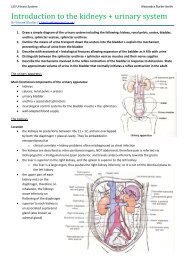
1. Introduction to Medical Sociology
1. Introduction to Medical Sociology
1. Introduction to Medical Sociology
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
FOCP Alexandra Burke-Smith<br />
Poverty<br />
Relative poverty – refers <strong>to</strong> a standard of living below that which is considered normal or acceptable.<br />
“ The resources are so seriously below those commanded by the average individual or family that they are in effect,<br />
excluded from ordinary living patterns, cus<strong>to</strong>ms and activities”<br />
Three main groups:<br />
� Those employed on low wages/ casual/ routine work<br />
� Disabled, long term sick, elderly retired<br />
� Unemployed, single parent families<br />
Living Conditions<br />
Homes of low income families likely <strong>to</strong> be:<br />
� lacking basic hygiene amenities<br />
� in poor repair<br />
� No central heating<br />
� Less basic goods ‘ consumer durables’<br />
� lacking gardens<br />
� overcrowded<br />
Working Conditions<br />
� Routine workers hourly rate<br />
� Work a greater number of hours<br />
� Work shifts – overtime, shift payment, production bonus<br />
� Income varies from week <strong>to</strong> week<br />
� Greater risk of redundancy<br />
<strong>Medical</strong> Consequences<br />
Childhood Adulthood Old age<br />
- Poor maternal nutrition<br />
- Low birth weight /<br />
premature birth<br />
- Poor nutrition during<br />
childhood<br />
- Inhibits normal growth and<br />
development<br />
- Lack of hygienic facilities<br />
- Damp housing – respira<strong>to</strong>ry<br />
problems<br />
- Poor educational record<br />
- Lack of play facilities<br />
hinders psychological<br />
development<br />
- Risk of accidents<br />
- Health hazards from<br />
maximising income<br />
- hazardous jobs ‘danger<br />
money’<br />
- Overtime / taking second job<br />
- Poor health & safety<br />
conditions<br />
- Physical exhaustion<br />
- Risk of accidents<br />
- Disrupted family life<br />
- Vulnerability <strong>to</strong> depression<br />
- Psychological effects – low<br />
self esteem<br />
- Feelings of failure and shame<br />
- Reflect immediate<br />
problems and<br />
accumulation<br />
- of past effects<br />
- Malnutrition<br />
- Hypothermia<br />
- Increased<br />
vulnerability <strong>to</strong><br />
chronic/ acute illness<br />
- Social isolation –<br />
mental illness<br />
- Risk of accidents<br />
- Institutionalised care<br />
“...The longer people live in stressful economic and social circumstances, the greater the physiological wear and<br />
tear they suffer, and the less likely they are <strong>to</strong> enjoy a healthy old age” Wilkinson and Marmot, 2003<br />
6