Zinc Sheet Environmental Profile - Life Cycle Assessment
Zinc Sheet Environmental Profile - Life Cycle Assessment
Zinc Sheet Environmental Profile - Life Cycle Assessment
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
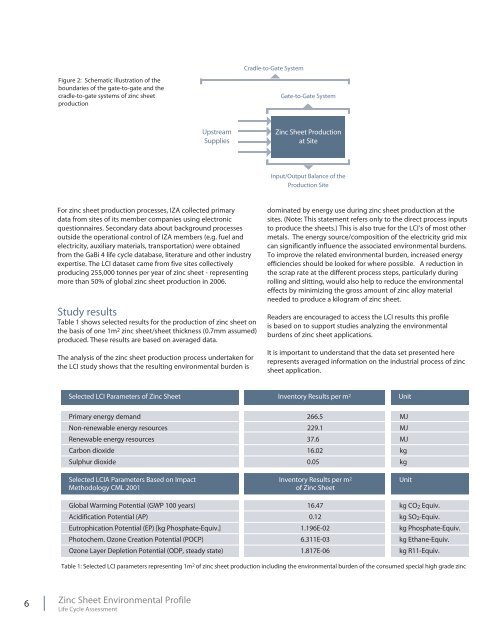
Cradle-to-Gate System<br />
Figure 2: Schematic illustration of the<br />
boundaries of the gate‐to‐gate and the<br />
cradle‐to‐gate systems of zinc sheet<br />
production<br />
Gate-to-Gate System<br />
Upstream<br />
Supplies<br />
<strong>Zinc</strong> <strong>Sheet</strong> Production<br />
at Site<br />
Input/Output Balance of the<br />
Production Site<br />
For zinc sheet production processes, IZA collected primary<br />
data from sites of its member companies using electronic<br />
questionnaires. Secondary data about background processes<br />
outside the operational control of IZA members (e.g. fuel and<br />
electricity, auxiliary materials, transportation) were obtained<br />
from the GaBi 4 life cycle database, literature and other industry<br />
expertise. The LCI dataset came from five sites collectively<br />
producing 255,000 tonnes per year of zinc sheet - representing<br />
more than 50% of global zinc sheet production in 2006.<br />
Study results<br />
Table 1 shows selected results for the production of zinc sheet on<br />
the basis of one 1m 2 zinc sheet/sheet thickness (0.7mm assumed)<br />
produced. These results are based on averaged data.<br />
The analysis of the zinc sheet production process undertaken for<br />
the LCI study shows that the resulting environmental burden is<br />
dominated by energy use during zinc sheet production at the<br />
sites. (Note: This statement refers only to the direct process inputs<br />
to produce the sheets.) This is also true for the LCI’s of most other<br />
metals. The energy source/composition of the electricity grid mix<br />
can significantly influence the associated environmental burdens.<br />
To improve the related environmental burden, increased energy<br />
efficiencies should be looked for where possible. A reduction in<br />
the scrap rate at the different process steps, particularly during<br />
rolling and slitting, would also help to reduce the environmental<br />
effects by minimizing the gross amount of zinc alloy material<br />
needed to produce a kilogram of zinc sheet.<br />
Readers are encouraged to access the LCI results this profile<br />
is based on to support studies analyzing the environmental<br />
burdens of zinc sheet applications.<br />
It is important to understand that the data set presented here<br />
represents averaged information on the industrial process of zinc<br />
sheet application.<br />
Selected LCI Parameters of <strong>Zinc</strong> <strong>Sheet</strong> Inventory Results per m 2 Unit<br />
Primary energy demand 266.5 MJ<br />
Non-renewable energy resources 229.1 MJ<br />
Renewable energy resources 37.6 MJ<br />
Carbon dioxide 16.02 kg<br />
Sulphur dioxide 0.05 kg<br />
Selected LCIA Parameters Based on Impact Inventory Results per m 2 Unit<br />
Methodology CML 2001<br />
of <strong>Zinc</strong> <strong>Sheet</strong><br />
Global Warming Potential (GWP 100 years) 16.47 kg CO 2 Equiv.<br />
Acidification Potential (AP) 0.12 kg SO 2 -Equiv.<br />
Eutrophication Potential (EP) [kg Phosphate-Equiv.] 1.196E-02 kg Phosphate-Equiv.<br />
Photochem. Ozone Creation Potential (POCP) 6.311E-03 kg Ethane-Equiv.<br />
Ozone Layer Depletion Potential (ODP, steady state) 1.817E-06 kg R11-Equiv.<br />
Table 1: Selected LCI parameters representing 1m 2 of zinc sheet production including the environmental burden of the consumed special high grade zinc<br />
6 <strong>Zinc</strong> <strong>Sheet</strong> <strong>Environmental</strong> <strong>Profile</strong><br />
<strong>Life</strong> <strong>Cycle</strong> <strong>Assessment</strong>