Guidelines for Soil Quality Assessment in Conservation Planning
Guidelines for Soil Quality Assessment in Conservation Planning
Guidelines for Soil Quality Assessment in Conservation Planning
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
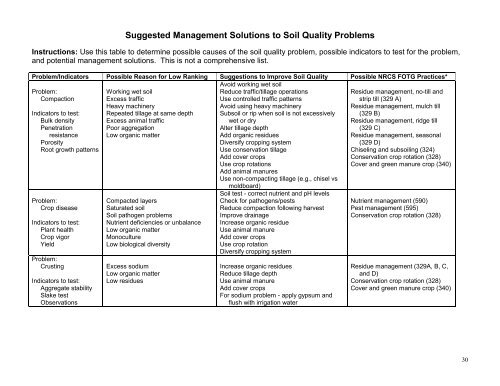
Suggested Management Solutions to <strong>Soil</strong> <strong>Quality</strong> Problems<br />
Instructions: Use this table to determ<strong>in</strong>e possible causes of the soil quality problem, possible <strong>in</strong>dicators to test <strong>for</strong> the problem,<br />
and potential management solutions. This is not a comprehensive list.<br />
Problem/Indicators Possible Reason <strong>for</strong> Low Rank<strong>in</strong>g Suggestions to Improve <strong>Soil</strong> <strong>Quality</strong> Possible NRCS FOTG Practices*<br />
Problem:<br />
Compaction<br />
Indicators to test:<br />
Bulk density<br />
Penetration<br />
resistance<br />
Porosity<br />
Root growth patterns<br />
Work<strong>in</strong>g wet soil<br />
Excess traffic<br />
Heavy mach<strong>in</strong>ery<br />
Repeated tillage at same depth<br />
Excess animal traffic<br />
Poor aggregation<br />
Low organic matter<br />
Avoid work<strong>in</strong>g wet soil<br />
Reduce traffic/tillage operations<br />
Use controlled traffic patterns<br />
Avoid us<strong>in</strong>g heavy mach<strong>in</strong>ery<br />
Subsoil or rip when soil is not excessively<br />
wet or dry<br />
Alter tillage depth<br />
Add organic residues<br />
Diversify cropp<strong>in</strong>g system<br />
Use conservation tillage<br />
Add cover crops<br />
Use crop rotations<br />
Add animal manures<br />
Use non-compact<strong>in</strong>g tillage (e.g., chisel vs<br />
moldboard)<br />
Residue management, no-till and<br />
strip till (329 A)<br />
Residue management, mulch till<br />
(329 B)<br />
Residue management, ridge till<br />
(329 C)<br />
Residue management, seasonal<br />
(329 D)<br />
Chisel<strong>in</strong>g and subsoil<strong>in</strong>g (324)<br />
<strong>Conservation</strong> crop rotation (328)<br />
Cover and green manure crop (340)<br />
Problem:<br />
Crop disease<br />
Indicators to test:<br />
Plant health<br />
Crop vigor<br />
Yield<br />
Problem:<br />
Crust<strong>in</strong>g<br />
Indicators to test:<br />
Aggregate stability<br />
Slake test<br />
Observations<br />
Compacted layers<br />
Saturated soil<br />
<strong>Soil</strong> pathogen problems<br />
Nutrient deficiencies or unbalance<br />
Low organic matter<br />
Monoculture<br />
Low biological diversity<br />
Excess sodium<br />
Low organic matter<br />
Low residues<br />
<strong>Soil</strong> test - correct nutrient and pH levels<br />
Check <strong>for</strong> pathogens/pests<br />
Reduce compaction follow<strong>in</strong>g harvest<br />
Improve dra<strong>in</strong>age<br />
Increase organic residue<br />
Use animal manure<br />
Add cover crops<br />
Use crop rotation<br />
Diversify cropp<strong>in</strong>g system<br />
Increase organic residues<br />
Reduce tillage depth<br />
Use animal manure<br />
Add cover crops<br />
For sodium problem - apply gypsum and<br />
flush with irrigation water<br />
Nutrient management (590)<br />
Pest management (595)<br />
<strong>Conservation</strong> crop rotation (328)<br />
Residue management (329A, B, C,<br />
and D)<br />
<strong>Conservation</strong> crop rotation (328)<br />
Cover and green manure crop (340)<br />
30