Stud. Geophys. Geod., 51 (2007) - SW3D
Stud. Geophys. Geod., 51 (2007) - SW3D
Stud. Geophys. Geod., 51 (2007) - SW3D
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
Retrieval of Source Parameters of Earthquake Swarm Assuming an Anisotropic Crust<br />
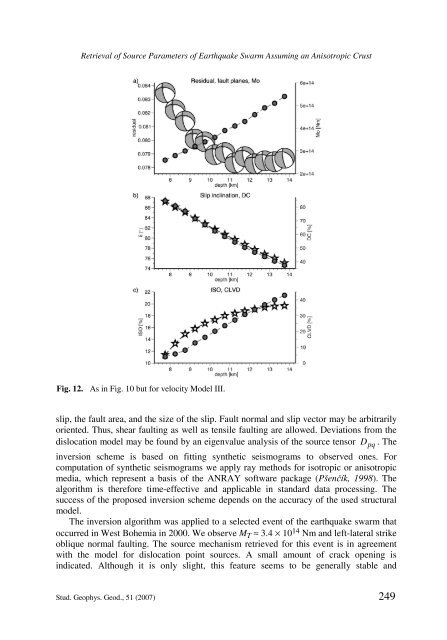
Fig. 12. As in Fig. 10 but for velocity Model III.<br />
slip, the fault area, and the size of the slip. Fault normal and slip vector may be arbitrarily<br />
oriented. Thus, shear faulting as well as tensile faulting are allowed. Deviations from the<br />
dislocation model may be found by an eigenvalue analysis of the source tensor D pq . The<br />
inversion scheme is based on fitting synthetic seismograms to observed ones. For<br />
computation of synthetic seismograms we apply ray methods for isotropic or anisotropic<br />
media, which represent a basis of the ANRAY software package (Pšenčík, 1998). The<br />
algorithm is therefore time-effective and applicable in standard data processing. The<br />
success of the proposed inversion scheme depends on the accuracy of the used structural<br />
model.<br />
The inversion algorithm was applied to a selected event of the earthquake swarm that<br />
occurred in West Bohemia in 2000. We observe MT ≈ 3.4 × 1014 Nm and left-lateral strike<br />
oblique normal faulting. The source mechanism retrieved for this event is in agreement<br />
with the model for dislocation point sources. A small amount of crack opening is<br />
indicated. Although it is only slight, this feature seems to be generally stable and<br />
<strong>Stud</strong>. <strong>Geophys</strong>. <strong>Geod</strong>., <strong>51</strong> (<strong>2007</strong>) 249