larger file size version in PDF format
larger file size version in PDF format
larger file size version in PDF format
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
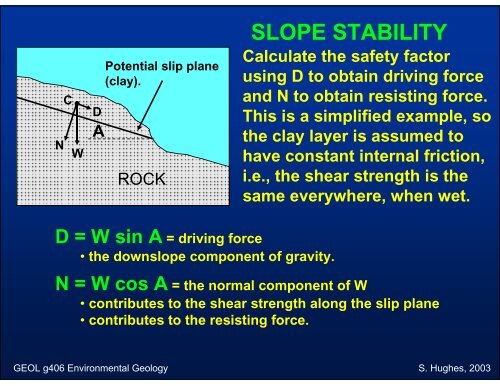
N<br />
C<br />
W<br />
D<br />
A<br />
Potential slip plane<br />
(clay).<br />
ROCK<br />
SLOPE STABILITY<br />
Calculate the safety factor<br />
us<strong>in</strong>g D to obta<strong>in</strong> driv<strong>in</strong>g force<br />
and N to obta<strong>in</strong> resist<strong>in</strong>g force.<br />
This is a simplified example, so<br />
the clay layer is assumed to<br />
have constant <strong>in</strong>ternal friction,<br />
i.e., the shear strength is the<br />
same everywhere, when wet.<br />
D = W s<strong>in</strong> A = driv<strong>in</strong>g force<br />
• the downslope component of gravity.<br />
N = W cos A = the normal component of W<br />
• contributes to the shear strength along the slip plane<br />
• contributes to the resist<strong>in</strong>g force.<br />
GEOL g406 Environmental Geology S. Hughes, 2003