Resonance in a Closed Air Column - Lab Instructions - classconnect
Resonance in a Closed Air Column - Lab Instructions - classconnect
Resonance in a Closed Air Column - Lab Instructions - classconnect
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
Answer the follow<strong>in</strong>g questions. Always use full sentences. When necessary, be sure to show your<br />
calculations <strong>in</strong> a neat and organized way.<br />
Knowledge and Understand<strong>in</strong>g<br />
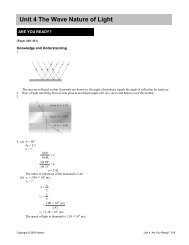
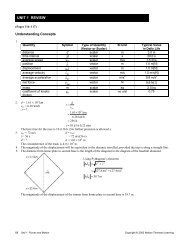
1) What is the wavelength of sound emitted by each tun<strong>in</strong>g fork <strong>in</strong> this <strong>in</strong>vestigation? (4 marks)<br />
2) Use the wavelength from each tun<strong>in</strong>g fork to calculate the speed of the waves us<strong>in</strong>g the universal<br />
wave equation. (4 marks)<br />
3) How does the wave speed of the first tun<strong>in</strong>g fork compare to the wave speed of the second tun<strong>in</strong>g<br />
fork when they are at the same temperature – are they the same speed, or is one faster/slower? Are<br />
you surprised? (2 marks)<br />
4) How does the wave speed of the tun<strong>in</strong>g forks at room temperature compare to the wave speed of<br />
the tun<strong>in</strong>g forks at a different temperature – are they the same speed, or is one faster/slower? Are<br />
you surprised? (2 marks)<br />
5) Calculate what the speed of sound should be based on the temperature of the air <strong>in</strong> each location.<br />
(2 marks)<br />
Th<strong>in</strong>k<strong>in</strong>g and Investigation<br />
6) Calculate the % error of your experimental results us<strong>in</strong>g the formula on page 565 of your<br />
textbook. (Note: This is a comparison of the “experimental” speed obta<strong>in</strong>ed <strong>in</strong> question 2, to the<br />
“accepted” speed from question 5) Does your % error seem reasonable for this type of lab?<br />
Expla<strong>in</strong>. (4 marks)<br />
7) Describe at least two sources of read<strong>in</strong>g error and systematic error <strong>in</strong> your <strong>in</strong>vestigation. Expla<strong>in</strong><br />
how each error may have affected the f<strong>in</strong>al results. Estimate a +/– value for the read<strong>in</strong>g error of<br />
your measurements and expla<strong>in</strong> how you determ<strong>in</strong>ed it. (5 marks)<br />
8) Reflect on the process of collect<strong>in</strong>g data. Identify at least one th<strong>in</strong>g you would do differently to<br />
improve the lab if you were to do it aga<strong>in</strong>. (2 marks)<br />
9) Write a conclusion that answers the questions at the beg<strong>in</strong>n<strong>in</strong>g of the lab. Address whether or not<br />
you believe the conclusions formed from this lab are correct and why. (3 marks)<br />
Application<br />
10) In this <strong>in</strong>vestigation you observed resonance <strong>in</strong> a closed air column. You can also observe<br />
resonance by push<strong>in</strong>g a child on a sw<strong>in</strong>g. Compare the child on the sw<strong>in</strong>g to the column of air.<br />
Expla<strong>in</strong> how they are both demonstrations of the same phenomenon? (5 marks)<br />
11) W<strong>in</strong>d <strong>in</strong>struments typically consist of a mouthpiece or reed attached to a long tube filled with air.<br />
The metal tube merely serves as a conta<strong>in</strong>er for a column of air. Expla<strong>in</strong> how these <strong>in</strong>struments<br />
are a specific application of resonance <strong>in</strong> a closed air column. Be specific: What causes the<br />
vibration? What changes the length of the tube? (5 marks)