Chapter 5.1 Notes
Chapter 5.1 Notes
Chapter 5.1 Notes
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
<strong>Chapter</strong> 5<br />
Cell Growth and Division<br />
<strong>Chapter</strong> 5<br />
Cell Growth and Division<br />
Why It’s Important<br />
Cells must copy<br />
their chromosomes<br />
and divide properly in<br />
order to make new<br />
cells that function<br />
________________<br />
properly<br />
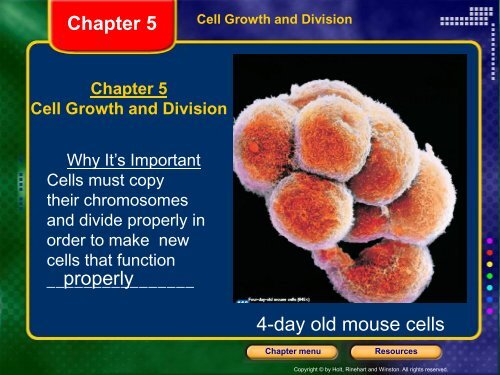
4-day old mouse cells<br />
<strong>Chapter</strong> menu<br />
Resources<br />
Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. All rights reserved.
<strong>Chapter</strong> 5<br />
Objectives<br />
• Identify four examples of cell division in eukaryotes<br />
and one example in prokaryotes.<br />
• Differentiate between a gene, a DNA molecule, a<br />
chromosome, and a chromatid.<br />
• Differentiate between homologous chromosomes,<br />
autosomes, and sex chromosomes.<br />
<strong>Chapter</strong> menu<br />
Resources<br />
Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. All rights reserved.
<strong>Chapter</strong> 5<br />
Formation of New Cells by Cell Division<br />
reproduction<br />
• Cell division, also called cell _________________,<br />
occurs in humans and other organisms at different<br />
times in their life<br />
repair<br />
________<br />
growth<br />
__________<br />
<strong>Chapter</strong> menu<br />
Resources<br />
Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. All rights reserved.
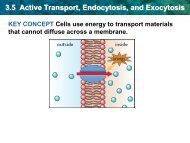
• Before a cell can divide, the DNA must first<br />
be __________ copied and then _______________<br />
distributed<br />
to new cells<br />
• Why does each new cell need an identical<br />
copy of DNA?<br />
DNA codes for the proteins made by<br />
the cell…incorrect DNA will lead to<br />
altered proteins<br />
<strong>Chapter</strong> menu<br />
Resources<br />
Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. All rights reserved.
• Prokaryotes carryout a very simple type<br />
of cell division called ______________ binary<br />
___________ fission<br />
– Occurs in two stages:<br />
• 1st DNA is _____________<br />
copied<br />
• 2 nd the original cell divides<br />
into _______ two new cells<br />
<strong>Chapter</strong> menu<br />
Resources<br />
Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. All rights reserved.
• The original cell divides by adding<br />
a new cell _____________<br />
membrane<br />
between the copied DNA<br />
• As new material is added, the<br />
membrane _________ pinches in<br />
• Next, a new cell ____________ wall<br />
forms around the membrane<br />
• Last, the original cell pinches off<br />
into two _______________ identical cells<br />
<strong>Chapter</strong> menu<br />
Resources<br />
Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. All rights reserved.
• Binary fission is a form of _________________<br />
reproduction because….<br />
single<br />
– It only involves a _____________ parent that<br />
passes ___________ exact copies of its DNA to its<br />
offspring<br />
exact<br />
asexual<br />
– So the offspring are __________ copies of the<br />
parent prokaryotic cell.<br />
<strong>Chapter</strong> menu<br />
Resources<br />
Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. All rights reserved.
Eukaryotic Cells<br />
• Before eukaryotic cells divide, their<br />
DNA is ____________ uncoiled and referred<br />
to as _______________<br />
chromatin<br />
double<br />
• Recall that DNA is a _____________<br />
helix made up of subunits called<br />
_________________<br />
nucleotides<br />
<strong>Chapter</strong> menu<br />
Resources<br />
Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. All rights reserved.
• Your DNA is normally uncoiled<br />
because the _________ code it contains is<br />
being used to make<br />
_______________<br />
proteins<br />
• Recall that specific segments of your<br />
DNA, called ___________, genes code for<br />
the production of _____________ different<br />
proteins<br />
<strong>Chapter</strong> menu<br />
Resources<br />
Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. All rights reserved.
• Before a eukaryotic cell divides, the DNA is<br />
____________, copied and it __________ coils up to form a<br />
chromosome<br />
• First, DNA coils around<br />
histones<br />
proteins called _________<br />
to form small structures<br />
nucleosomes<br />
called ______________<br />
nucleosome<br />
<strong>Chapter</strong> menu<br />
Resources<br />
Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. All rights reserved.
