SRI in Orissa - Cornell International Institute for Food, Agriculture ...
SRI in Orissa - Cornell International Institute for Food, Agriculture ...
SRI in Orissa - Cornell International Institute for Food, Agriculture ...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
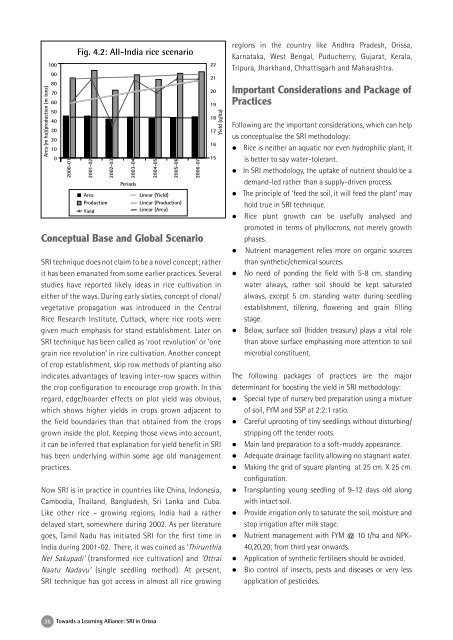
Area (m ha)/production (m tons)<br />
100<br />
90<br />
80<br />
70<br />
60<br />
50<br />
40<br />
30<br />
20<br />
10<br />
0<br />
2000-01<br />
Fig. 4.2: All-India rice scenario<br />
2001-02<br />
2002-03<br />
Area<br />
Production<br />
Yield<br />
L<strong>in</strong>ear (Yield)<br />
L<strong>in</strong>ear (Production)<br />
L<strong>in</strong>ear (Area)<br />
Conceptual Base and Global Scenario<br />
2003-04<br />
Periods<br />
<strong>SRI</strong> technique does not claim to be a novel concept; rather<br />
it has been emanated from some earlier practices. Several<br />
studies have reported likely ideas <strong>in</strong> rice cultivation <strong>in</strong><br />
either of the ways. Dur<strong>in</strong>g early sixties, concept of clonal/<br />
vegetative propagation was <strong>in</strong>troduced <strong>in</strong> the Central<br />
Rice Research <strong>Institute</strong>, Cuttack, where rice roots were<br />
given much emphasis <strong>for</strong> stand establishment. Later on<br />
<strong>SRI</strong> technique has been called as ‘root revolution’ or ‘one<br />
gra<strong>in</strong> rice revolution’ <strong>in</strong> rice cultivation. Another concept<br />
of crop establishment, skip row methods of plant<strong>in</strong>g also<br />
<strong>in</strong>dicates advantages of leav<strong>in</strong>g <strong>in</strong>ter-row spaces with<strong>in</strong><br />
the crop configuration to encourage crop growth. In this<br />
regard, edge/boarder effects on plot yield was obvious,<br />
which shows higher yields <strong>in</strong> crops grown adjacent to<br />
the field boundaries than that obta<strong>in</strong>ed from the crops<br />
grown <strong>in</strong>side the plot. Keep<strong>in</strong>g those views <strong>in</strong>to account,<br />
it can be <strong>in</strong>ferred that explanation <strong>for</strong> yield benefit <strong>in</strong> <strong>SRI</strong><br />
has been underly<strong>in</strong>g with<strong>in</strong> some age old management<br />
practices.<br />
Now <strong>SRI</strong> is <strong>in</strong> practice <strong>in</strong> countries like Ch<strong>in</strong>a, Indonesia,<br />
Cambodia, Thailand, Bangladesh, Sri Lanka and Cuba.<br />
Like other rice – grow<strong>in</strong>g regions, India had a rather<br />
delayed start, somewhere dur<strong>in</strong>g 2002. As per literature<br />
goes, Tamil Nadu has <strong>in</strong>itiated <strong>SRI</strong> <strong>for</strong> the first time <strong>in</strong><br />
India dur<strong>in</strong>g 2001-02. There, it was co<strong>in</strong>ed as ‘Thirunthia<br />
Nel Sakupadi’ (trans<strong>for</strong>med rice cultivation) and ‘Ottrai<br />
Naatu Nadavu’ (s<strong>in</strong>gle seedl<strong>in</strong>g method). At present,<br />
<strong>SRI</strong> technique has got access <strong>in</strong> almost all rice grow<strong>in</strong>g<br />
