For all your heating, cooling & stirring needs - Clarkson Laboratory ...
For all your heating, cooling & stirring needs - Clarkson Laboratory ...
For all your heating, cooling & stirring needs - Clarkson Laboratory ...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
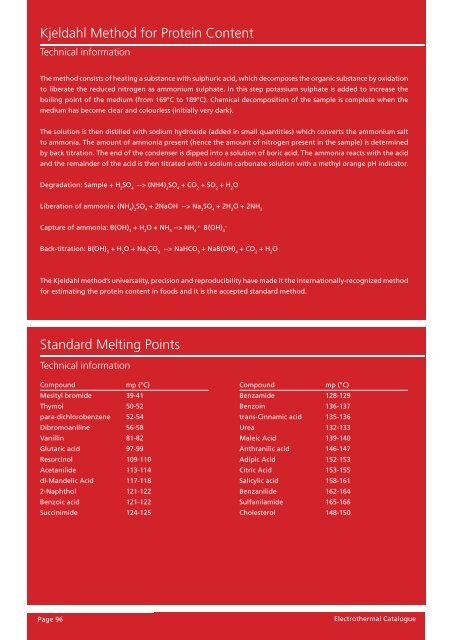
Kjeldahl Method for Protein Content<br />
Technical information<br />
The method consists of <strong>heating</strong> a substance with sulphuric acid, which decomposes the organic substance by oxidation<br />
to liberate the reduced nitrogen as ammonium sulphate. In this step potassium sulphate is added to increase the<br />
boiling point of the medium (from 169°C to 189°C). Chemical decomposition of the sample is complete when the<br />
medium has become clear and colourless (initi<strong>all</strong>y very dark).<br />
The solution is then distilled with sodium hydroxide (added in sm<strong>all</strong> quantities) which converts the ammonium salt<br />
to ammonia. The amount of ammonia present (hence the amount of nitrogen present in the sample) is determined<br />
by back titration. The end of the condenser is dipped into a solution of boric acid. The ammonia reacts with the acid<br />
and the remainder of the acid is then titrated with a sodium carbonate solution with a methyl orange pH indicator.<br />
Degradation: Sample + H 2 SO 4 --> (NH4) 2 SO 4 + CO 2 + SO 2 + H 2 O<br />
Liberation of ammonia: (NH 4 ) 2 SO 4 + 2NaOH --> Na 2 SO 4 + 2H 2 O + 2NH 3<br />
+ –<br />
Capture of ammonia: B(OH) + H O + NH --> NH B(OH)4<br />
3 2 3 4<br />
Back-titration: B(OH) 3 + H 2 O + Na 2 CO 3 --> NaHCO 3 + NaB(OH) 4 + CO 2 + H 2 O<br />
The Kjeldahl method’s universality, precision and reproducibility have made it the internation<strong>all</strong>y-recognized method<br />
for estimating the protein content in foods and it is the accepted standard method.<br />
Standard Melting Points<br />
Technical information<br />
Compound mp (°C)<br />
Mesityl bromide 39-41<br />
Thymol 50-52<br />
para-dichlorobenzene 52-54<br />
Dibromoaniline 56-58<br />
Vanillin 81-82<br />
Glutaric acid 97-99<br />
Resorcinol 109-110<br />
Acetanilide 113-114<br />
dl-Mandelic Acid 117-118<br />
2-Naphthol 121-122<br />
Benzoic acid 121-122<br />
Succinimide 124-125<br />
Page 96 Electrothermal Catalogue<br />
Compound mp (°C)<br />
Benzamide 128-129<br />
Benzoin 136-137<br />
trans-Cinnamic acid 135-136<br />
Urea 132-133<br />
Maleic Acid 139-140<br />
Anthranilic acid 146-147<br />
Adipic Acid 152-153<br />
Citric Acid 153-155<br />
Salicylic acid 158-161<br />
Benzanilide 162-164<br />
Sulfanilamide 165-166<br />
Cholesterol 148-150<br />
Electrothermal Catalogue