Part-based PCA for Facial Feature Extraction and Classification
Part-based PCA for Facial Feature Extraction and Classification
Part-based PCA for Facial Feature Extraction and Classification
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
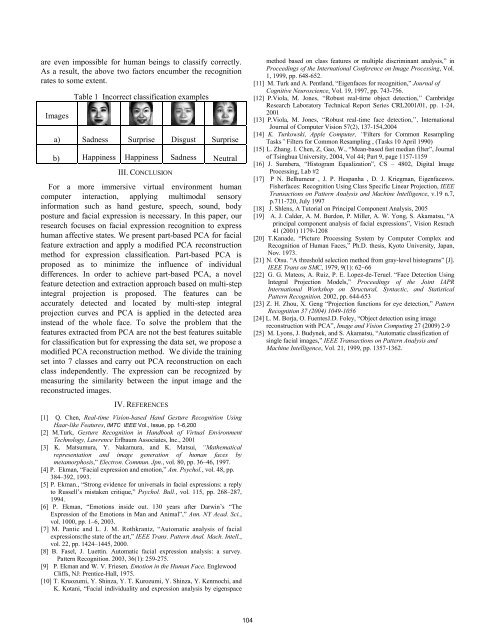
are even impossible <strong>for</strong> human beings to classify correctly.<br />
As a result, the above two factors encumber the recognition<br />
rates to some extent.<br />
Images<br />
Table 1 Incorrect classification examples<br />
a) Sadness Surprise Disgust Surprise<br />
b) Happiness Happiness Sadness Neutral<br />
III. CONCLUSION<br />
For a more immersive virtual environment human<br />
computer interaction, applying multimodal sensory<br />
in<strong>for</strong>mation such as h<strong>and</strong> gesture, speech, sound, body<br />
posture <strong>and</strong> facial expression is necessary. In this paper, our<br />
research focuses on facial expression recognition to express<br />
human affective states. We present part-<strong>based</strong> <strong>PCA</strong> <strong>for</strong> facial<br />
feature extraction <strong>and</strong> apply a modified <strong>PCA</strong> reconstruction<br />
method <strong>for</strong> expression classification. <strong>Part</strong>-<strong>based</strong> <strong>PCA</strong> is<br />
proposed as to minimize the influence of individual<br />
differences. In order to achieve part-<strong>based</strong> <strong>PCA</strong>, a novel<br />
feature detection <strong>and</strong> extraction approach <strong>based</strong> on multi-step<br />
integral projection is proposed. The features can be<br />
accurately detected <strong>and</strong> located by multi-step integral<br />
projection curves <strong>and</strong> <strong>PCA</strong> is applied in the detected area<br />
instead of the whole face. To solve the problem that the<br />
features extracted from <strong>PCA</strong> are not the best features suitable<br />
<strong>for</strong> classification but <strong>for</strong> expressing the data set, we propose a<br />
modified <strong>PCA</strong> reconstruction method. We divide the training<br />
set into 7 classes <strong>and</strong> carry out <strong>PCA</strong> reconstruction on each<br />
class independently. The expression can be recognized by<br />
measuring the similarity between the input image <strong>and</strong> the<br />
reconstructed images.<br />
method <strong>based</strong> on class features or multiple discriminant analysis,” in<br />
Proceedings of the International Conference on Image Processing, Vol.<br />
1, 1999, pp. 648-652.<br />
[11] M. Turk <strong>and</strong> A. Pentl<strong>and</strong>, “Eigenfaces <strong>for</strong> recognition,” Journal of<br />
Cognitive Neuroscience, Vol. 19, 1997, pp. 743-756.<br />
[12] P.Viola, M. Jones, ‘‘Robust real-time object detection,’’ Cambridge<br />
Research Laboratory Technical Report Series CRL2001/01, pp. 1-24,<br />
2001<br />
[13] P.Viola, M. Jones, ‘‘Robust real-time face detection,’’, International<br />
Journal of Computer Vision 57(2), 137-154,2004<br />
[14] K. Turkowski, Apple Computer, “Filters <strong>for</strong> Common Resampling<br />
Tasks” Filters <strong>for</strong> Common Resampling , (Tasks 10 April 1990)<br />
[15] L. Zhang. I. Chen, Z, Gao, W., “Mean-<strong>based</strong> fast median filter”, Journal<br />
of Tsinghua University, 2004, Vol 44; <strong>Part</strong> 9, page 1157-1159<br />
[16] J. Sumbera, “Histogram Equalization”, CS – 4802, Digital Image<br />
