Bioremediation - Asian Journal of Pharmacy and Life Science
Bioremediation - Asian Journal of Pharmacy and Life Science
Bioremediation - Asian Journal of Pharmacy and Life Science
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
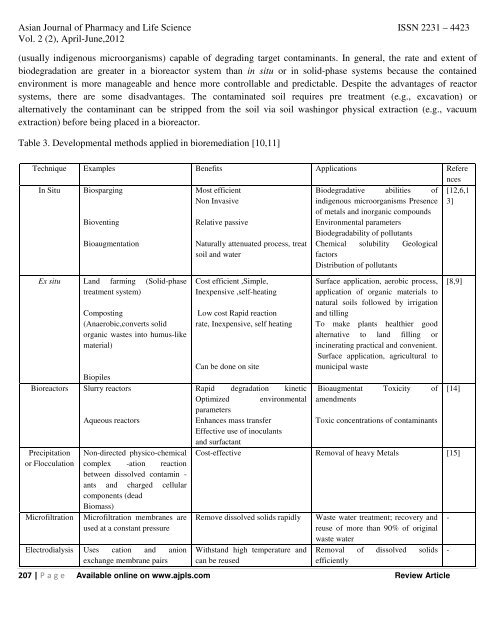
<strong>Asian</strong> <strong>Journal</strong> <strong>of</strong> <strong>Pharmacy</strong> <strong>and</strong> <strong>Life</strong> <strong>Science</strong> ISSN 2231 – 4423Vol. 2 (2), April-June,2012(usually indigenous microorganisms) capable <strong>of</strong> degrading target contaminants. In general, the rate <strong>and</strong> extent <strong>of</strong>biodegradation are greater in a bioreactor system than in situ or in solid-phase systems because the containedenvironment is more manageable <strong>and</strong> hence more controllable <strong>and</strong> predictable. Despite the advantages <strong>of</strong> reactorsystems, there are some disadvantages. The contaminated soil requires pre treatment (e.g., excavation) oralternatively the contaminant can be stripped from the soil via soil washingor physical extraction (e.g., vacuumextraction) before being placed in a bioreactor.Table 3. Developmental methods applied in bioremediation [10,11]Technique Examples Benefits Applications ReferencesIn Situ BiospargingMost efficient[12,6,1Non Invasive3]BioventingBioaugmentationEx situ L<strong>and</strong> farming (Solid-phasetreatment system)BioreactorsPrecipitationor FlocculationMicr<strong>of</strong>iltrationComposting(Anaerobic,converts solidorganic wastes into humus-likematerial)BiopilesSlurry reactorsAqueous reactorsNon-directed physico-chemicalcomplex -ation reactionbetween dissolved contamin -ants <strong>and</strong> charged cellularcomponents (deadBiomass)Micr<strong>of</strong>iltration membranes areused at a constant pressureElectrodialysis Uses cation <strong>and</strong> anionexchange membrane pairsRelative passiveNaturally attenuated process, treatsoil <strong>and</strong> waterCost efficient ,Simple,Inexpensive ,self-heatingLow cost Rapid reactionrate, Inexpensive, self heatingCan be done on siteBiodegradative abilities <strong>of</strong>indigenous microorganisms Presence<strong>of</strong> metals <strong>and</strong> inorganic compoundsEnvironmental parametersBiodegradability <strong>of</strong> pollutantsChemical solubility GeologicalfactorsDistribution <strong>of</strong> pollutantsSurface application, aerobic process,application <strong>of</strong> organic materials tonatural soils followed by irrigation<strong>and</strong> tillingTo make plants healthier goodalternative to l<strong>and</strong> filling orincinerating practical <strong>and</strong> convenient.Surface application, agricultural tomunicipal waste207 | P a g e Available online on www.ajpls.com Review Article[8,9]Rapid degradation kinetic Bioaugmentat Toxicity <strong>of</strong> [14]Optimized environmental amendmentsparametersEnhances mass transferToxic concentrations <strong>of</strong> contaminantsEffective use <strong>of</strong> inoculants<strong>and</strong> surfactantCost-effective Removal <strong>of</strong> heavy Metals [15]Remove dissolved solids rapidlyWithst<strong>and</strong> high temperature <strong>and</strong>can be reusedWaste water treatment; recovery <strong>and</strong>reuse <strong>of</strong> more than 90% <strong>of</strong> originalwaste waterRemoval <strong>of</strong> dissolved solidsefficiently--