Chapter 5 Vibration Analysis
Chapter 5 Vibration Analysis
Chapter 5 Vibration Analysis
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
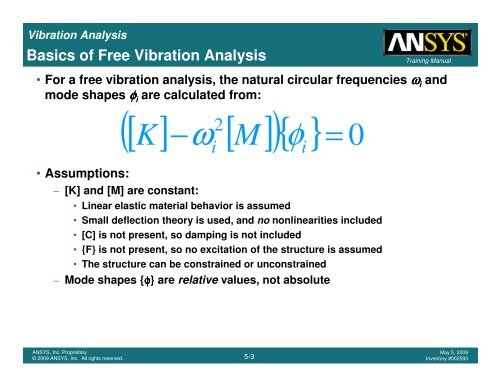
<strong>Vibration</strong> <strong>Analysis</strong><br />
Basics of Free <strong>Vibration</strong> <strong>Analysis</strong><br />
ANSYS, Inc. Proprietary<br />
© 2009 ANSYS, Inc. All rights reserved.<br />
5-3<br />
Training Manual<br />
• For a free vibration analysis, the natural circular frequencies ωωωω i and<br />
mode shapes φφφφ i are calculated from:<br />
• Assumptions:<br />
( [ K] ω<br />
2[<br />
] ){ φ } = 0<br />
– [K] and [M] are constant:<br />
− M i i<br />
• Linear elastic material behavior is assumed<br />
• Small deflection theory is used, and no nonlinearities included<br />
• [C] is not present, so damping is not included<br />
• {F} is not present, so no excitation of the structure is assumed<br />
• The structure can be constrained or unconstrained<br />
– Mode shapes {φ} are relative values, not absolute<br />
May 5, 2009<br />
Inventory #002593