IMSI-report-SimulaResearch-Laboratory
IMSI-report-SimulaResearch-Laboratory
IMSI-report-SimulaResearch-Laboratory
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
2. Technical Background<br />
This section gives a brief technical overview that is necessary for understanding<br />
the analysis in the upcoming sections. We describe the architecture of a typical<br />
GSM network and how mobile devices move between cells in such a network.<br />
Note that we limit ourselves to GSM networks, because the measurements we<br />
analyze in this <strong>report</strong> were mostly performed on 2G networks. For more details<br />
about GSM networks we refer the reader to [2].<br />
2.1 GSM network architecture<br />
BTS%<br />
BSC%<br />
!HLR%<br />
MSC%<br />
!VLR%<br />
%<br />
PSTN%<br />
PSPDN%<br />
MS%<br />
BTS%<br />
BSC%<br />
BTS%<br />
Base%Sta(on%Subsystem%<br />
!EIR%<br />
!AuC%<br />
Network%Subsystem%<br />
MS% Mobile%Sta(on% VLR% Visitor%Loca(on%Register%<br />
BTS% Base%Transceiver%Sta(on% MSC% Mobile%Services%Switching%Center%<br />
BSC% Base%Sta(on%Controller% EIR% Equipment%Iden(ty%Register%<br />
HLR% Home%Loca(on%Register% AuC% Authen(ca(on%Center%<br />
PSTN%<br />
Public%Switched%Telephone%<br />
Network%<br />
PSPDN%<br />
PacketHSwitched%Public%Data%Network%<br />
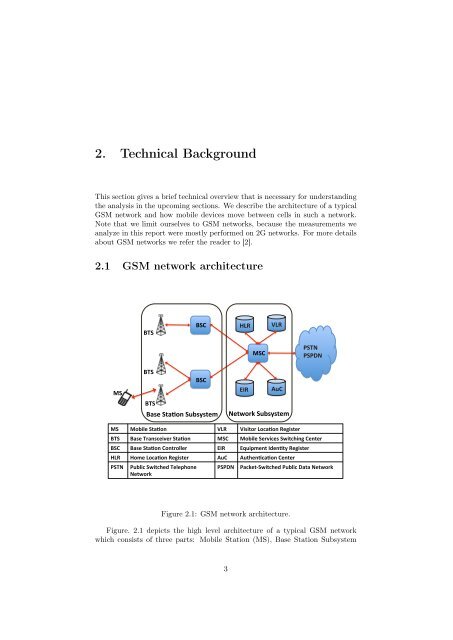
Figure 2.1: GSM network architecture.<br />
Figure. 2.1 depicts the high level architecture of a typical GSM network<br />
which consists of three parts: Mobile Station (MS), Base Station Subsystem<br />
3