Single vs. double focus in English statements and yes/no questions
Single vs. double focus in English statements and yes/no questions
Single vs. double focus in English statements and yes/no questions
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
3.1. Graphic analysis<br />
3. Results<br />
Consequently, the F 0 difference between these two sentence<br />
types becomes salient start<strong>in</strong>g from the stressed syllable of the<br />
first content word, whether or <strong>no</strong>t it is <strong>focus</strong>ed (Fig. 3).<br />
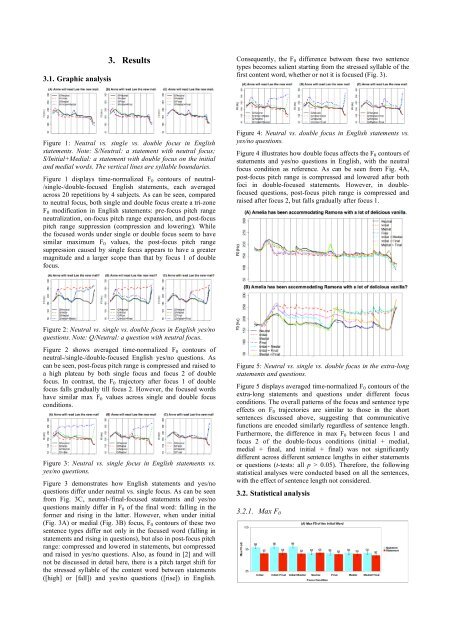
Figure 1: Neutral <strong>vs</strong>. s<strong>in</strong>gle <strong>vs</strong>. <strong>double</strong> <strong>focus</strong> <strong>in</strong> <strong>English</strong><br />
<strong>statements</strong>. Note: S/Neutral: a statement with neutral <strong>focus</strong>;<br />
S/Initial+Medial: a statement with <strong>double</strong> <strong>focus</strong> on the <strong>in</strong>itial<br />
<strong>and</strong> medial words. The vertical l<strong>in</strong>es are syllable boundaries.<br />
Figure 1 displays time-<strong>no</strong>rmalized F 0 contours of neutral-<br />
/s<strong>in</strong>gle-/<strong>double</strong>-<strong>focus</strong>ed <strong>English</strong> <strong>statements</strong>, each averaged<br />
across 20 repetitions by 4 subjects. As can be seen, compared<br />
to neutral <strong>focus</strong>, both s<strong>in</strong>gle <strong>and</strong> <strong>double</strong> <strong>focus</strong> create a tri-zone<br />
F 0 modification <strong>in</strong> <strong>English</strong> <strong>statements</strong>: pre-<strong>focus</strong> pitch range<br />
neutralization, on-<strong>focus</strong> pitch range expansion, <strong>and</strong> post-<strong>focus</strong><br />
pitch range suppression (compression <strong>and</strong> lower<strong>in</strong>g). While<br />
the <strong>focus</strong>ed words under s<strong>in</strong>gle or <strong>double</strong> <strong>focus</strong> seem to have<br />
similar maximum F 0 values, the post-<strong>focus</strong> pitch range<br />
suppression caused by s<strong>in</strong>gle <strong>focus</strong> appears to have a greater<br />
magnitude <strong>and</strong> a larger scope than that by <strong>focus</strong> 1 of <strong>double</strong><br />
<strong>focus</strong>.<br />
Figure 4: Neutral <strong>vs</strong>. <strong>double</strong> <strong>focus</strong> <strong>in</strong> <strong>English</strong> <strong>statements</strong> <strong>vs</strong>.<br />
<strong>yes</strong>/<strong>no</strong> <strong>questions</strong>.<br />
Figure 4 illustrates how <strong>double</strong> <strong>focus</strong> affects the F 0 contours of<br />
<strong>statements</strong> <strong>and</strong> <strong>yes</strong>/<strong>no</strong> <strong>questions</strong> <strong>in</strong> <strong>English</strong>, with the neutral<br />
<strong>focus</strong> condition as reference. As can be seen from Fig. 4A,<br />
post-<strong>focus</strong> pitch range is compressed <strong>and</strong> lowered after both<br />
foci <strong>in</strong> <strong>double</strong>-<strong>focus</strong>ed <strong>statements</strong>. However, <strong>in</strong> <strong>double</strong><strong>focus</strong>ed<br />
<strong>questions</strong>, post-<strong>focus</strong> pitch range is compressed <strong>and</strong><br />
raised after <strong>focus</strong> 2, but falls gradually after <strong>focus</strong> 1.<br />
Figure 2: Neutral <strong>vs</strong>. s<strong>in</strong>gle <strong>vs</strong>. <strong>double</strong> <strong>focus</strong> <strong>in</strong> <strong>English</strong> <strong>yes</strong>/<strong>no</strong><br />
<strong>questions</strong>. Note: Q/Neutral: a question with neutral <strong>focus</strong>.<br />
Figure 2 shows averaged time-<strong>no</strong>rmalized F 0 contours of<br />
neutral-/s<strong>in</strong>gle-/<strong>double</strong>-<strong>focus</strong>ed <strong>English</strong> <strong>yes</strong>/<strong>no</strong> <strong>questions</strong>. As<br />
can be seen, post-<strong>focus</strong> pitch range is compressed <strong>and</strong> raised to<br />
