Research area 1 Superconductivity and superconductors
Research area 1 Superconductivity and superconductors
Research area 1 Superconductivity and superconductors
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
Reports from <strong>Research</strong> <strong>area</strong>s<br />
<strong>Research</strong> <strong>area</strong> 1<br />
Co-ordinators:<br />
Prof. H. Eschrig<br />
Prof. J. Fink<br />
Prof. L. Schultz<br />
<strong>Superconductivity</strong> <strong>and</strong> <strong>superconductors</strong><br />
The basic research in the <strong>area</strong> of high-<br />
T c <strong>superconductors</strong> was focused on<br />
theoretical <strong>and</strong> experimental electronic<br />
structure studies <strong>and</strong> on investigations<br />
of the influence of the grain boundary<br />
network on the critical currents in these<br />
materials. In the field of the transition<br />
metal borocarbides, most of the activities<br />
were related to the coexistence of<br />
magnetism <strong>and</strong> superconductivity. The<br />
analytical tools <strong>and</strong> the possibilities to<br />
prepare new compounds, single crystals<br />
<strong>and</strong> thin films of interesting new<br />
<strong>superconductors</strong> have been improved.<br />
Technology development were continued<br />
successfully in the field of high-T c<br />
<strong>superconductors</strong>. In particular, using<br />
the Rolling Assisted Biaxially Textured<br />
Substrated (RABITS) method superconducting<br />
tapes with exceptional high<br />
current densities <strong>and</strong> increased<br />
mechanical strength could be achieved<br />
on new substrated developed in the<br />
IFW Dresden. Using the powder in tube<br />
technique the overall critical current<br />
density of high-T c wires for cables <strong>and</strong><br />
transformer could be improved. Finally,<br />
by chemical replacement or introduction<br />
of impurities in superconducting<br />
permanent magnet materials new<br />
record values for magnetic fields could<br />
be obtained. The use of these materials<br />
for friction-free superconducting<br />
bearings, for the development of a<br />
pump for liquid gases <strong>and</strong> the construction<br />
of a reluctance motor has<br />
been pushed forward.<br />
Torsten Fahr,<br />
Claus Fischer,<br />
Volker Haas,<br />
Wolfgang Häßler,<br />
Bernhard Holzapfel,<br />
Christian Rodig,<br />
Margitta Schubert,<br />
Hans-Peter Trinks<br />
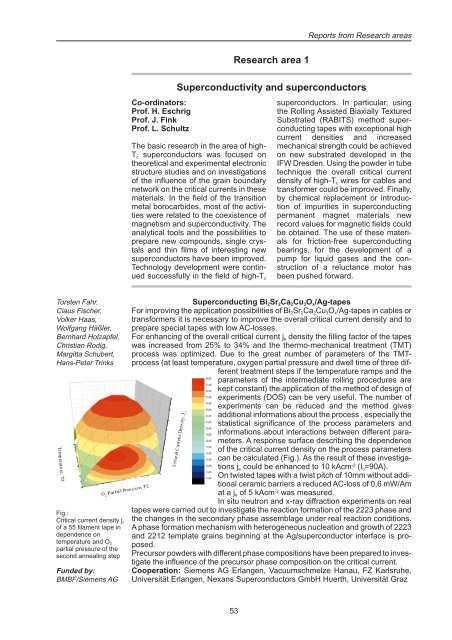
Fig.:<br />
Critical current density j c<br />
of a 55 filament tape in<br />
dependence on<br />
temperature <strong>and</strong> O 2<br />
partial pressure of the<br />
second annealing step<br />
Funded by:<br />
BMBF/Siemens AG<br />
Superconducting Bi 2 Sr 2 Ca 2 Cu 3 O x /Ag-tapes<br />
For improving the application possibilities of Bi 2 Sr 2 Ca 2 Cu 3 O x /Ag-tapes in cables or<br />
transformers it is necessary to improve the overall critical current density <strong>and</strong> to<br />
prepare special tapes with low AC-losses.<br />
For enhancing of the overall critical current j e density the filling factor of the tapes<br />
was increased from 25% to 34% <strong>and</strong> the thermo-mechanical treatment (TMT)<br />
process was optimized. Due to the great number of parameters of the TMTprocess<br />
(at least temperature, oxygen partial pressure <strong>and</strong> dwell time of three different<br />
treatment steps if the temperature ramps <strong>and</strong> the<br />
parameters of the intermediate rolling procedures are<br />
kept constant) the application of the method of design of<br />
experiments (DOS) can be very useful. The number of<br />
experiments can be reduced <strong>and</strong> the method gives<br />