2004-05<br />
2005-06<br />
2006-07<br />
22<br />
21<br />
20<br />
19<br />
18<br />
17<br />
16<br />
15<br />
Yield (q/ha)<br />
regions <strong>in</strong> the country like Andhra Pradesh, <strong>Orissa</strong>,<br />
Karnataka, West Bengal, Puducherry, Gujarat, Kerala,<br />
Tripura, Jharkhand, Chhattisgarh and Maharashtra.<br />
Important Considerations and Package of<br />
Practices<br />
Follow<strong>in</strong>g are the important considerations, which can help<br />
us conceptualise the <strong>SRI</strong> methodology:<br />
• Rice is neither an aquatic nor even hydrophilic plant, it<br />
is better to say water-tolerant.<br />
• In <strong>SRI</strong> methodology, the uptake of nutrient should be a<br />
demand-led rather than a supply-driven process.<br />
• The pr<strong>in</strong>ciple of ‘feed the soil, it will feed the plant’ may<br />
hold true <strong>in</strong> <strong>SRI</strong> technique.<br />
• Rice plant growth can be usefully analysed and<br />
promoted <strong>in</strong> terms of phyllocrons, not merely growth<br />
phases.<br />
• Nutrient management relies more on organic sources<br />
than synthetic/chemical sources.<br />
• No need of pond<strong>in</strong>g the field with 5-8 cm. stand<strong>in</strong>g<br />
water always, rather soil should be kept saturated<br />
always, except 5 cm. stand<strong>in</strong>g water dur<strong>in</strong>g seedl<strong>in</strong>g<br />
establishment, tiller<strong>in</strong>g, flower<strong>in</strong>g and gra<strong>in</strong> fill<strong>in</strong>g<br />
stage.<br />
• Below, surface soil (hidden treasury) plays a vital role<br />
than above surface emphasis<strong>in</strong>g more attention to soil<br />
microbial constituent.<br />
The follow<strong>in</strong>g packages of practices are the major<br />
determ<strong>in</strong>ant <strong>for</strong> boost<strong>in</strong>g the yield <strong>in</strong> <strong>SRI</strong> methodology:<br />
• Special type of nursery bed preparation us<strong>in</strong>g a mixture<br />
of soil, FYM and SSP at 2:2:1 ratio.<br />
• Careful uproot<strong>in</strong>g of t<strong>in</strong>y seedl<strong>in</strong>gs without disturb<strong>in</strong>g/<br />
stripp<strong>in</strong>g off the tender roots.<br />
• Ma<strong>in</strong> land preparation to a soft-muddy appearance.<br />
• Adequate dra<strong>in</strong>age facility allow<strong>in</strong>g no stagnant water.<br />
• Mak<strong>in</strong>g the grid of square plant<strong>in</strong>g at 25 cm. X 25 cm.<br />
configuration.<br />
• Transplant<strong>in</strong>g young seedl<strong>in</strong>g of 9-12 days old along<br />
with <strong>in</strong>tact soil.<br />
• Provide irrigation only to saturate the soil, moisture and<br />
stop irrigation after milk stage.<br />
• Nutrient management with FYM @ 10 t/ha and NPK-<br />
40,20,20; from third year onwards.<br />
• Application of synthetic fertilisers should be avoided.<br />
• Bio control of <strong>in</strong>sects, pests and diseases or very less<br />
application of pesticides.<br />
26<br />
Towards a Learn<strong>in</strong>g Alliance: <strong>SRI</strong> <strong>in</strong> <strong>Orissa</strong>