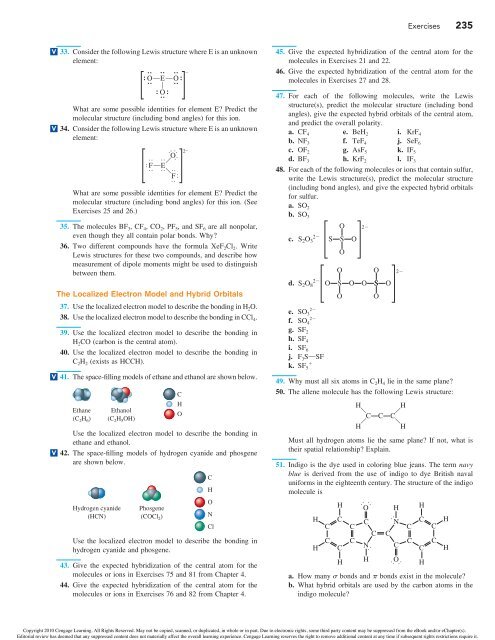
33. Consider the following Lewis structure where E is an unknown<br />
element:<br />
OOEOO A<br />
O<br />
What are some possible identities for element E? Predict the<br />
molecular structure (including bond angles) for this ion.<br />
34. Consider the following Lewis structure where E is an unknown<br />
element:<br />
−<br />
O 2–<br />
D<br />
SOFOO Q QE<br />
G<br />
O<br />
QF<br />
S<br />
What are some possible identities for element E? Predict the<br />
molecular structure (including bond angles) for this ion. (See<br />
Exercises 25 <strong>and</strong> 26.)<br />
35. The molecules BF 3, CF 4, CO 2, PF 5, <strong>and</strong> SF 6 are all nonpolar,<br />
even though they all contain polar bonds. Why?<br />
36. Two different compounds have the formula XeF 2Cl 2. Write<br />
Lewis structures for these two compounds, <strong>and</strong> describe how<br />
measurement of dipole moments might be used to distinguish<br />
between them.<br />
The Localized Electron Model <strong>and</strong> Hybrid <strong>Orbitals</strong><br />
37. Use the localized electron model to describe the bonding in H 2O.<br />
38. Use the localized electron model to describe the bonding in CCl 4.<br />
39. Use the localized electron model to describe the bonding in<br />
H 2CO (carbon is the central atom).<br />
40. Use the localized electron model to describe the bonding in<br />
C 2H 2 (exists as HCCH).<br />
41. The space- lling models of ethane <strong>and</strong> ethanol are shown below.<br />
Ethane<br />
(C 2H 6)<br />
Ethanol<br />
(C 2H 5OH)<br />
Use the localized electron model to describe the bonding in<br />
ethane <strong>and</strong> ethanol.<br />
42. The space- lling models of hydrogen cyanide <strong>and</strong> phosgene<br />
are shown below.<br />
Hydrogen cyanide<br />
(HCN)<br />
Phosgene<br />
(COCl 2)<br />
Use the localized electron model to describe the bonding in<br />
hydrogen cyanide <strong>and</strong> phosgene.<br />
43. Give the expected hybridization of the central atom for the<br />
molecules or ions in Exercises 75 <strong>and</strong> 81 from Chapter 4.<br />
44. Give the expected hybridization of the central atom for the<br />
molecules or ions in Exercises 76 <strong>and</strong> 82 from Chapter 4.<br />
Q<br />
Q<br />
Q<br />
C<br />
H<br />
O<br />
C<br />
H<br />
O<br />
N<br />
Cl<br />
Exercises 235<br />
45. Give the expected hybridization of the central atom for the<br />
molecules in Exercises 21 <strong>and</strong> 22.<br />
46. Give the expected hybridization of the central atom for the<br />
molecules in Exercises 27 <strong>and</strong> 28.<br />
47. For each of the following molecules, write the Lewis<br />
structure(s), predict the molecular structure (including bond<br />
angles), give the expected hybrid orbitals of the central atom,<br />
<strong>and</strong> predict the overall polarity.<br />
a. CF 4 e. BeH 2 i. KrF 4<br />
b. NF 3 f. TeF 4 j. SeF 6<br />
c. OF 2 g. AsF 5 k. IF 5<br />
d. BF 3 h. KrF 2 l. IF 3<br />
48. For each of the following molecules or ions that contain sulfur,<br />
write the Lewis structure(s), predict the molecular structure<br />
(including bond angles), <strong>and</strong> give the expected hybrid orbitals<br />
for sulfur.<br />
a. SO 2<br />
b. SO 3<br />
c.<br />
d.<br />
O<br />
S 2O 3 2− S S<br />
O<br />
O<br />
O<br />
2−<br />
2− S2O8 O S O O S<br />
O<br />
e. SO 3 2<br />
f. SO 4 2<br />
g. SF 2<br />
h. SF 4<br />
i. SF 6<br />
j. F 3SOSF<br />
k. SF 5 <br />
O<br />
49. Why must all six atoms in C 2H 4 lie in the same plane?<br />
50. The allene molecule has the following Lewis structure:<br />
O<br />
O<br />
2−<br />
H<br />
H<br />
G<br />
CPCPC<br />
D<br />
H<br />
H<br />
Must all hydrogen atoms lie the same plane? If not, what is<br />
their spatial relationship? Explain.<br />
51. Indigo is the dye used in coloring blue jeans. The term navy<br />
blue is derived from the use of indigo to dye British naval<br />
uniforms in the eighteenth century. The structure of the indigo<br />
molecule is<br />
H<br />
O<br />
H C C N C H<br />
C C<br />
C C<br />
C C<br />
C C<br />
C C<br />
H C N C C H<br />
H<br />
H<br />
a. How many bonds <strong>and</strong> bonds exist in the molecule?<br />
b. What hybrid orbitals are used by the carbon atoms in the<br />
indigo molecule?<br />
Copyright 2010 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved. May not be copied, scanned, or duplicated, in whole or in part. Due to electronic rights, some third party content may be suppressed from the eBook <strong>and</strong>/or eChapter(s).<br />
Editorial review has deemed that any suppressed content does not materially affect the overall learning experience. Cengage Learning reserves the right to remove additional content at any time if subsequent rights restrictions require it.<br />
D<br />
G<br />
H<br />
O<br />
H<br />
H