additional informations about the process , especially the<br />
statistical significance of the process parameters <strong>and</strong><br />
informations about interactions between different parameters.<br />
A response surface describing the dependence<br />
of the critical current density on the process parameters<br />
can be calculated (Fig.). As the result of these investigations<br />
j e could be enhanced to 10 kAcm -2 (I c =90A).<br />
On twisted tapes with a twist pitch of 10mm without additional<br />
ceramic barriers a reduced AC-loss of 0,6 mW/Am<br />
at a j e of 5 kAcm -2 was measured.<br />
In situ neutron <strong>and</strong> x-ray diffraction experiments on real<br />
tapes were carried out to investigate the reaction formation of the 2223 phase <strong>and</strong><br />
the changes in the secondary phase assemblage under real reaction conditions.<br />
A phase formation mechanism with heterogeneous nucleation <strong>and</strong> growth of 2223<br />
<strong>and</strong> 2212 template grains beginning at the Ag/superconductor interface is proposed.<br />
Precursor powders with different phase compositions have been prepared to investigate<br />
the influence of the precursor phase composition on the critical current.<br />
Cooperation: Siemens AG Erlangen, Vacuumschmelze Hanau, FZ Karlsruhe,<br />
Universität Erlangen, Nexans Superconductors GmbH Huerth, Universität Graz<br />
53
Reports from <strong>Research</strong> <strong>area</strong>s<br />
Sergey V. Borisenko,<br />
Alex<strong>and</strong>er A. Kordyuk,<br />
Sibylle Legner,<br />
Konstantin Nenkov,<br />
Mark S. Golden,<br />
Jörg Fink<br />
Fig.: Fermi surface maps of<br />
Pb-Bi2212 compounds with<br />
different hole doping levels:<br />
underdoped (UD), as<br />
grown (AG) <strong>and</strong> overdoped<br />
(OD). Critical temperatures<br />
are also indicated.<br />
Funded by:<br />
BMBF, DFG<br />
Holger Bitterlich,<br />
Günter Behr,<br />
Stephan-Ludwig<br />
Drechsler,<br />
Jörg Fink,<br />
Günter Fuchs,<br />
Gerald Graw,<br />
Wolfgang Löser,<br />
Konstantin Nenkov,<br />
Ludwig Schultz<br />
Fig.<br />
Upper critical fields<br />
H c2<br />
ll <br />
<strong>and</strong> H c2<br />
ll <br />
vs.<br />
temperature T of a<br />
Tb 0.2 Y 0.8 Ni 2 B 2 C single<br />
crystal for different<br />
orientations parallel to<br />
the a-axis <strong>and</strong> parallel to<br />
the c-axis, respectively.<br />
Inset: Magnetization vs.<br />
external field plots for<br />
two different orientations<br />
M(H ll ) <strong>and</strong> M(H ll )<br />
at T = 4.5 K.<br />
Funded by:<br />
DFG<br />
Doping dependence of the Fermi surface<br />
in Bi-based superconducting cuprates<br />
We have continued our systematic studies of the Fermi surface (FS) of<br />
Pb 0.44 Bi 1.56 Sr 2 CaCu 2 O 8+d by studying the evolution of the FS topology as a function<br />
of the hole doping level range, covering from underdoped (Tc=76 K) to overdoped<br />
(Tc=69K) samples. Utilizing the high energy <strong>and</strong> momentum resolution offered by<br />
our angle-scanning photoemission set-up, we recorded maps of the momentum<br />
distribution of the Fermi level photemission intensity, which give direct image of<br />
the FS (see Fig.).<br />
A visual inspection of the data already reveals that the size of the rounded barrels<br />
(representing the hole-like FS) increases on going from the underdoped to the<br />
overdoped regime. A more quantitative analysis is currently underway to determine<br />
the charge carrier concentration directly from the ARPES results. A further<br />
result is that the FS topology tends towards stronger nesting as the doping increases<br />
– i.e. the form changes from more circular to a squarer shape (with rounded<br />
corners). We stress however, that for all doping levels concerned, the FS remains<br />
