Diploma Thesis Santiago Gómez Sáez - IAAS
Diploma Thesis Santiago Gómez Sáez - IAAS
Diploma Thesis Santiago Gómez Sáez - IAAS
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
7. Validation and Evaluation<br />
problem in the evaluation, which leads us to discard the scenario 2.1.2.2 (see Table 7.1). The<br />
throughput obtained in the scenario 2.1.1.2 (see Table 7.1) is in average 3,3 requests per minute,<br />
and lasts approximately 10 hours. This fact makes us delete the last scenario execution, due to<br />
the low performance obtained, which we assume that it is related with the Quality of Service<br />
assigned to the student grants credits profile in Amazon RDS.<br />
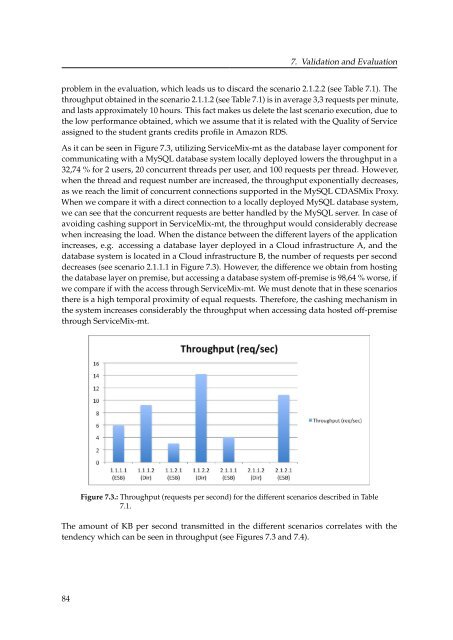
As it can be seen in Figure 7.3, utilizing ServiceMix-mt as the database layer component for<br />
communicating with a MySQL database system locally deployed lowers the throughput in a<br />
32,74 % for 2 users, 20 concurrent threads per user, and 100 requests per thread. However,<br />
when the thread and request number are increased, the throughput exponentially decreases,<br />
as we reach the limit of concurrent connections supported in the MySQL CDASMix Proxy.<br />
When we compare it with a direct connection to a locally deployed MySQL database system,<br />
we can see that the concurrent requests are better handled by the MySQL server. In case of<br />
avoiding cashing support in ServiceMix-mt, the throughput would considerably decrease<br />
when increasing the load. When the distance between the different layers of the application<br />
increases, e.g. accessing a database layer deployed in a Cloud infrastructure A, and the<br />
database system is located in a Cloud infrastructure B, the number of requests per second<br />
decreases (see scenario 2.1.1.1 in Figure 7.3). However, the difference we obtain from hosting<br />
the database layer on premise, but accessing a database system off-premise is 98,64 % worse, if<br />
we compare if with the access through ServiceMix-mt. We must denote that in these scenarios<br />
there is a high temporal proximity of equal requests. Therefore, the cashing mechanism in<br />
the system increases considerably the throughput when accessing data hosted off-premise<br />
through ServiceMix-mt.<br />
Figure 7.3.: Throughput (requests per second) for the different scenarios described in Table<br />
7.1.<br />
The amount of KB per second transmitted in the different scenarios correlates with the<br />
tendency which can be seen in throughput (see Figures 7.3 and 7.4).<br />
84