Philippine National Standards for Drinking Water - LWUA
Philippine National Standards for Drinking Water - LWUA
Philippine National Standards for Drinking Water - LWUA
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
when coli<strong>for</strong>ms are present along with high populations of HPC bacteria. The<br />
presence of HPC bacteria may restrict the activities of coli<strong>for</strong>m group bacteria.<br />
Thermotolerant fecal coli<strong>for</strong>ms are a subgroup of total coli<strong>for</strong>ms that are<br />
differentiated from the total coli<strong>for</strong>ms through laboratory examinations using<br />
elevated temperature (43 to 44.5 o C). Although fecal coli<strong>for</strong>ms provide stronger<br />
evidence of fecal contamination than total coli<strong>for</strong>ms, they could not be<br />
distinguished as human or animal origin. E. coli is the indicator organism of choice<br />
<strong>for</strong> fecal contamination.<br />
On the other hand, Heterotrophic Plate Count (HPC) describes a broad group of<br />
bacteria that include pathogens, nonpathogens and opportunistic microorganisms.<br />
HPC could be used to indicate general biological condition of drinking-water as a<br />
consequence of insufficiency of treatment processes, regrowth or recontamination<br />
of drinking water in the distribution system.<br />
<strong>Water</strong> intended <strong>for</strong> human consumption should contain no indicator organisms.<br />
However, pathogens more resistant to conventional environmental conditions or<br />
treatment technologies may be present in treated drinking-water in the absence of<br />
E. coli or total coli<strong>for</strong>ms. Protozoa and some enteroviruses are more resistant to<br />
many disinfectants including chlorine, and may remain viable and pathogenic in<br />
drinking-water following disinfection process.<br />
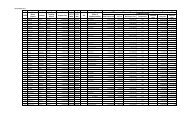
1.3. Standard Methods of Detection and Values <strong>for</strong> Microbiological Quality<br />
Parameters<br />
Total coli<strong>for</strong>m<br />
Method of<br />
Determination<br />
Multiple Tube<br />
Fermentation<br />
Technique (MTFT)<br />
Chromogenic<br />
substrate test<br />
(Presence-Absence) *<br />
Value * Units of<br />
Measurement<br />
< 1.1 MPN/ 100 mL<br />
Absent<br />