hole-like, indicating that even for the strongest overdoped crystals the flat b<strong>and</strong>s<br />
located near to the [p,0] point are still below the chemical potential. As regards the<br />
lifetime of the states involved, an analysis of the width of the E F momentum distribution<br />
curves crossing the FS shows that the lifetime varies along the FS following<br />
sin 2 (2f), where f is the angle with respect to the nodal direction measured<br />
with [p,p] as the origin. This would fit into a hot-spot / cold-spot scenario describing<br />
the k-dependence of the interactions in the system. Remarkably, however, the<br />
f dependence of the lifetime is independent of doping, which would not be expected<br />
from this picture. Finally, we note that relative intensity of the shadow FS to the<br />
main FS is found to be maximal at optimal doping, decreasing on going either to<br />
the under- or overdoped side, which suggests that the origin of this feature is<br />
important for our underst<strong>and</strong>ing the mechanism of the high temperature superconductivity.<br />
Cooperation: Institut de Physique Applique, EPFL, Lausanne, Switzerl<strong>and</strong>,<br />
DP/IGA, EPFL, Lausanne, Switzerl<strong>and</strong>, Univ. Birmingham, MPI für Festkörperforschung<br />
Stuttgart<br />
Crystal growth <strong>and</strong> intrinsic properties<br />
of Rare earth-Transition metal intermetallic compounds<br />
Bulk single crystals of Y 1-x Tb x Ni 2 B 2 C borocarbides have been grown by the floating<br />
zone method with inductive <strong>and</strong> optical heating, respectively, in order to study the<br />
interplay of paramagnetic Tb-ions with superconducting properties. Substitution of<br />
Y- by Tb-ions not only reduces the upper critical field H c2 , but an anisotropy of H c2<br />
along the c-axis <strong>and</strong> in the plane perpendicular to the c-axis was induced. Moreover,<br />
the magnitude of the anisotropy can be tuned by changing the fraction x of<br />
Tb-ions. The maximum anisotropy was reached at x = 0.2 (Fig. 1). The anisotropy<br />
H c2<br />
ll[001]<br />
> H c2<br />
ll[100]<br />
is induced by the in-plane magnetic moments of Tb-ions, which is<br />
emphasized by the magnetization measurements. The behaviour is explained by<br />
a simplified theoretical model, which is primarily based on the interaction of conduction<br />
electrons with magnetic moments of the rare earth ions.<br />
For YNi 1-x Cu x BC compounds the effect of alloy composition<br />
on phase relations <strong>and</strong> superconducting<br />
properties was revealed. The peritectic solidification<br />
mode could be proven. A maximum Cu solubility<br />
of x Å 0.42 of YNi 1-x Cu x BC compounds was<br />
inferred. The superconducting transition temperature<br />
increases with both the Cu <strong>and</strong> B content up to<br />
a maximum T C = 9.1 K.<br />
For the Tb 2 PdSi 3 intermetallic compound the interaction<br />
between magnetic moments of Tb-ions with conduction electrons leads to<br />
a considerable anisotropy of the negative giant magnetoresistance (GMR) at low<br />
temperatures. An unusual anisotropy of the magnetocaloric effect was found for<br />
the first time for bulk Tb 2 PdSi 3 single crystals prepared.<br />
Cooperation: INPG-ENSPG Grenoble, Univ. Frankfurt, Tata Institute of Fundamental<br />
<strong>Research</strong> India, TU Clausthal, TU Dresden, Univ. of Minsk<br />
54
Reports from <strong>Research</strong> <strong>area</strong>s<br />
Karl-Hartmut Müller,<br />
Günter Fuchs,<br />
Axel H<strong>and</strong>stein,<br />
Stefan-Ludwig<br />
Drechsler,<br />
Helge Rosner,<br />
Sergej Shulga,<br />
Jens Freudenberger,<br />
Konstantin Nenkov,<br />
Kerstin Häse,<br />