a high plateau by both s<strong>in</strong>gle <strong>focus</strong> <strong>and</strong> <strong>focus</strong> 2 of <strong>double</strong><br />
<strong>focus</strong>. In contrast, the F 0 trajectory after <strong>focus</strong> 1 of <strong>double</strong><br />
<strong>focus</strong> falls gradually till <strong>focus</strong> 2. However, the <strong>focus</strong>ed words<br />
have similar max F 0 values across s<strong>in</strong>gle <strong>and</strong> <strong>double</strong> <strong>focus</strong><br />
conditions.<br />
Figure 3: Neutral <strong>vs</strong>. s<strong>in</strong>gle <strong>focus</strong> <strong>in</strong> <strong>English</strong> <strong>statements</strong> <strong>vs</strong>.<br />
<strong>yes</strong>/<strong>no</strong> <strong>questions</strong>.<br />
Figure 3 demonstrates how <strong>English</strong> <strong>statements</strong> <strong>and</strong> <strong>yes</strong>/<strong>no</strong><br />
<strong>questions</strong> differ under neutral <strong>vs</strong>. s<strong>in</strong>gle <strong>focus</strong>. As can be seen<br />
from Fig. 3C, neutral-/f<strong>in</strong>al-<strong>focus</strong>ed <strong>statements</strong> <strong>and</strong> <strong>yes</strong>/<strong>no</strong><br />
<strong>questions</strong> ma<strong>in</strong>ly differ <strong>in</strong> F 0 of the f<strong>in</strong>al word: fall<strong>in</strong>g <strong>in</strong> the<br />
former <strong>and</strong> ris<strong>in</strong>g <strong>in</strong> the latter. However, when under <strong>in</strong>itial<br />
(Fig. 3A) or medial (Fig. 3B) <strong>focus</strong>, F 0 contours of these two<br />
sentence types differ <strong>no</strong>t only <strong>in</strong> the <strong>focus</strong>ed word (fall<strong>in</strong>g <strong>in</strong><br />
<strong>statements</strong> <strong>and</strong> ris<strong>in</strong>g <strong>in</strong> <strong>questions</strong>), but also <strong>in</strong> post-<strong>focus</strong> pitch<br />
range: compressed <strong>and</strong> lowered <strong>in</strong> <strong>statements</strong>, but compressed<br />
<strong>and</strong> raised <strong>in</strong> <strong>yes</strong>/<strong>no</strong> <strong>questions</strong>. Also, as found <strong>in</strong> [2] <strong>and</strong> will<br />
<strong>no</strong>t be discussed <strong>in</strong> detail here, there is a pitch target shift for<br />
the stressed syllable of the content word between <strong>statements</strong><br />
([high] or [fall]) <strong>and</strong> <strong>yes</strong>/<strong>no</strong> <strong>questions</strong> ([rise]) <strong>in</strong> <strong>English</strong>.<br />
Figure 5: Neutral <strong>vs</strong>. s<strong>in</strong>gle <strong>vs</strong>. <strong>double</strong> <strong>focus</strong> <strong>in</strong> the extra-long<br />
<strong>statements</strong> <strong>and</strong> <strong>questions</strong>.<br />
Figure 5 displays averaged time-<strong>no</strong>rmalized F 0 contours of the<br />
extra-long <strong>statements</strong> <strong>and</strong> <strong>questions</strong> under different <strong>focus</strong><br />
conditions. The overall patterns of the <strong>focus</strong> <strong>and</strong> sentence type<br />
effects on F 0 trajectories are similar to those <strong>in</strong> the short<br />
sentences discussed above, suggest<strong>in</strong>g that communicative<br />
functions are encoded similarly regardless of sentence length.<br />
Furthermore, the difference <strong>in</strong> max F 0 between <strong>focus</strong> 1 <strong>and</strong><br />
<strong>focus</strong> 2 of the <strong>double</strong>-<strong>focus</strong> conditions (<strong>in</strong>itial + medial,<br />
medial + f<strong>in</strong>al, <strong>and</strong> <strong>in</strong>itial + f<strong>in</strong>al) was <strong>no</strong>t significantly<br />
different across different sentence lengths <strong>in</strong> either <strong>statements</strong><br />
or <strong>questions</strong> (t-tests: all p > 0.05). Therefore, the follow<strong>in</strong>g<br />
statistical analyses were conducted based on all the sentences,<br />
with the effect of sentence length <strong>no</strong>t considered.<br />
3.2. Statistical analysis<br />
3.2.1. Max F 0