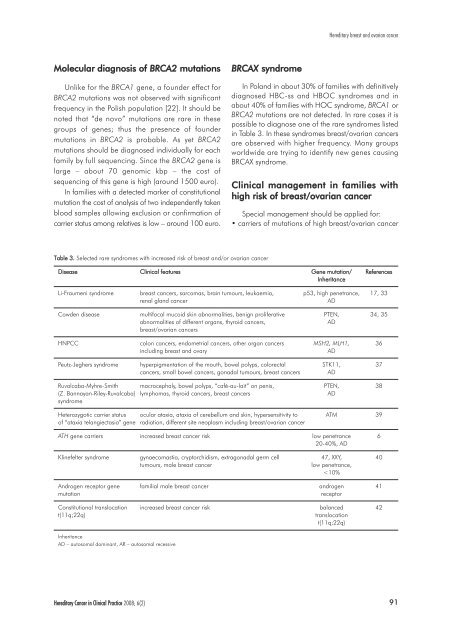
<strong>Hereditary</strong> <strong>breast</strong> <strong>and</strong> <strong>ovarian</strong> <strong>cancer</strong>Molecular diagnosis of BRCA2 mutationsUnlike for the BRCA1 gene, a founder effect forBRCA2 mutations was not observed with significantfrequency in the Polish population [22]. It should benoted that “de novo” mutations are rare in thesegroups of genes; thus the presence of foundermutations in BRCA2 is probable. As yet BRCA2mutations should be diagnosed individually for eachfamily by full sequencing. Since the BRCA2 gene islarge – about 70 genomic kbp – the cost ofsequencing of this gene is high (around 1500 euro).In families with a detected marker of constitutionalmutation the cost of analysis of two independently takenblood samples allowing exclusion or confirmation ofcarrier status among relatives is low – around 100 euro.BRCAX syndromeIn Pol<strong>and</strong> in about 30% of families with definitivelydiagnosed HBC-ss <strong>and</strong> HBOC syndromes <strong>and</strong> inabout 40% of families with HOC syndrome, BRCA1 orBRCA2 mutations are not detected. In rare cases it ispossible to diagnose one of the rare syndromes listedin Table 3. In these syndromes <strong>breast</strong>/<strong>ovarian</strong> <strong>cancer</strong>sare observed with higher frequency. Many groupsworldwide are trying to identify new genes causingBRCAX syndrome.Clinical management in families withhigh risk of <strong>breast</strong>/<strong>ovarian</strong> <strong>cancer</strong>Special management should be applied for:• carriers of mutations of high <strong>breast</strong>/<strong>ovarian</strong> <strong>cancer</strong>Table 3. Selected rare syndromes with increased risk of <strong>breast</strong> <strong>and</strong>/or <strong>ovarian</strong> <strong>cancer</strong>Disease Clinical features Gene mutation/ ReferencesInheritanceLi-Fraumeni syndrome <strong>breast</strong> <strong>cancer</strong>s, sarcomas, brain tumours, leukaemia, p53, high penetrance, 17, 33renal gl<strong>and</strong> <strong>cancer</strong>ADCowden disease multifocal mucoid skin abnormalities, benign proliferative PTEN, 34, 35abnormalities of different organs, thyroid <strong>cancer</strong>s,AD<strong>breast</strong>/<strong>ovarian</strong> <strong>cancer</strong>sHNPCC colon <strong>cancer</strong>s, endometrial <strong>cancer</strong>s, other organ <strong>cancer</strong>s MSH2, MLH1, 36including <strong>breast</strong> <strong>and</strong> ovaryADPeutz-Jeghers syndrome hyperpigmentation of the mouth, bowel polyps, colorectal STK11, 37<strong>cancer</strong>s, small bowel <strong>cancer</strong>s, gonadal tumours, <strong>breast</strong> <strong>cancer</strong>s ADRuvalcaba-Myhre-Smith macrocephaly, bowel polyps, “café-au-lait” on penis, PTEN, 38(Z. Bannayan-Riley-Ruvalcaba) lymphomas, thyroid <strong>cancer</strong>s, <strong>breast</strong> <strong>cancer</strong>sADsyndromeHeterozygotic carrier status ocular ataxia, ataxia of cerebellum <strong>and</strong> skin, hypersensitivity to ATM 39of “ataxia telangiectasia” gene radiation, different site neoplasm including <strong>breast</strong>/<strong>ovarian</strong> <strong>cancer</strong>ATH gene carriers increased <strong>breast</strong> <strong>cancer</strong> risk low penetrance 620-40%, ADKlinefelter syndrome gynaecomastia, cryptorchidism, extragonadal germ cell 47, XXY, 40tumours, male <strong>breast</strong> <strong>cancer</strong>low penetrance,
Jacek Gronwald, Tomasz Byrski, Tomasz Huzarski, Oleg Oszurek, Anna Janicka, Jolanta Szymañska-Pasternak, Bohdan Górski, Janusz Menkiszak, Izabella Rzepka-Górska, Jan Lubiñskirisk; usually around 50% of female family membersshould be included in the programme;• all family members of families with HBC-ss, HBOCor HOC diagnosed definitively or with highprobability according to pedigree criteria shown inTable 1, if constitutional mutations predisposing to<strong>cancer</strong> were not detected.Special management concerns:• prophylactics,• surveillance,• treatment.ProphylacticsOral contraceptivesContraindications for use of oral contraceptives (OC)by BRCA1 carriers aged below 25 are well documented.It was shown that OC used for 5 years by young womenincrease <strong>breast</strong> <strong>cancer</strong> risk by about 35% [43]. Since inabout 50% of BRCA1 carriers family history is negativeit seems to be necessary to perform the BRCA1 test inevery young woman who wishes to use