Stuart Wimbush,<br />
Bernhard Holzapfel,<br />
Holger Bitterlich,<br />
Wolfgang Löser,<br />
Günter Behr,<br />
Ludwig Schultz<br />
Fig.: Several quantities<br />
for Y x Lu 1-x Ni 2 B 2 C<br />
compounds determined<br />
by resisitivity (left panel)<br />
<strong>and</strong> specific heat<br />
measurements (right<br />
panel) vs. Y concentration:<br />
Superconducting<br />
transition temperature T c ,<br />
the upper critical field<br />
parameters a <strong>and</strong> H c2 *<br />
(according to<br />
H c2 (T)=H c2 *[1-T/T c ] 1+a ), the<br />
residual resisitivity ratio<br />
RRR, the parameter ( of<br />
the relation g(H)/g N µ<br />
[H/H c2 (0)] 1-b <strong>and</strong> the Sommerfeld<br />
parameter g N .<br />
Funded by:<br />
DFG (SFB 463)<br />
Magnetism <strong>and</strong> superconductivity of borocarbides<br />
The effect of substitutional disorder-induced local lattice distortions on the superconducting<br />
properties of nonmagnetic Y x Lu 1-x Ni 2 B 2 C compounds was studied by<br />
resistivity <strong>and</strong> specific heat measurements. Substitutional disorder was found to<br />
reduce several relevant quantities as the superconducting transition temperature<br />
T c , the upper critical field H c2 (0) at T=0, a characteristic positive curvature of H c2 (T)<br />
observed for these compounds, the Sommerfeld parameter g N in the normal state<br />
as well as the curvature of g (H) with g as the electronic specific heat coefficient in<br />
the mixed state. These quantities have their highest values for the pure compounds<br />
<strong>and</strong> show a minimum for the highest degree of substitutional disorder at<br />
x ~ 0.5 without reaching the case of dirty limit where the curvatures of g(H) <strong>and</strong> of<br />
H c2 (T) at T c would disappear (i.e. b=0 <strong>and</strong> a=0). Starting from a two-b<strong>and</strong> model<br />
description of H c2 (T) within the clean limit, a correlation between H c2 (0) <strong>and</strong> the<br />
unusual g(H) dependence was established <strong>and</strong> related to the impurity scattering<br />
rate. Also epitaxial YNi 2 B 2 C <strong>and</strong> HoNi 2 B 2 C thin films were prepared for the first time<br />
by UHV laser deposition. Epitaxial c-axis oriented films were produced at high<br />
deposition temperatures, whereas a-axis oriented YNi 2 B 2 C films could be prepared<br />
by a low deposition temperature. The<br />
availibilty of epitaxial thin films of nonmagnetic<br />
borocarbides enables<br />
phase-sensitive tunneling experiments<br />
which could help to clarify the<br />
symmetry of the superconducting<br />
order parameter in borocarbides. Furthermore,<br />
the effect of paramagnetic<br />
Tb-ions on H c2 (T) of Tb x Y 1-x Ni 2 B 2 C<br />
bulk single crystals was studied. With<br />
increasing Tb content x both T c <strong>and</strong><br />
H c2 are reduced. Different from YNi 2 B 2 C a reversed anisotropy H c2 || (001) > H c2 ||<br />
(100) was observed resulting from the in-plane magnetic moments of uncoupled<br />
Tb-ions. The magnitude of this anisotropy was found to rise up to a Tb concentration<br />
of x = 0.2. The reduction of the anisotropy for higher Tb concentrations can<br />
be explained by magnetic ordering of Tb-ions.<br />
Cooperation: TU Dresden, MPG cPfS, ILL Grenoble<br />
Stefan-Ludwig<br />
Drechsler,<br />
Helge Rosner,<br />
Ingo Opahle,<br />
Sergey Shulga,<br />
Helmut Eschrig<br />
Fig.1<br />
Fermi surface <strong>and</strong> Fermi<br />
velocity (in atomic units)<br />
distribution of a b<strong>and</strong><br />
composed mainly by Ni<br />
3d xy <strong>and</strong> Ni 3d z2 states<br />
for the Y(NiB) 2 C<br />
superconductor.<br />
Fig.2<br />
Fermi surface <strong>and</strong> Fermi<br />
velocity (in atomic units)<br />
