Cápsulas / Capsules - Universidad de Navarra
Cápsulas / Capsules - Universidad de Navarra
Cápsulas / Capsules - Universidad de Navarra
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
Hard Gelatin vs Soft Gelatin "Softgels" <strong>Capsules</strong><br />
Criterion Soft gelatin<br />
Hard Gelatin<br />
<strong>Capsules</strong><br />
<strong>Capsules</strong><br />
Shell Plasticized (glycerin,<br />
propylene glycol, sorbitol)<br />
Not plasticized<br />
Content Usually liquids or suspensions Usually dry solids (liquids/<br />
(dry solids possible) semi-solid matrices possible)<br />
Manufacture Formed/filled in one Shells ma<strong>de</strong> in one operation<br />
operation<br />
and filled in a separate<br />
process<br />
Closure Hermetically sealed Traditional friction-fit;<br />
(inherent)<br />
mechanical interlock,<br />
banding and liquid sealing<br />
possible<br />
Sizes and<br />
Shapes<br />
Many Limited<br />
Formulation<br />
Technology<br />
Liquids Solids<br />
Fill Accuracy 1-3% 2-5% (with mo<strong>de</strong>rn<br />
automatic machines)<br />
Farmacia y Tecnología Farmacéutica<br />
<strong>Universidad</strong> <strong>de</strong> <strong>Navarra</strong><br />
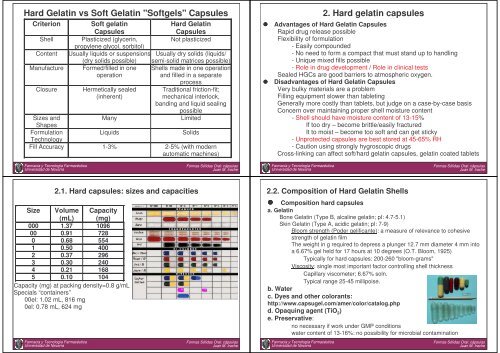
2.1. Hard capsules: sizes and capacities<br />
Size Volume Capacity<br />
(mL) (mg)<br />
000 1.37 1096<br />
00 0.91 728<br />
0 0.68 554<br />
1 0.50 400<br />
2 0.37 296<br />
3 0.30 240<br />
4 0.21 168<br />
5 0.10 104<br />
Capacity (mg) at packing <strong>de</strong>nsity=0.8 g/mL<br />
Specials “containers”<br />
00el: 1.02 mL, 816 mg<br />
0el: 0.78 mL, 624 mg<br />
Farmacia y Tecnología Farmacéutica<br />
<strong>Universidad</strong> <strong>de</strong> <strong>Navarra</strong><br />
Formas Sólidas Oral: cápsulas<br />
Juan M. Irache<br />
Formas Sólidas Oral: cápsulas<br />
Juan M. Irache<br />
2. Hard gelatin capsules<br />
Advantages of Hard Gelatin <strong>Capsules</strong><br />
Rapid drug release possible<br />
Flexibility of formulation<br />
- Easily compoun<strong>de</strong>d<br />
- No need to form a compact that must stand up to handling<br />
- Unique mixed fills possible<br />
- Role in drug <strong>de</strong>velopment / Role in clinical tests<br />
Sealed HGCs are good barriers to atmospheric oxygen.<br />
Disadvantages of Hard Gelatin <strong>Capsules</strong><br />
Very bulky materials are a problem<br />
Filling equipment slower than tableting<br />
Generally more costly than tablets, but judge on a case-by-case basis<br />
Concern over maintaining proper shell moisture content<br />
- Shell should have moisture content of 13-15%<br />
If too dry – become brittle/easily fractured<br />
It to moist – become too soft and can get sticky<br />
- Unprotected capsules are best stored at 45-65% RH<br />
- Caution using strongly hygroscopic drugs<br />
Cross-linking can affect soft/hard gelatin capsules, gelatin coated tablets<br />
Farmacia y Tecnología Farmacéutica<br />
<strong>Universidad</strong> <strong>de</strong> <strong>Navarra</strong><br />
2.2. Composition of Hard Gelatin Shells<br />
Formas Sólidas Oral: cápsulas<br />
Juan M. Irache<br />
Composition hard capsules<br />
a. Gelatin<br />
Bone Gelatin (Type B, alcaline gelatin; pI: 4.7-5.1)<br />
Skin Gelatin (Type A, acidic gelatin; pI: 7-9)<br />
Bloom strength (Po<strong>de</strong>r gelificante): a measure of relevance to cohesive<br />
strength of gelatin film<br />
The weight in g required to <strong>de</strong>press a plunger 12.7 mm diameter 4 mm into<br />
a 6.67% gel held for 17 hours at 10 <strong>de</strong>grees (O.T. Bloom, 1925)<br />
Typically for hard capsules: 200-260 "bloom-grams"<br />
Viscosity: single most important factor controlling shell thickness<br />
Capillary viscometer; 6.67% soln.<br />
Typical range 25-45 millipoise.<br />
b. Water<br />
c. Dyes and other colorants:<br />
http://www.capsugel.com/amer/color/catalog.php<br />
d. Opaquing agent (TiO 2 )<br />
e. Preservative:<br />
no necessary if work un<strong>de</strong>r GMP conditions<br />
water content of 13-16%: no possibility for microbial contamination<br />
Farmacia y Tecnología Farmacéutica<br />
<strong>Universidad</strong> <strong>de</strong> <strong>Navarra</strong><br />
Formas Sólidas Oral: cápsulas<br />
Juan M. Irache