Canadian Smoking Cessation Clinical Practice Guideline
Canadian Smoking Cessation Clinical Practice Guideline
Canadian Smoking Cessation Clinical Practice Guideline
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
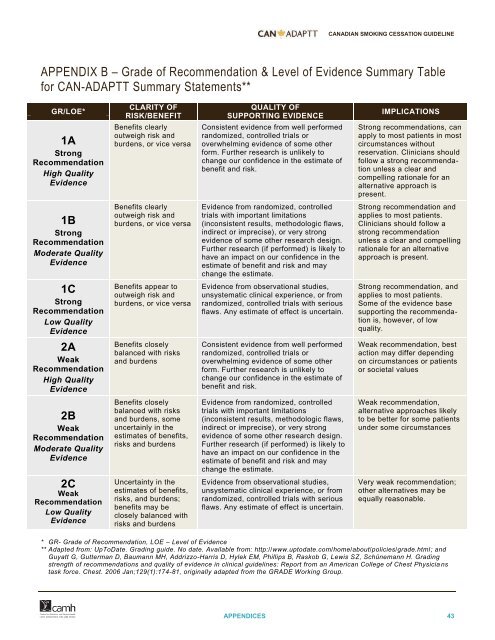
CANADIAN SMOKING CESSATION GUIDELINEAPPENDIX B – Grade of Recommendation & Level of Evidence Summary Tablefor CAN-ADAPTT Summary Statements**GR/LOE*1AStrongRecommendationHigh QualityEvidenceCLARITY OFRISK/BENEFITBenefits clearlyoutweigh risk andburdens, or vice versaQUALITY OFSUPPORTING EVIDENCEConsistent evidence from well performedrandomized, controlled trials oroverwhelming evidence of some otherform. Further research is unlikely tochange our confidence in the estimate ofbenefit and risk.IMPLICATIONSStrong recommendations, canapply to most patients in mostcircumstances withoutreservation. Clinicians shouldfollow a strong recommendationunless a clear andcompelling rationale for analternative approach ispresent.1BStrongRecommendationModerate QualityEvidenceBenefits clearlyoutweigh risk andburdens, or vice versaEvidence from randomized, controlledtrials with important limitations(inconsistent results, methodologic flaws,indirect or imprecise), or very strongevidence of some other research design.Further research (if performed) is likely tohave an impact on our confidence in theestimate of benefit and risk and maychange the estimate.Strong recommendation andapplies to most patients.Clinicians should follow astrong recommendationunless a clear and compellingrationale for an alternativeapproach is present.1CStrongRecommendationLow QualityEvidenceBenefits appear tooutweigh risk andburdens, or vice versaEvidence from observational studies,unsystematic clinical experience, or fromrandomized, controlled trials with seriousflaws. Any estimate of effect is uncertain.Strong recommendation, andapplies to most patients.Some of the evidence basesupporting the recommendationis, however, of lowquality.2AWeakRecommendationHigh QualityEvidenceBenefits closelybalanced with risksand burdensConsistent evidence from well performedrandomized, controlled trials oroverwhelming evidence of some otherform. Further research is unlikely tochange our confidence in the estimate ofbenefit and risk.Weak recommendation, bestaction may differ dependingon circumstances or patientsor societal values2BWeakRecommendationModerate QualityEvidence2CWeakRecommendationLow QualityEvidenceBenefits closelybalanced with risksand burdens, someuncertainly in theestimates of benefits,risks and burdensUncertainty in theestimates of benefits,risks, and burdens;benefits may beclosely balanced withrisks and burdensEvidence from randomized, controlledtrials with important limitations(inconsistent results, methodologic flaws,indirect or imprecise), or very strongevidence of some other research design.Further research (if performed) is likely tohave an impact on our confidence in theestimate of benefit and risk and maychange the estimate.Evidence from observational studies,unsystematic clinical experience, or fromrandomized, controlled trials with seriousflaws. Any estimate of effect is uncertain.Weak recommendation,alternative approaches likelyto be better for some patientsunder some circumstancesVery weak recommendation;other alternatives may beequally reasonable.* GR- Grade of Recommendation, LOE – Level of Evidence** Adapted from: UpToDate. Grading guide. No date. Available from: http://www.uptodate.com/home/about/policies/grade.html; andGuyatt G, Gutterman D, Baumann MH, Addrizzo-Harris D, Hylek EM, Phillips B, Raskob G, Lewis SZ, Schünemann H. Gradingstrength of recommendations and quality of evidence in clinical guidelines: Report from an American College of Chest Physicia nstask force. Chest. 2006 Jan;129(1):174-81, originally adapted from the GRADE Working Group.APPENDICES 43