• Next, the nucleosomes actually end up coiling<br />
__________ twice on themselves to form a<br />
_________________<br />
supercoil<br />
<strong>Chapter</strong> menu<br />
Resources<br />
Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. All rights reserved.
• This supercoil is tightly packed in a structure called a<br />
________________<br />
chromosome<br />
<strong>Chapter</strong> menu<br />
Resources<br />
Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. All rights reserved.
• Chromosomes have two<br />
________________ identical sides<br />
because they contain DNA that<br />
has already been ____________ copied<br />
• Each side is called a sister<br />
_____________ chromatid and they are<br />
attached at a point called a<br />
_________________<br />
centromere<br />
<strong>Chapter</strong> menu<br />
Resources<br />
Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. All rights reserved.
• These sister chromatids<br />
_______________ separate at the<br />
centromere during cell division to<br />
ensure that each new cell has the<br />
_________ same genetic information as<br />
the original cell<br />
<strong>Chapter</strong> menu<br />
Resources<br />
Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. All rights reserved.
<strong>Chapter</strong> 5<br />
Different species<br />
contain different<br />
numbers of<br />
chromosomes<br />
Ex: Humans<br />
have ______ 46<br />
chromosomes<br />
while a dog has<br />
_______ 78<br />
chromosomes<br />
<strong>Chapter</strong> menu<br />
Resources<br />
Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. All rights reserved.
Asexual Reproduction – Eukaryotic cells<br />
exact<br />
• Eukaryotic cells will make _________ copies of<br />
themselves during asexual reproduction for four<br />
different types of cell division<br />
– One type is simply for ___________________<br />
– Eukaryotes may also make new cells for<br />
_________________, repair ________________, growth or<br />
_____________________<br />
development<br />
reproduction<br />
<strong>Chapter</strong> menu<br />
Resources<br />
Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. All rights reserved.
• Asexual reproduction only occurs in body cells which are<br />
also called ___________________ cells<br />
• Examples of somatic cells are _______________,<br />
_____________, and ________________ cells<br />
muscle<br />
• You want these new cells to do the same job as their<br />
parent cell, so it is good that they make exact<br />
__________of each other<br />
copies<br />
somatic<br />
skin<br />
nerve<br />
• Overtime…the ends of your DNA strands start to<br />
deteriorate so your cells ______ age and change slightly even<br />
though they are “copies”<br />
<strong>Chapter</strong> menu<br />
Resources<br />
Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. All rights reserved.
46<br />
• All of your somatic cells contain ____ chromosomes,<br />
which means they are _________ diploid cells<br />
• A diploid cell is mathematically written as ______,<br />
which means they have two _______ sets of<br />
chromosomes…<br />
mother<br />
2n<br />
– you inherit one set from your _____________ and<br />
____________ father<br />
<strong>Chapter</strong> menu<br />
Resources<br />
Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. All rights reserved.
Sexual Reproduction – Eukaryotic Cells<br />
One<br />
• ______ pair of your chromosomes are called your<br />
_______ sex chromosomes, because they are involved<br />
with determining your ____________ gender<br />
• Your other 22 pairs of chromosomes are called<br />
________________<br />
autosomes<br />
<strong>Chapter</strong> menu<br />
Resources<br />
Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. All rights reserved.
• Your two sex chromosomes are referred to as _____<br />
and _____ Y<br />
– You inherit one from each parent<br />
• ______ XY = male<br />
• ______ = female<br />
XX<br />
• Females can donate only X’s while males can donate<br />
an X or a Y…<br />
• Do males or females determine the sex of an<br />
offspring?<br />
males<br />
X<br />
<strong>Chapter</strong> menu<br />
Resources<br />
Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. All rights reserved.
Objective 1<br />
• Identify four examples of cell division in eukaryotes<br />
and one example in prokaryotes.<br />
Binary fission<br />
reproduction<br />
repair<br />
growth<br />
development<br />
<strong>Chapter</strong> menu<br />
Resources<br />
Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. All rights reserved.
Objective 2<br />
• Differentiate between a gene, a DNA molecule, a<br />
chromosome, and a chromatid.<br />
Gene – Segment of a DNA that codes for a protein<br />
Chromosome – coiled DNA molecule (x shape<br />
means it has been copied already)<br />
Chromatid – identical copy of DNA found in a<br />
chromosome…held together by<br />
centromeres<br />
<strong>Chapter</strong> menu<br />
Resources<br />
Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. All rights reserved.
Objective 3<br />
• Differentiate between homologous chromosomes,<br />
autosomes, and sex chromosomes.<br />
Homologous<br />
(22 Pairs)<br />
Nonhomologous…<br />
determine gender<br />
Similar in<br />
structure<br />
<strong>Chapter</strong> menu<br />
Resources<br />
Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. All rights reserved.