A Survey on Seeded Region Growing based Segmentation ... - ijcsmr
A Survey on Seeded Region Growing based Segmentation ... - ijcsmr
A Survey on Seeded Region Growing based Segmentation ... - ijcsmr
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
Internati<strong>on</strong>al Journal of Computer Science and Management Research Vol 2 Issue 6 June 2013<br />
ISSN 2278-733X<br />
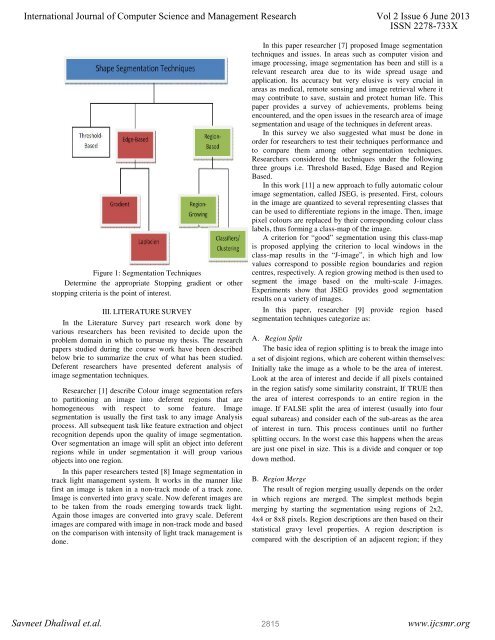
Figure 1: Segmentati<strong>on</strong> Techniques<br />
Determine the appropriate Stopping gradient or other<br />
stopping criteria is the point of interest.<br />
III. LITERATURE SURVEY<br />
In the Literature <str<strong>on</strong>g>Survey</str<strong>on</strong>g> part research work d<strong>on</strong>e by<br />
various researchers has been revisited to decide up<strong>on</strong> the<br />
problem domain in which to pursue my thesis. The research<br />
papers studied during the course work have been described<br />
below brie to summarize the crux of what has been studied.<br />
Deferent researchers have presented deferent analysis of<br />
image segmentati<strong>on</strong> techniques.<br />
Researcher [1] describe Colour image segmentati<strong>on</strong> refers<br />
to partiti<strong>on</strong>ing an image into deferent regi<strong>on</strong>s that are<br />
homogeneous with respect to some feature. Image<br />
segmentati<strong>on</strong> is usually the first task to any image Analysis<br />
process. All subsequent task like feature extracti<strong>on</strong> and object<br />
recogniti<strong>on</strong> depends up<strong>on</strong> the quality of image segmentati<strong>on</strong>.<br />
Over segmentati<strong>on</strong> an image will split an object into deferent<br />
regi<strong>on</strong>s while in under segmentati<strong>on</strong> it will group various<br />
objects into <strong>on</strong>e regi<strong>on</strong>.<br />
In this paper researchers tested [8] Image segmentati<strong>on</strong> in<br />
track light management system. It works in the manner like<br />
first an image is taken in a n<strong>on</strong>-track mode of a track z<strong>on</strong>e.<br />
Image is c<strong>on</strong>verted into gravy scale. Now deferent images are<br />
to be taken from the roads emerging towards track light.<br />
Again those images are c<strong>on</strong>verted into gravy scale. Deferent<br />
images are compared with image in n<strong>on</strong>-track mode and <strong>based</strong><br />
<strong>on</strong> the comparis<strong>on</strong> with intensity of light track management is<br />
d<strong>on</strong>e.<br />
In this paper researcher [7] proposed Image segmentati<strong>on</strong><br />
techniques and issues. In areas such as computer visi<strong>on</strong> and<br />
image processing, image segmentati<strong>on</strong> has been and still is a<br />
relevant research area due to its wide spread usage and<br />
applicati<strong>on</strong>. Its accuracy but very elusive is very crucial in<br />
areas as medical, remote sensing and image retrieval where it<br />
may c<strong>on</strong>tribute to save, sustain and protect human life. This<br />
paper provides a survey of achievements, problems being<br />
encountered, and the open issues in the research area of image<br />
segmentati<strong>on</strong> and usage of the techniques in deferent areas.<br />
In this survey we also suggested what must be d<strong>on</strong>e in<br />
order for researchers to test their techniques performance and<br />
to compare them am<strong>on</strong>g other segmentati<strong>on</strong> techniques.<br />
Researchers c<strong>on</strong>sidered the techniques under the following<br />
three groups i.e. Threshold Based, Edge Based and Regi<strong>on</strong><br />
Based.<br />
In this work [11] a new approach to fully automatic colour<br />
image segmentati<strong>on</strong>, called JSEG, is presented. First, colours<br />
in the image are quantized to several representing classes that<br />
can be used to differentiate regi<strong>on</strong>s in the image. Then, image<br />
pixel colours are replaced by their corresp<strong>on</strong>ding colour class<br />
labels, thus forming a class-map of the image.<br />
A criteri<strong>on</strong> for “good” segmentati<strong>on</strong> using this class-map<br />
is proposed applying the criteri<strong>on</strong> to local windows in the<br />
class-map results in the “J-image”, in which high and low<br />
values corresp<strong>on</strong>d to possible regi<strong>on</strong> boundaries and regi<strong>on</strong><br />
centres, respectively. A regi<strong>on</strong> growing method is then used to<br />
segment the image <strong>based</strong> <strong>on</strong> the multi-scale J-images.<br />
Experiments show that JSEG provides good segmentati<strong>on</strong><br />
results <strong>on</strong> a variety of images.<br />
In this paper, researcher [9] provide regi<strong>on</strong> <strong>based</strong><br />
segmentati<strong>on</strong> techniques categorize as:<br />
A. Regi<strong>on</strong> Split<br />
The basic idea of regi<strong>on</strong> splitting is to break the image into<br />
a set of disjoint regi<strong>on</strong>s, which are coherent within themselves:<br />
Initially take the image as a whole to be the area of interest.<br />
Look at the area of interest and decide if all pixels c<strong>on</strong>tained<br />
in the regi<strong>on</strong> satisfy some similarity c<strong>on</strong>straint, If TRUE then<br />
the area of interest corresp<strong>on</strong>ds to an entire regi<strong>on</strong> in the<br />
image. If FALSE split the area of interest (usually into four<br />
equal subareas) and c<strong>on</strong>sider each of the sub-areas as the area<br />
of interest in turn. This process c<strong>on</strong>tinues until no further<br />
splitting occurs. In the worst case this happens when the areas<br />
are just <strong>on</strong>e pixel in size. This is a divide and c<strong>on</strong>quer or top<br />
down method.<br />
B. Regi<strong>on</strong> Merge<br />
The result of regi<strong>on</strong> merging usually depends <strong>on</strong> the order<br />
in which regi<strong>on</strong>s are merged. The simplest methods begin<br />
merging by starting the segmentati<strong>on</strong> using regi<strong>on</strong>s of 2x2,<br />
4x4 or 8x8 pixels. Regi<strong>on</strong> descripti<strong>on</strong>s are then <strong>based</strong> <strong>on</strong> their<br />
statistical gravy level properties. A regi<strong>on</strong> descripti<strong>on</strong> is<br />
compared with the descripti<strong>on</strong> of an adjacent regi<strong>on</strong>; if they<br />
Savneet Dhaliwal et.al.<br />
2815<br />
www.<strong>ijcsmr</strong>.org