distribution of a b<strong>and</strong><br />
composed mainly by<br />
Ni 3d xy <strong>and</strong> Ni 3d z2 states<br />
for the La(NiB) 2 C<br />
nonsuperconductor.<br />
Electronic structure <strong>and</strong> superconductivity<br />
of transition metal borocarbides<br />
The role of the electronic structure in the mechanism of superconductivity <strong>and</strong><br />
selected thermodynamic properties has been investigated in the frame of modern<br />
density functional theory as well as multi-b<strong>and</strong> Eliashberg theory. The b<strong>and</strong>structure,<br />
density of states, the distribution of Fermi velocities v F , the orbital character,<br />
<strong>and</strong> nesting properties of rather complex Fermi surfaces of both superconducting<br />
as well as nonsuperconducting members of the R(TB) 2 C<br />
family with R=Y, Lu, Sc, Th, La, Ho <strong>and</strong> T=Ni, Co, Pt, Pd,<br />
Re, Ru have been studied in detail. The great complexity of<br />
the first glance b<strong>and</strong>structure can be resolved into relatively<br />
separate subsystems providing a well-defined basis for a<br />
systematic study of interesting many-body problems in near<br />
future. R(TB) 2 C-Superconductors are characterized by a<br />
broad distribution of Fermi velocities containing both very<br />
slow <strong>and</strong> very fast electrons as well as the presence of<br />
nested regions which play a decisive also in the phonon<br />
softening as well as in special incommensurate magnetic<br />
structures for R(TB)2C compounds with magnetic<br />
rare earth ions R. These features are absent in the nonsuperconducting<br />
members of the R(TB) 2 C family. C<strong>and</strong>idates<br />
for relatively isolated b<strong>and</strong>s have been figured out<br />
which might alter conventional properties such as the shape<br />
of the upper critical field as well as the field dependence of<br />
the electronic specific heat in the mixed state.<br />
55
Reports from <strong>Research</strong> <strong>area</strong>s<br />
Carla Vogt,<br />
Wolfgang Gruner,<br />
Rolf Kucharkowski,<br />
Alexei Plotnikov,<br />
Günter Behr<br />
Fig. 1<br />
a) Microscopic view of<br />
the laser ablation trace<br />
on YNi 2.02 B 2.00 C system;<br />
length 20 mm, width<br />
60 µm, ablation rate<br />
20 µm/s.<br />
b) ICP-MS signal of the<br />
ablated material. In<br />
heterogenic samples the<br />
composition of phases<br />
could be calculated from<br />
isotopic ratios (shown<br />
here 11 B/ 58 Ni) of all<br />
elements.<br />
Funded by:<br />
DFG<br />
Stoichiometry, purity <strong>and</strong> homogeneity of superconducting materials<br />
Precise analysis was performed for Ca-Mg-Cu-O, Y(RE)-Ni-B-C, Bi-Pb-Sr-Ca-Cu-<br />
O <strong>and</strong> some other material systems by ICP-OES <strong>and</strong> carrier gas hot extraction<br />
methods for accurate oxygen determinations. In ICP-OES measurements optimised<br />
multicomponent determination was realised by multi-line measurements<br />
complemented by specially adapted data evaluation routines for precursors <strong>and</strong><br />
multi-filament super conductors. For a typical Bi-Pb-Sr-Ca-Cu-O 2223-phase precursor<br />
with lead in the oxidation state 4 the cationic stoichiometry was determined<br />
with optimum accuracy, e.g. Bi 1.734±0.006 Pb 0.3864±0.0003 Sr 1.935±0.006 Ca 1.74±0.02 Cu 3.000±0.003 .<br />
The development of a special method for precise oxygen determination in oxides<br />
was the prerequisite to determine the total composition of Ca-Mg-Cu-O compounds<br />
experimentally for the first time. Thus, the exact stoichiometry of such complex<br />
composed cuprates, like Ca 2.42±0.05 Mg 0.446±0.012 Cu 6.979±0.022 O 10.000±0.027 , could be<br />
