Principles of Immunology - Health and Social Services
Principles of Immunology - Health and Social Services
Principles of Immunology - Health and Social Services
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
Community Nursing<br />
Yukon Immunization Program<br />
Section 14 - <strong>Principles</strong> <strong>of</strong> <strong>Immunology</strong><br />
2011 March<br />
Page 13<br />
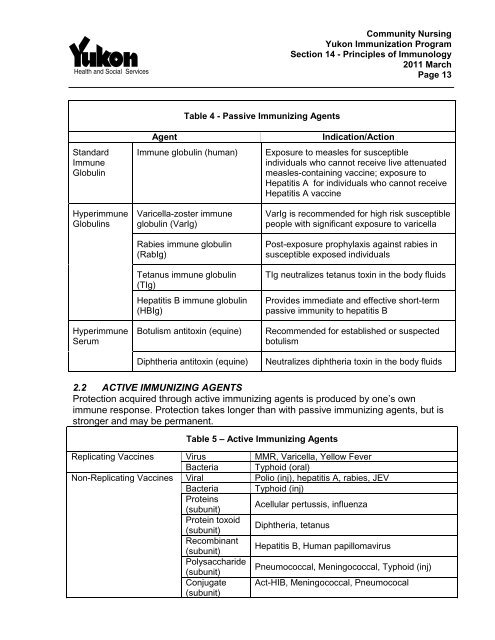
Table 4 - Passive Immunizing Agents<br />
St<strong>and</strong>ard<br />
Immune<br />
Globulin<br />
Hyperimmune<br />
Globulins<br />
Hyperimmune<br />
Serum<br />
Agent<br />
Immune globulin (human)<br />
Varicella-zoster immune<br />
globulin (VarIg)<br />
Rabies immune globulin<br />
(RabIg)<br />
Tetanus immune globulin<br />
(TIg)<br />
Hepatitis B immune globulin<br />
(HBIg)<br />
Botulism antitoxin (equine)<br />
Diphtheria antitoxin (equine)<br />
Indication/Action<br />
Exposure to measles for susceptible<br />
individuals who cannot receive live attenuated<br />
measles-containing vaccine; exposure to<br />
Hepatitis A for individuals who cannot receive<br />
Hepatitis A vaccine<br />
VarIg is recommended for high risk susceptible<br />
people with significant exposure to varicella<br />
Post-exposure prophylaxis against rabies in<br />
susceptible exposed individuals<br />
TIg neutralizes tetanus toxin in the body fluids<br />
Provides immediate <strong>and</strong> effective short-term<br />
passive immunity to hepatitis B<br />
Recommended for established or suspected<br />
botulism<br />
Neutralizes diphtheria toxin in the body fluids<br />
2.2 ACTIVE IMMUNIZING AGENTS<br />
Protection acquired through active immunizing agents is produced by one’s own<br />
immune response. Protection takes longer than with passive immunizing agents, but is<br />
stronger <strong>and</strong> may be permanent.<br />
Table 5 – Active Immunizing Agents<br />
Replicating Vaccines Virus MMR, Varicella, Yellow Fever<br />
Bacteria Typhoid (oral)<br />
Non-Replicating Vaccines Viral Polio (inj), hepatitis A, rabies, JEV<br />
Bacteria Typhoid (inj)<br />
Proteins<br />
(subunit)<br />
Acellular pertussis, influenza<br />
Protein toxoid<br />
(subunit)<br />
Diphtheria, tetanus<br />
Recombinant<br />
(subunit)<br />
Hepatitis B, Human papillomavirus<br />
Polysaccharide<br />
(subunit)<br />
Pneumococcal, Meningococcal, Typhoid (inj)<br />
Conjugate<br />
(subunit)<br />
Act-HIB, Meningococcal, Pneumococal



![Women and Alcohol: A women's health resource [2326.26 KB ]](https://img.yumpu.com/22340649/1/190x245/women-and-alcohol-a-womens-health-resource-232626-kb-.jpg?quality=85)