Chapter 6 Lecture: Principle of Equivalence
Chapter 6 Lecture: Principle of Equivalence
Chapter 6 Lecture: Principle of Equivalence
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
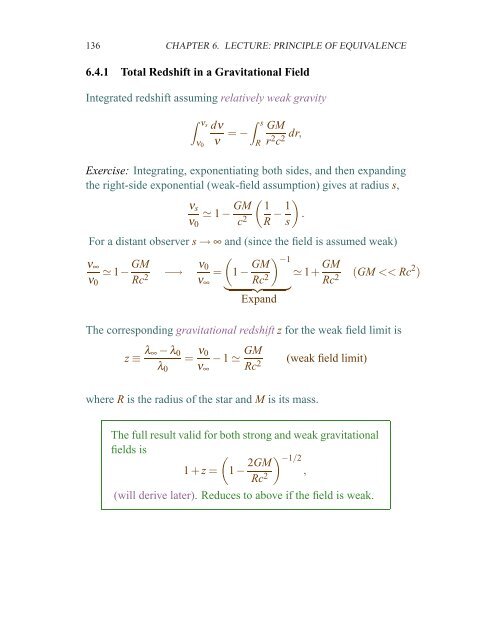
136 CHAPTER 6. LECTURE: PRINCIPLE OF EQUIVALENCE<br />
6.4.1 Total Redshift in a Gravitational Field<br />
Integrated redshift assuming relatively weak gravity<br />
� νs<br />
ν0<br />
ν0<br />
dν<br />
ν<br />
� s<br />
= −<br />
R<br />
GM<br />
r2 dr,<br />
c2 Exercise: Integrating, exponentiating both sides, and then expanding<br />
the right-side exponential (weak-field assumption) gives at radius s,<br />
νs<br />
≃ 1 − GM<br />
c2 � �<br />
1 1<br />
− .<br />
R s<br />
For a distant observer s → ∞ and (since the field is assumed weak)<br />
ν∞<br />
≃ 1−<br />
ν0<br />
GM<br />
Rc2 −→<br />
�<br />
ν0<br />
= 1 −<br />
ν∞<br />
GM<br />
Rc2 �−1 ≃ 1+<br />
� �� �<br />
Expand<br />
GM<br />
Rc2 (GM