determined without any assumptions.<br />
Laser ablation ICP-MS has been optimised<br />
for the fast control of materials<br />
homogeneity in cm-regions (Fig.1)<br />
with lateral resolution down to 20 µm.<br />
This makes the identification of phases<br />
with dimensions below 200 µm<br />
possible. The quantification of YNiBC systems was successful within 2 % RSD<br />
using binary, ternary <strong>and</strong> quaternary synthetical st<strong>and</strong>ards.<br />
Gernot Krabbes,<br />
Günter Fuchs,<br />
Stefan Gruß,<br />
Gudrun Stöver,<br />
Peter Verges,<br />
Rol<strong>and</strong> Hayn,<br />
Larisa Shlyk,<br />
Karl-Hartmut Müller,<br />
Ludwig Schultz,<br />
Jörg Fink<br />
Fig. top:<br />
Bulk cylinders, tiles <strong>and</strong><br />
rings<br />
Fig. right:<br />
Contours of the trapped<br />
magnetic field of a<br />
YBCO multiseeded ring<br />
(diameter 80 mm)<br />
Funded by:<br />
BMBF<br />
High performance HTSC bulk materials<br />
High performance bulk materials are one of the preconditions for a new type of permanent<br />
magnets <strong>and</strong> its application in newly designed electromotors, frictionless<br />
bearings <strong>and</strong> physical technologies. Remanent induction („trapped field“) <strong>and</strong><br />
appearing forces between the superconductor <strong>and</strong> an applied field depend on both<br />
the critical current density j c <strong>and</strong> diameter of the pseudo single crystalline material.<br />
With respect to applications materials of appropriate size <strong>and</strong> shape are needed.<br />
The properties of YBa 2 Cu 3 O 7 based melt grown material (YBCO) have been<br />
remarkably altered by chemical modifications. Substitutions by cations of differing<br />
valence, i.e. Y 3+ by Ca 2+ , influence the hole density in (CuO 2 ) x -planes, thus affecting<br />
the critical temperature T c . On the other h<strong>and</strong>, substitution of in plane Cu 2+<br />
especially by Zn 2+ was found to result in remarkably improved critical current densities<br />
in applied fields of more than 2 T already at 77 K. An explanation can be<br />
based on local magnetic moments which appear if Cu 2+ (S = 1/2) is substituted by<br />
cations of differing spins S (Ni 2+ , S = 1; Zn 2+ , S = 0), thus causing alternative pinning<br />
centres. An optimum dop<strong>and</strong> level was observed since the appearing<br />
moments decrease T c . The trapped field on the top surface of a YBCO cylinder at<br />
77 K achieves 1.2 T. The trapped field increases to nearly 2 T, if additional columnar<br />
defects have been generated by neutron irradiation (co-operation H. Weber,<br />
Vienna).<br />
YBCO materials grown by the modified<br />
melt crystallisation process (MMCP,<br />
developed in IFW) distinguish by a<br />
remarkable mechanical strength. Thus it<br />
was possible to generate a mini-magnet<br />
from YBCO : Zn material – reinforced by<br />
an applied ring b<strong>and</strong>age from stainless<br />
steel – with a trapped field of 11.2 T<br />
already at T = 47 K. This is the highest<br />
field ever achieved in bulk material at T ><br />
40 K.<br />
A multiseeding technique was developed to produce large tiles or rings consisting<br />
of uniformly <strong>and</strong> well aligned <strong>and</strong> coherently bounded single grains. At 77 K,<br />
the intergrain j c amounts to 10 % of the intragrain critical current density. Size <strong>and</strong><br />
shape are appropriate to its use in bearings <strong>and</strong> rotors of electrical motors.<br />
Cooperation: Oswald Elektromotoren GmbH Miltenberg, Solvay Barium Strontium<br />
GmbH, Bad Hönningen, IPHT Jena, Atominstitut der Österreichischen Universitäten<br />
Wien, ZFW Göttingen, Univ. Stuttgart, MAI Moskau<br />
56