Solutions to Chapter 6 - Communication Networks
Solutions to Chapter 6 - Communication Networks
Solutions to Chapter 6 - Communication Networks
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
<strong>Communication</strong> <strong>Networks</strong> (2 nd Edition)<br />
<strong>Chapter</strong> 6 <strong>Solutions</strong><br />
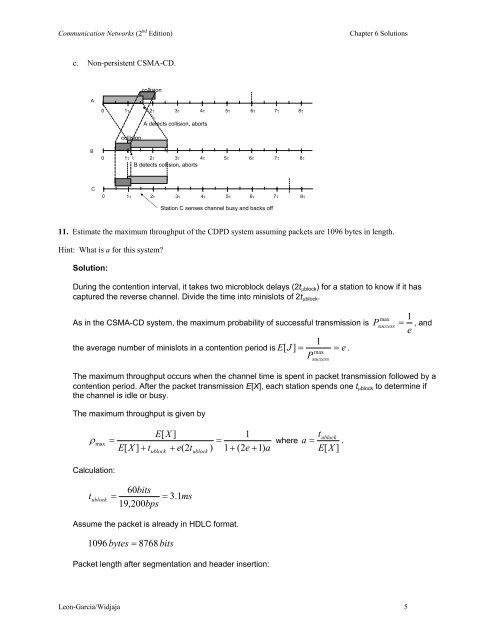
c. Non-persistent CSMA-CD.<br />
collision<br />
A<br />
0 1τ 2τ 3τ 4τ 5τ 6τ 7τ 8τ<br />
A detects collision, aborts<br />
collision<br />
B<br />
0 1τ 2τ 3τ 4τ 5τ 6τ 7τ 8τ<br />
B detects collision, aborts<br />
C<br />
0 1τ 2τ 3τ 4τ 5τ 6τ 7τ 8τ<br />
Station C senses channel busy and backs off<br />
11. Estimate the maximum throughput of the CDPD system assuming packets are 1096 bytes in length.<br />
Hint: What is a for this system<br />
Solution:<br />
During the contention interval, it takes two microblock delays (2t µblock ) for a station <strong>to</strong> know if it has<br />
captured the reverse channel. Divide the time in<strong>to</strong> minislots of 2t µblock .<br />
As in the CSMA-CD system, the maximum probability of successful transmission is<br />
the average number of minislots in a contention period is<br />
E J ]<br />
1<br />
P<br />
[ .<br />
= max<br />
success<br />
= e<br />
max 1<br />
P success<br />
= , and<br />
e<br />
The maximum throughput occurs when the channel time is spent in packet transmission followed by a<br />
contention period. After the packet transmission E[X], each station spends one t µblock <strong>to</strong> determine if<br />
the channel is idle or busy.<br />
The maximum throughput is given by<br />
max<br />
E[<br />
X ]<br />
1<br />
=<br />
=<br />
E[<br />
X ] + tublock + e(2tublock<br />
) 1+<br />
(2e<br />
+ 1)<br />
a<br />
ρ where<br />
t ublock<br />
a = .<br />
E[X ]<br />
Calculation:<br />
60bits<br />
t ublock<br />
= = 3. 1ms<br />
19,200bps<br />
Assume the packet is already in HDLC format.<br />
1096 bytes = 8768 bits<br />
Packet length after segmentation and header insertion:<br />
Leon-Garcia/Widjaja 5