Quds University Small Scale Waste Water Treatment Plants in West ...
Quds University Small Scale Waste Water Treatment Plants in West ...
Quds University Small Scale Waste Water Treatment Plants in West ...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
4-Tertiary (or advanced): removal of specific components and/ or complementary<br />
removal of components which were not sufficiently removed by the secondary<br />
treatment, e.g. nutrients or pathogenic organisms.<br />
A further stage <strong>in</strong>volves the treatment of the surplus sludge generated along the process by<br />
stabilization and/or thicken<strong>in</strong>g and dewater<strong>in</strong>g prior to reuse or disposal. The stages of the<br />
treatment are usually classified by the nature of the treatment applied. In the mechanical<br />
treatment, the use of physical forces (screen<strong>in</strong>g, sedimentation and filtration) prevails; the<br />
chemical treatments <strong>in</strong>volve the use of external reagents and chemical reactions<br />
(flocculation, precipitation, redox, dis<strong>in</strong>fection), the biological treatments are based<br />
upon the activities of micro organisms, ma<strong>in</strong>ly bacteria, which use the biodegradable<br />
organic pollutants as a substrate for their metabolism (activated sludge, trickl<strong>in</strong>g filters,<br />
lagoons, aerobic and anaerobic digestion); the thermal treatments use heat for the<br />
evaporation of water, the destruction of the organic components or for sludge treatment<br />
(dehydration, <strong>in</strong>c<strong>in</strong>eration) (Bouwer, 1978).<br />
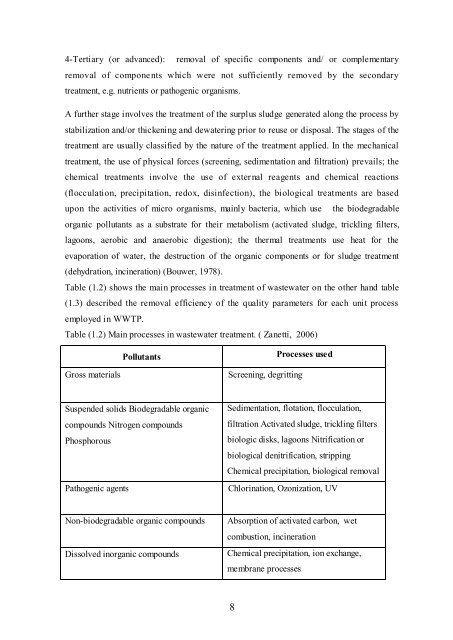
Table (1.2) shows the ma<strong>in</strong> processes <strong>in</strong> treatment of wastewater on the other hand table<br />
(1.3) described the removal efficiency of the quality parameters for each unit process<br />
employed <strong>in</strong> WWTP.<br />
Table (1.2) Ma<strong>in</strong> processes <strong>in</strong> wastewater treatment. ( Zanetti, 2006)<br />
Pollutants<br />
Processes used<br />
Gross materials<br />
Screen<strong>in</strong>g, degritt<strong>in</strong>g<br />
Suspended solids Biodegradable organic<br />
compounds Nitrogen compounds<br />
Phosphorous<br />
Pathogenic agents<br />
Sedimentation, flotation, flocculation,<br />
filtration Activated sludge, trickl<strong>in</strong>g filters<br />
biologic disks, lagoons Nitrification or<br />
biological denitrification, stripp<strong>in</strong>g<br />
Chemical precipitation, biological removal<br />
Chlor<strong>in</strong>ation, Ozonization, UV<br />
Non-biodegradable organic compounds<br />
Dissolved <strong>in</strong>organic compounds<br />
Absorption of activated carbon, wet<br />
combustion, <strong>in</strong>c<strong>in</strong>eration<br />
Chemical precipitation, ion exchange,<br />
membrane processes<br />
8