METI-LIS Technical Manual
METI-LIS Technical Manual
METI-LIS Technical Manual
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
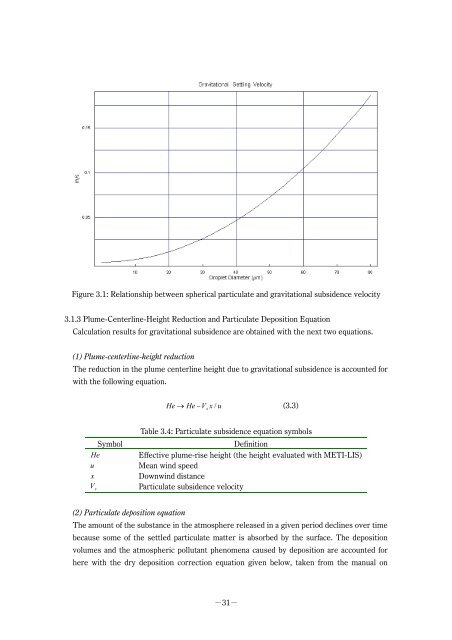
Figure 3.1: Relationship between spherical particulate and gravitational subsidence velocity<br />
3.1.3 Plume-Centerline-Height Reduction and Particulate Deposition Equation<br />
Calculation results for gravitational subsidence are obtained with the next two equations.<br />
(1) Plume-centerline-height reduction<br />
The reduction in the plume centerline height due to gravitational subsidence is accounted for<br />
with the following equation.<br />
He → He −Vs x / u<br />
(3.3)<br />
Symbol<br />
He<br />
u<br />
x<br />
V<br />
s<br />
Table 3.4: Particulate subsidence equation symbols<br />
Definition<br />
Effective plume-rise height (the height evaluated with <strong>METI</strong>-<strong>LIS</strong>)<br />
Mean wind speed<br />
Downwind distance<br />
Particulate subsidence velocity<br />
(2) Particulate deposition equation<br />
The amount of the substance in the atmosphere released in a given period declines over time<br />
because some of the settled particulate matter is absorbed by the surface. The deposition<br />
volumes and the atmospheric pollutant phenomena caused by deposition are accounted for<br />
here with the dry deposition correction equation given below, taken from the manual on<br />
-31-