16. Monopolistic Competition
16. Monopolistic Competition
16. Monopolistic Competition
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
Economics 2010-200<br />
University of Colorado<br />
Soojae Moon Fall 2009<br />
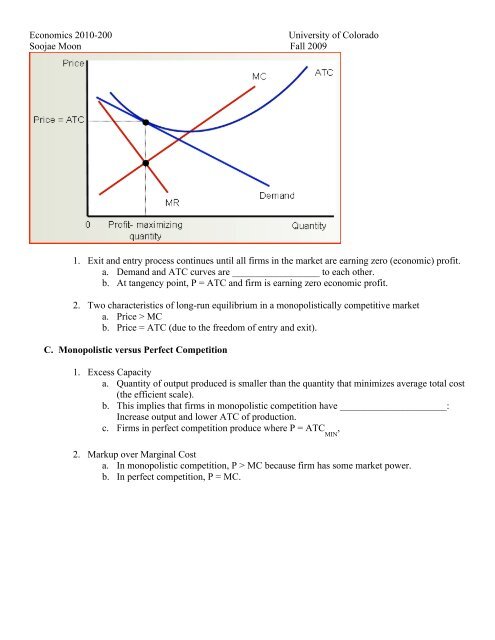
1. Exit and entry process continues until all firms in the market are earning zero (economic) profit.<br />
a. Demand and ATC curves are __________________ to each other.<br />
b. At tangency point, P = ATC and firm is earning zero economic profit.<br />
2. Two characteristics of long-run equilibrium in a monopolistically competitive market<br />
a. Price > MC<br />
b. Price = ATC (due to the freedom of entry and exit).<br />
C. <strong>Monopolistic</strong> versus Perfect <strong>Competition</strong><br />
1. Excess Capacity<br />
a. Quantity of output produced is smaller than the quantity that minimizes average total cost<br />
(the efficient scale).<br />
b. This implies that firms in monopolistic competition have ______________________:<br />
Increase output and lower ATC of production.<br />
c. Firms in perfect competition produce where P = ATC<br />
MIN<br />
,<br />
2. Markup over Marginal Cost<br />
a. In monopolistic competition, P > MC because firm has some market power.<br />
b. In perfect competition, P = MC.