OC. OC usedby BRCA1 carriers after the age of 30 seems not toinfluence <strong>breast</strong> <strong>cancer</strong> risk [43-45] but shows a 50%reduction of <strong>ovarian</strong> <strong>cancer</strong> risk [34], so use of OC afterthe age of 30 appears to be justified. As yet, there areno verified data concerning the effects of OC in familiesnot related to BRCA1 mutation. However, there arestudies indicating several-fold increased <strong>breast</strong> <strong>cancer</strong>risk in OC users from families with <strong>breast</strong> <strong>cancer</strong>aggregation [46]; thus it seams reasonable to avoid OCin families with HBC-ss <strong>and</strong>/or HBOC.Hormone replacement therapy (HRT)Prophylactic oopherectomy at the age of 35-40 is thegold st<strong>and</strong>ard for BRCA1/2 carriers <strong>and</strong> corresponds withrisk reduction for both <strong>breast</strong> <strong>and</strong> <strong>ovarian</strong> <strong>cancer</strong>. It wasshown that carriers after oopherectomy, who useoestrogen HRT, show a similar protective effect as patientswho do not use HRT [47, 48]. The influence of HRT incarriers without prophylactic oopherectomy is not welldocumented. Three-fold increased risk of <strong>breast</strong> <strong>cancer</strong>in HRT users with positive <strong>breast</strong> <strong>cancer</strong> family historywas reported [49]. Therefore, the decision about HRTuse should be made with particular caution.Breast feedingLong-term <strong>breast</strong> feeding is indicated in all femalesfrom families with HBC-ss, HBOC <strong>and</strong> HOC. It wasshown in BRCA1 carriers that <strong>breast</strong> feeding over 18months, counting together all pregnancies, reduces<strong>breast</strong> <strong>cancer</strong> risk – from 50-80% to 25-40% [50, 51].Early deliveryWomen from the general population who deliveredthe first child before the age of 20 are at 50% lower<strong>breast</strong> <strong>cancer</strong> risk than nulliparous women. Thisobservation was not confirmed in women with BRCA1or BRCA2 mutation [52]. However, taking intoconsideration the fact that mutation carriers shouldelect prophylactic oopherectomy at age 35-40, theyshould not delay maternity significantly.ChemopreventionTamoxifenLiterature data clearly indicate that tamoxifen reducesby about 50% the risk of ER+ <strong>breast</strong> <strong>cancer</strong>s. This effectwas observed in healthy women as well as in womentreated for <strong>breast</strong> <strong>cancer</strong>, where tamoxifen reduced therisk of contralateral <strong>breast</strong> <strong>cancer</strong>. A protective effect oftamoxifen was also observed in BRCA1 carriers in spiteof the fact that most <strong>cancer</strong>s in these patients are ER-.Such an effect of tamoxifen was observed in pre- <strong>and</strong>postmenopausal women [53, 54]. According to presentdata it is justified to propose 5 year chemoprevention withtamoxifen to patients from families with HBC-ss, HBOC<strong>and</strong> BRCA1 mutation carriers as well after exclusion ofall contraindications, especially related to clottingproblems <strong>and</strong> endometrial hypertrophy.SeleniumStudies performed in our centre showed increasedmutagen sensitivity in BRCA1 carriers as measured withthe bleomycin test. This sensitivity may be normalizedwith some selenium supplements [55]. Chemopreventionwith selenium has been observed to reduce <strong>cancer</strong> riskin both humans <strong>and</strong> animals. This question should beanswered in BRCA1 carriers.AdnexectomyBoth retrospective <strong>and</strong> prospective observations ofpatients with BRCA1/2 mutations indicate thatprophylactic adnexectomy decreases the risk of<strong>ovarian</strong>/peritoneal <strong>cancer</strong> to about 5% <strong>and</strong> <strong>breast</strong><strong>cancer</strong> to 30-40%. Application of adnexectomytogether with tamoxifen reduces <strong>breast</strong> <strong>cancer</strong> risk toabout 10% in BRCA1 carriers [14]. Therefore, in ourcentre adnexectomy is recommended to all BRCA1/2carriers aged over 35. This surgery is proposed towomen from families with HBC-ss, HBOC <strong>and</strong> HOCbut without detected BRCA1/BRCA2 mutation only ifother pathologies of the female genital tract wererecorded during control examinations. About 85% ofour patients accept this type of prophylaxis [56].92<strong>Hereditary</strong> Cancer in Clinical Practice 2008; 6(2)