Subdivision Surfaces
Subdivision Surfaces
Subdivision Surfaces
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
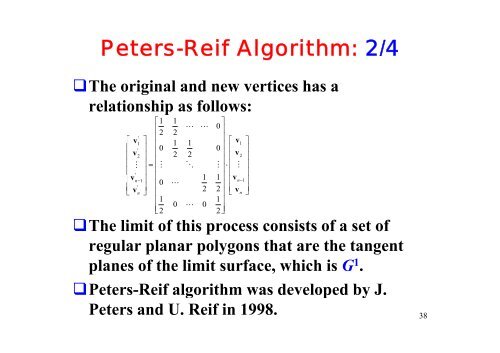
Peters-Reif Algorithm: 2/4<br />
The original and new vertices has a<br />
relationship as follows:<br />
⎡1 1<br />
⎢2 ⎢<br />
2<br />
<br />
<br />
⎤<br />
0<br />
⎥<br />
⎥<br />
'<br />
⎡ v<br />
⎤<br />
1 1 1<br />
⎡ 1<br />
⎤<br />
⎢ ' ⎥ ⎢0 0⎥<br />
⎢ ⎥<br />
v2<br />
⎢<br />
⎥ v2<br />
⎢ ⎥ 2 2 ⎢ ⎥<br />
⎢ ⎢<br />
⎥<br />
⎥ = ⎢ ⎥<br />
⎢<br />
<br />
⎥<br />
⋅ <br />
⎢<br />
'<br />
⎥ ⎢ ⎥<br />
⎢ v<br />
1 1<br />
n−1<br />
⎥ ⎢ ⎥<br />
1<br />
0<br />
⎢vn−<br />
⎥<br />
' ⎢ <br />
⎢ ⎥ ⎥<br />
2 2 ⎢ ⎥<br />
⎣ vn<br />
⎦ ⎢ ⎥ ⎣ vn<br />
⎦<br />
⎢1 1⎥<br />
⎢<br />
0 0<br />
⎣2 2⎥⎦<br />
v<br />
The limit of this process consists of a set of<br />
regular planar polygons that are the tangent<br />
planes of the limit surface, which is G 1 .<br />
Peters-Reif algorithm was developed by J.<br />
Peters and U. Reif in 1998.<br />
38