Ron Chance
Ron Chance
Ron Chance
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
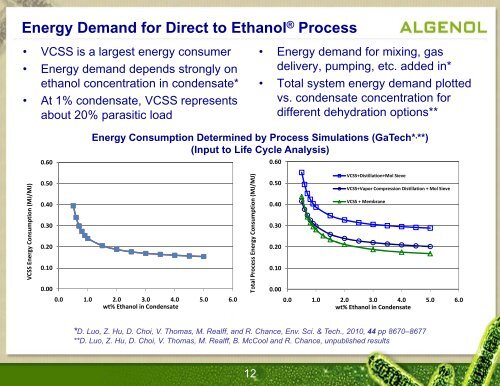
Energy Demand for Direct to Ethanol ® Process<br />
• VCSS is a largest energy consumer • Energy demand d for mixing, i gas<br />
• Energy demand depends strongly on delivery, pumping, etc. added in*<br />
ethanol concentration in condensate* • Total system energy demand plotted<br />
• At 1% condensate, VCSS represents<br />
vs. condensate concentration for<br />
about 20% parasitic load<br />
different dehydration options**<br />
0.60<br />
Energy Consumption Determined by Process Simulations (GaTech* , **)<br />
(Input to Life Cycle Analysis)<br />
0.60<br />
onsumption (MJ/M MJ)<br />
VCSS Energy C<br />
0.50<br />
0.40<br />
0.30<br />
0.20<br />
0.10<br />
000 0.00<br />
0.0 1.0 2.0 3.0 4.0 5.0 6.0<br />
wt% Ethanol in Condensate<br />
T otal Process Energ gy Consumption (M MJ/MJ)<br />
0.50<br />
0.40<br />
0.30<br />
0.20<br />
0.10<br />
000 0.00<br />
VCSS+Distillation+Mol Sieve<br />
VCSS+Vapor Compression Distillation + Mol Sieve<br />
VCSS + Membrane<br />
0.0 1.0 2.0 3.0 4.0 5.0 6.0<br />
wt% Ethanol in Condensate<br />
*D. Luo, Z. Hu, D. Choi, V. Thomas, M. Realff, and R. <strong>Chance</strong>, Env. Sci. & Tech., 2010, 44 pp 8670–8677<br />
**D. Luo, Z. Hu, D. Choi, V. Thomas, M. Realff, B. McCool and R. <strong>Chance</strong>, unpublished results<br />
12