Colour images RGB to YCbCr Example Example, RGB
Colour images RGB to YCbCr Example Example, RGB
Colour images RGB to YCbCr Example Example, RGB
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
<strong>Colour</strong> <strong>images</strong><br />
<strong>RGB</strong> <strong>to</strong> <strong>YCbCr</strong><br />
When coding <strong>images</strong> we usually don’t use the <strong>RGB</strong> colour space. Instead<br />
the image is described in another colour space, where the pixel values are<br />
given using a luminance (or luma) component (called Y), that tells us how<br />
bright the pixel is (ie basically a grayscale signal) and two chrominance (or<br />
chroma) components (called Cb and Cr) that tells the actual colour of the<br />
pixel.<br />
The chrominance components can often be downsampled <strong>to</strong> a lower<br />
resolution, without a human observer noticing any reduction in image<br />
quality.<br />
There are many variants of luminance-chrominance colour spaces, but<br />
they are rather similar <strong>to</strong> each other.<br />
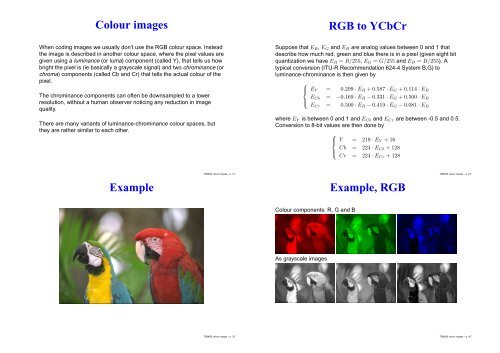
Suppose that E R , E G and E B are analog values between 0 and 1 that<br />
describe how much red, green and blue there is in a pixel (given eight bit<br />
quantization we have E R = R/255, E G = G/255 and E B = B/255). A<br />
typical conversion (ITU-R Recommendation 624-4 System B,G) <strong>to</strong><br />
luminance-chrominance is then given by<br />
⎧<br />
⎪⎨<br />
⎪⎩<br />
E Y = 0.299 · E R +0.587 · E G +0.114 · E B<br />
E Cb = −0.169 · E R − 0.331 · E G +0.500 · E B<br />
E Cr = 0.500 · E R − 0.419 · E G − 0.081 · E B<br />
where E Y is between 0 and 1 and E Cb and E Cr are between -0.5 and 0.5.<br />
Conversion <strong>to</strong> 8-bit values are then done by<br />
⎧<br />
⎪⎨<br />
⎪⎩<br />
Y = 219 · E Y +16<br />
Cb = 224 · E Cb + 128<br />
Cr = 224 · E Cr + 128<br />
<strong>Example</strong><br />
TSBK06 colour <strong>images</strong> – p. 1/7<br />
<strong>Example</strong>, <strong>RGB</strong><br />
TSBK06 colour <strong>images</strong> – p. 2/7<br />
<strong>Colour</strong> components: R, G and B<br />
As grayscale <strong>images</strong><br />
TSBK06 colour <strong>images</strong> – p. 3/7<br />
TSBK06 colour <strong>images</strong> – p. 4/7
<strong>Example</strong>, <strong>YCbCr</strong><br />
<strong>Example</strong><br />
<strong>Colour</strong> components: Y, Cb and Cr<br />
As grayscale <strong>images</strong><br />
Image where Cb and Cr have been downsampled a fac<strong>to</strong>r 2 both<br />
horizontally and vertically, ie half of the image information has been<br />
removed.<br />
<strong>Example</strong><br />
TSBK06 colour <strong>images</strong> – p. 5/7<br />
TSBK06 colour <strong>images</strong> – p. 6/7<br />
Image where R, G and B have been downsampled a fac<strong>to</strong>r √ 2 both<br />
horizontally and vertically, ie half of the image information has been<br />
removed.<br />
TSBK06 colour <strong>images</strong> – p. 7/7