Sustainability of cattle farming using analysis approach of Structural Equation Modeling (a study on dry land of Tanah Laut Regency, South Kalimantan, Indonesia)
The study was conducted in the village of Sumber Makmur and Central Banua, Takisung Sub-district, Tanah Laut Regency, South Kalimantan Province, Indonesia. This study aims to determine (1) factors influencing the sustainability of beef cattle farming (2) factors influencing the welfare of farmers, in form of a case study on the dry land. The study was conducted with survey method to 111 respondents using questionnaires that had been prepared previously (structured). The respondents were chosen by purposive sampling with criteria of having or farming beef cattle. The data were analyzed using Structural Equation Modeling (SEM), completion of the data was conducted using AMOS software. In this study, there are seven endogenous variables and two exogenous variables. The endogenous variables are environmental, economic, social, technology, physical, human, and institutional resources. The results show that environmental, economic, technological, physical, human, and institutional resources influence the sustainability of beef cattle farming; environmental, economic, technological, physical, human, and institutional resources influence, either directly or indirectly, the welfare of farmers (except social); and cattle farming sustainability variable influences the welfare of farmers. According to the result of this study, it is suggested that for the sustainability of beef cattle farming and to improve the welfare of farmers, several things that should be improved and considered are the improvements of resources, primarily environmental, economic, technological, physical, human, and institutional resources.
The study was conducted in the village of Sumber Makmur and Central Banua, Takisung Sub-district, Tanah Laut Regency, South Kalimantan Province, Indonesia. This study aims to determine (1) factors influencing the
sustainability of beef cattle farming (2) factors influencing the welfare of farmers, in form of a case study on the dry land. The study was conducted with survey method to 111 respondents using questionnaires that had been prepared previously (structured). The respondents were chosen by purposive sampling with criteria of having or farming beef cattle. The data were analyzed using Structural Equation Modeling (SEM), completion of the data was conducted using AMOS software. In this study, there are seven endogenous variables and two exogenous variables. The endogenous variables are environmental, economic, social, technology, physical, human, and institutional resources. The results show that environmental, economic, technological, physical, human, and institutional resources influence the sustainability of beef cattle farming; environmental, economic,
technological, physical, human, and institutional resources influence, either directly or indirectly, the welfare of farmers (except social); and cattle farming sustainability variable influences the welfare of farmers. According to the result of this study, it is suggested that for the sustainability of beef cattle farming and to improve the welfare of farmers, several things that should be improved and considered are the improvements of resources, primarily environmental, economic, technological, physical, human, and institutional resources.
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
Results and Discussi<strong>on</strong><br />
Characteristics <str<strong>on</strong>g>of</str<strong>on</strong>g> resp<strong>on</strong>dents<br />
Based <strong>on</strong> the survey and Focus Group Discussi<strong>on</strong><br />
(FGD) c<strong>on</strong>ducted with community leaders, it was<br />
known that there were some comm<strong>on</strong> or quite<br />
dominant patterns <str<strong>on</strong>g>of</str<strong>on</strong>g> <str<strong>on</strong>g>farming</str<strong>on</strong>g> which were performed<br />
by farmers in <strong>Tanah</strong> <strong>Laut</strong> <strong>Regency</strong>. Patterns <str<strong>on</strong>g>of</str<strong>on</strong>g><br />
<str<strong>on</strong>g>farming</str<strong>on</strong>g> carried out c<strong>on</strong>sisted <str<strong>on</strong>g>of</str<strong>on</strong>g> food crops,<br />
sec<strong>on</strong>dary food crops (Palawija) and beef <str<strong>on</strong>g>cattle</str<strong>on</strong>g>. This<br />
reflected that the farmers in the research site carried<br />
out diversificati<strong>on</strong> with several commodities that<br />
were c<strong>on</strong>ducted integratedly. Characteristics <str<strong>on</strong>g>of</str<strong>on</strong>g> the<br />
resp<strong>on</strong>dent farmers observed in this <str<strong>on</strong>g>study</str<strong>on</strong>g> were<br />
categorized according to age, educati<strong>on</strong>, experience,<br />
<strong>land</strong> area, members <str<strong>on</strong>g>of</str<strong>on</strong>g> household and number <str<strong>on</strong>g>of</str<strong>on</strong>g><br />
<str<strong>on</strong>g>cattle</str<strong>on</strong>g> ownership.<br />
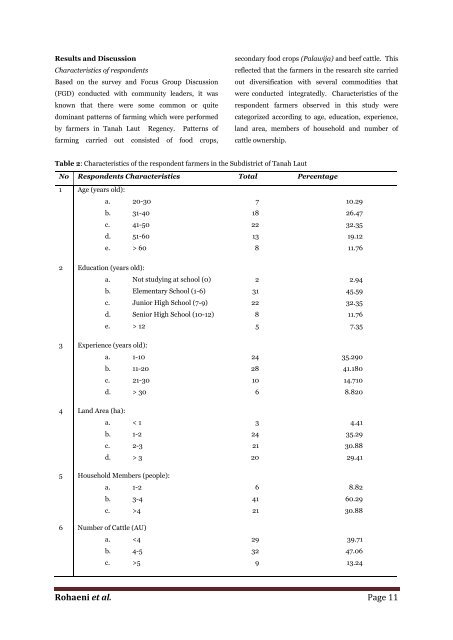
Table 2: Characteristics <str<strong>on</strong>g>of</str<strong>on</strong>g> the resp<strong>on</strong>dent farmers in the Subdistrict <str<strong>on</strong>g>of</str<strong>on</strong>g> <strong>Tanah</strong> <strong>Laut</strong><br />
No Resp<strong>on</strong>dents Characteristics Total Percentage<br />
1 Age (years old):<br />
a. 20-30<br />
b. 31-40<br />
c. 41-50<br />
d. 51-60<br />
e. > 60<br />
7<br />
18<br />
22<br />
13<br />
8<br />
10.29<br />
26.47<br />
32.35<br />
19.12<br />
11.76<br />
2 Educati<strong>on</strong> (years old):<br />
a. Not <str<strong>on</strong>g>study</str<strong>on</strong>g>ing at school (0)<br />
b. Elementary School (1-6)<br />
c. Junior High School (7-9)<br />
d. Senior High School (10-12)<br />
e. > 12<br />
2<br />
31<br />
22<br />
8<br />
5<br />
2.94<br />
45.59<br />
32.35<br />
11.76<br />
7.35<br />
3 Experience (years old):<br />
a. 1-10<br />
b. 11-20<br />
c. 21-30<br />
d. > 30<br />
24<br />
28<br />
10<br />
6<br />
35.290<br />
41.180<br />
14.710<br />
8.820<br />
4 Land Area (ha):<br />
a. < 1<br />
b. 1-2<br />
c. 2-3<br />
d. > 3<br />
5 Household Members (people):<br />
a. 1-2<br />
b. 3-4<br />
c. >4<br />
6 Number <str<strong>on</strong>g>of</str<strong>on</strong>g> Cattle (AU)<br />
a. 5<br />
3<br />
24<br />
21<br />
20<br />
6<br />
41<br />
21<br />
29<br />
32<br />
9<br />
4.41<br />
35.29<br />
30.88<br />
29.41<br />
8.82<br />
60.29<br />
30.88<br />
39.71<br />
47.06<br />
13.24<br />
Rohaeni et al. Page 11