Processing, Lab #2<br />
[17] P N. Belhumeur , J. P. Hespanha , D. J. Kriegman, Eigenfacesvs.<br />
Fisherfaces: Recognition Using Class Specific Linear Projection, IEEE<br />
Transactions on Pattern Analysis <strong>and</strong> Machine Intelligence, v.19 n.7,<br />
p.711-720, July 1997<br />
[18] J. Shlens, A Tutorial on Principal Component Analysis, 2005<br />
[19] A. J. Calder, A. M. Burdon, P. Miller, A. W. Yong, S. Akamatsu, “A<br />
principal component analysis of facial expressions”, Vision Resrach<br />
41 (2001) 1179-1208<br />
[20] T.Kanade, “Picture Processing System by Computer Complex <strong>and</strong><br />
Recognition of Human Faces,” Ph.D. thesis, Kyoto University, Japan,<br />
Nov. 1973.<br />
[21] N. Otsu. “A threshold selection method from gray-level histograms” [J].<br />
IEEE Trans on SMC, 1979, 9(1): 62~66<br />
[22] G. G. Mateos, A. Ruiz, P. E. Lopez-de-Teruel. “Face Detection Using<br />
Integral Projection Models,” Proceedings of the Joint IAPR<br />
International Workshop on Structural, Syntactic, <strong>and</strong> Statistical<br />
Pattern Recognition. 2002, pp. 644-653<br />
[23] Z. H. Zhou, X. Geng “Projection functions <strong>for</strong> eye detection,” Pattern<br />
Recognition 37 (2004) 1049-1056<br />
[24] L. M. Borja, O. FuentesJ.D. Foley, “Object detection using image<br />
reconstruction with <strong>PCA</strong>”, Image <strong>and</strong> Vision Computing 27 (2009) 2-9<br />
[25] M. Lyons, J. Budynek, <strong>and</strong> S. Akamatsu, “Automatic classification of<br />
single facial images,” IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis <strong>and</strong><br />
Machine Intelligence, Vol. 21, 1999, pp. 1357-1362.<br />
IV. REFERENCES<br />
[1] Q. Chen, Real-time Vision-<strong>based</strong> H<strong>and</strong> Gesture Recognition Using<br />
Haar-like <strong>Feature</strong>s, IMTC IEEE Vol., Issue, pp. 1-6,200<br />
[2] M.Turk, Gesture Recognition in H<strong>and</strong>book of Virtual Environment<br />
Technology, Lawrence Erlbaum Associates, Inc., 2001<br />
[3] K. Matsumura, Y. Nakamura, <strong>and</strong> K. Matsui, “Mathematical<br />
representation <strong>and</strong> image generation of human faces by<br />
metamorphosis,” Electron. Commun. Jpn., vol. 80, pp. 36–46, 1997.<br />
[4] P. Ekman, “<strong>Facial</strong> expression <strong>and</strong> emotion,” Am. Psychol., vol. 48, pp.<br />
384–392, 1993.<br />
[5] P. Ekman., “Strong evidence <strong>for</strong> universals in facial expressions: a reply<br />
to Russell’s mistaken critique,” Psychol. Bull., vol. 115, pp. 268–287,<br />
1994.<br />
[6] P. Ekman, “Emotions inside out. 130 years after Darwin’s “The<br />
Expression of the Emotions in Man <strong>and</strong> Animal”,” Ann. NY Acad. Sci.,<br />
vol. 1000, pp. 1–6, 2003.<br />
[7] M. Pantic <strong>and</strong> L. J. M. Rothkrantz, “Automatic analysis of facial<br />
expressions:the state of the art,” IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell.,<br />
vol. 22, pp. 1424–1445, 2000.<br />
[8] B. Fasel, J. Luettin. Automatic facial expression analysis: a survey.<br />
Pattern Recognition. 2003, 36(1): 259-275.<br />
[9] P. Ekman <strong>and</strong> W. V. Friesen, Emotion in the Human Face. Englewood<br />
Cliffs, NJ: Prentice-Hall, 1975.<br />
[10] T. Kruozumi, Y. Shinza, Y. T. Kurozumi, Y. Shinza, Y. Kenmochi, <strong>and</strong><br />
K. Kotani, “<strong>Facial</strong> individuality <strong>and</strong> expression analysis by eigenspace<br />
104