A guide for practitioners
A guide for practitioners
A guide for practitioners
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
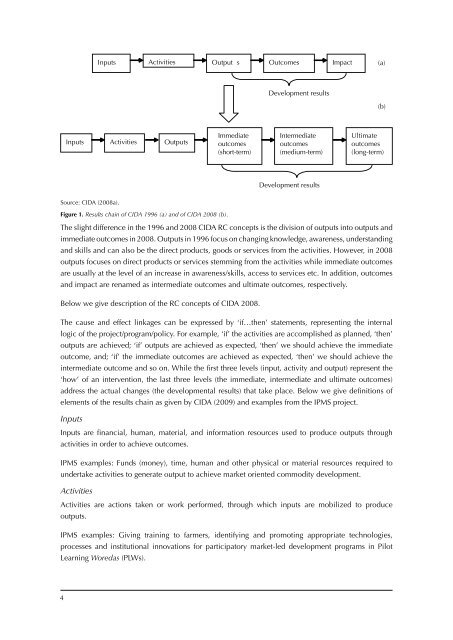
Inputs Activities Output s Outcomes Impact(a)Development results(b)Inputs Activities OutputsImmediateoutcomes(short-term)Intermediateoutcomes(medium-term)Ultimateoutcomes(long-term)Development resultsSource: CIDA (2008a).Figure 1. Results chain of CIDA 1996 (a) and of CIDA 2008 (b).The slight difference in the 1996 and 2008 CIDA RC concepts is the division of outputs into outputs andimmediate outcomes in 2008. Outputs in 1996 focus on changing knowledge, awareness, understandingand skills and can also be the direct products, goods or services from the activities. However, in 2008outputs focuses on direct products or services stemming from the activities while immediate outcomesare usually at the level of an increase in awareness/skills, access to services etc. In addition, outcomesand impact are renamed as intermediate outcomes and ultimate outcomes, respectively.Below we give description of the RC concepts of CIDA 2008.The cause and effect linkages can be expressed by ‘if…then’ statements, representing the internallogic of the project/program/policy. For example, ‘if’ the activities are accomplished as planned, ‘then’outputs are achieved; ‘if’ outputs are achieved as expected, ‘then’ we should achieve the immediateoutcome, and; ‘if’ the immediate outcomes are achieved as expected, ‘then’ we should achieve theintermediate outcome and so on. While the first three levels (input, activity and output) represent the‘how’ of an intervention, the last three levels (the immediate, intermediate and ultimate outcomes)address the actual changes (the developmental results) that take place. Below we give definitions ofelements of the results chain as given by CIDA (2009) and examples from the IPMS project.InputsInputs are financial, human, material, and in<strong>for</strong>mation resources used to produce outputs throughactivities in order to achieve outcomes.IPMS examples: Funds (money), time, human and other physical or material resources required toundertake activities to generate output to achieve market oriented commodity development.ActivitiesActivities are actions taken or work per<strong>for</strong>med, through which inputs are mobilized to produceoutputs.IPMS examples: Giving training to farmers, identifying and promoting appropriate technologies,processes and institutional innovations <strong>for</strong> participatory market-led development programs in PilotLearning Woredas (PLWs).4