Abiotic arising from non-living organisms. Adjuvant a - The Pew ...
Abiotic arising from non-living organisms. Adjuvant a - The Pew ...
Abiotic arising from non-living organisms. Adjuvant a - The Pew ...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
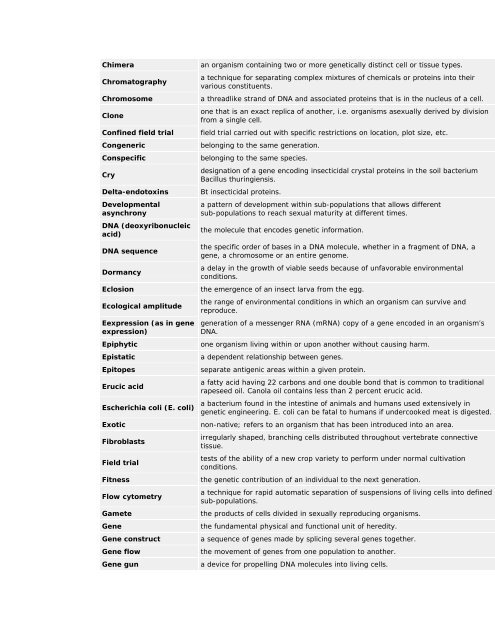
Chimera<br />
Chromatography<br />
Chromosome<br />
Clone<br />
Confined field trial<br />
Congeneric<br />
Conspecific<br />
Cry<br />
Delta-endotoxins<br />
Developmental<br />
asynchrony<br />
DNA (deoxyribonucleic<br />
acid)<br />
DNA sequence<br />
Dormancy<br />
Eclosion<br />
Ecological amplitude<br />
Eexpression (as in gene<br />
expression)<br />
Epiphytic<br />
Epistatic<br />
Epitopes<br />
Erucic acid<br />
Escherichia coli (E. coli)<br />
Exotic<br />
Fibroblasts<br />
Field trial<br />
Fitness<br />
Flow cytometry<br />
Gamete<br />
Gene<br />
Gene construct<br />
Gene flow<br />
Gene gun<br />
an organism containing two or more genetically distinct cell or tissue types.<br />
a technique for separating complex mixtures of chemicals or proteins into their<br />
various constituents.<br />
a threadlike strand of DNA and associated proteins that is in the nucleus of a cell.<br />
one that is an exact replica of another, i.e. <strong>organisms</strong> asexually derived by division<br />
<strong>from</strong> a single cell.<br />
field trial carried out with specific restrictions on location, plot size, etc.<br />
belonging to the same generation.<br />
belonging to the same species.<br />
designation of a gene encoding insecticidal crystal proteins in the soil bacterium<br />
Bacillus thuringiensis.<br />
Bt insecticidal proteins.<br />
a pattern of development within sub-populations that allows different<br />
sub-populations to reach sexual maturity at different times.<br />
the molecule that encodes genetic information.<br />
the specific order of bases in a DNA molecule, whether in a fragment of DNA, a<br />
gene, a chromosome or an entire genome.<br />
a delay in the growth of viable seeds because of unfavorable environmental<br />
conditions.<br />
the emergence of an insect larva <strong>from</strong> the egg.<br />
the range of environmental conditions in which an organism can survive and<br />
reproduce.<br />
generation of a messenger RNA (mRNA) copy of a gene encoded in an organism’s<br />
DNA.<br />
one organism <strong>living</strong> within or upon another without causing harm.<br />
a dependent relationship between genes.<br />
separate antigenic areas within a given protein.<br />
a fatty acid having 22 carbons and one double bond that is common to traditional<br />
rapeseed oil. Canola oil contains less than 2 percent erucic acid.<br />
a bacterium found in the intestine of animals and humans used extensively in<br />
genetic engineering. E. coli can be fatal to humans if undercooked meat is digested.<br />
<strong>non</strong>-native; refers to an organism that has been introduced into an area.<br />
irregularly shaped, branching cells distributed throughout vertebrate connective<br />
tissue.<br />
tests of the ability of a new crop variety to perform under normal cultivation<br />
conditions.<br />
the genetic contribution of an individual to the next generation.<br />
a technique for rapid automatic separation of suspensions of <strong>living</strong> cells into defined<br />
sub-populations.<br />
the products of cells divided in sexually reproducing <strong>organisms</strong>.<br />
the fundamental physical and functional unit of heredity.<br />
a sequence of genes made by splicing several genes together.<br />
the movement of genes <strong>from</strong> one population to another.<br />
a device for propelling DNA molecules into <strong>living</strong> cells.