Chapter 6
Chapter 6
Chapter 6
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
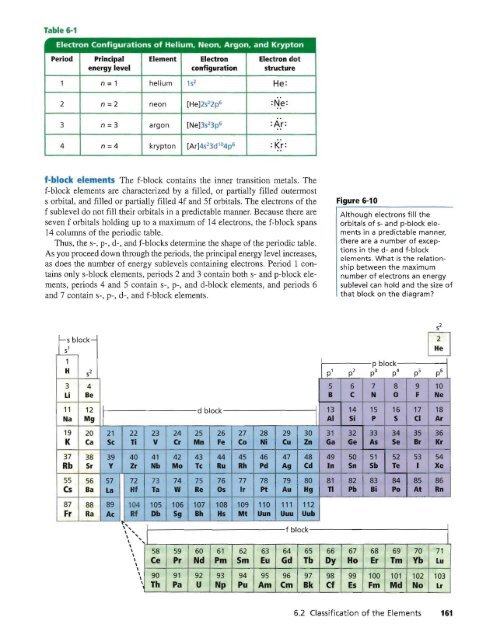
Electron Configurations of Helium, Neon, Argon, and Krypton<br />
Period<br />
-<br />
Principal Element Electron Electron dot<br />
energy level configuration structure<br />
1 n =1 helium 1S 2 He:<br />
2 n=2 neon [He)2s 2 2p6 =Ne: ..<br />
o.<br />
3 n=3 argon [Ne]3s 2 3p6 :Ar=<br />
4 n=4 krypton [Ar]4s 2 3d I04p =Kr:<br />
f- ock e 'emen The f-block contains the inner transition metals. The<br />
f-block elements are characterized by a filled, or partially filled outennost<br />
s orbital, and filled or partially filled 4f and 5f orbitals. The electrons of the<br />
f sublevel do not fill their orbitals in a predictable manner. Because there are<br />
seven f orbitals holding up to a maximum of 14 electrons, the f-block spans<br />
14 columns of the periodic table.<br />
Thus, the S-, p-, d-, and f-blocks determine the shape of the periodic table.<br />
As you proceed down through the periods, the principal energy level increases,<br />
as does the number of energy sublevels contalning electrons. Period I contains<br />
only s-block elements, periods 2 and 3 contain both s- and p-block elements,<br />
periods 4 and 5 contain S-, p-, and d-block elements, and periods 6<br />
and 7 contain S-, p-, d-, and f-block elements.<br />
Figure 6-10<br />
Although electrons fill the<br />
orbitals of s- and p-block elements<br />
in a predictable manner,<br />
there are a number of exceptions<br />
in the d- and f-block<br />
elements. What is the relationship<br />
between the maximum<br />
number of electrons an energy<br />
sublevel can hold and the size of<br />
that block on the diagram<br />
s block- 2<br />
s'<br />
He<br />
1 I<br />
P block<br />
H S2 I p1 p2 p3 p4 ps p 6 1<br />
3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10<br />
Li Be<br />
I<br />
B C N 0 F Ne<br />
: 11 12<br />
I<br />
d block<br />
13 14 15 16 17 18<br />
Na Mg AI<br />
1m<br />
I<br />
5i P 5 CI Ar<br />
-~<br />
i<br />
119 2.0 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 I 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36<br />
K Ca 5c Ti V Cr Mn Fe Co Ni Cu Zn Ga Ge As Se Br Kr<br />
1<br />
.. .- -<br />
37 38 39 40 41 42. 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54<br />
Rb Sr Y Zr Nb Mo Tc Ru Rh Pd Ag Cd In Sn 5b Te I Xe<br />
55 56 57 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 ! 80 81 I 82 83 84 85 86<br />
Cs Ba La Hf Ta W Re Os Ir Pt Au Hg TI Pb Bi Po<br />
~t.l Rn<br />
r-- ..<br />
87 88 89 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112<br />
Fr Ra Ac Rf Db Sg Bh H5 Mt Uun Uuu Uub<br />
to,<br />
, I<br />
,<br />
f block<br />
, '<br />
\ '<br />
\<br />
\<br />
\<br />
\<br />
\,<br />
\<br />
\<br />
\<br />
J<br />
58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71<br />
Ce Pr Nd Pm Sm Eu Gd Tb Dy Ho Er Tm Yb Lu<br />
90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103<br />
Th Pa U Np Pu Am Cm Bk Cf Es Fm Md No Lr<br />
.,- .<br />
6.2 Classification of the Elements 161<br />
I<br />
I