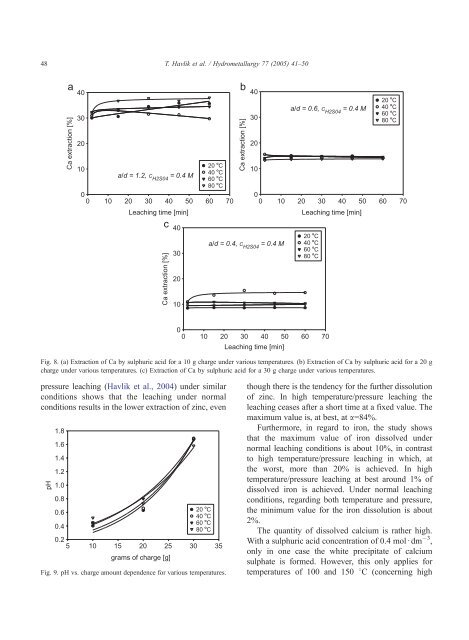
48T. Havlik et al. / Hydrometallurgy 77 (2005) 41–50aCa extraction [%]4030202010• C40 • Ca/d = 1.2, C H2S04 = 0.4 M60 • C80 • C00 10 20 30 40 50 60 70Leaching time [min]cCa extraction [%]40302010bCa extraction [%]40302010a/d = 0.4, C H2S04 = 0.4 Ma/d = 0.6, C H2S04 = 0.4 M00 10 20 30 40 50 60 70Leaching time [min]20 • C40 • C60 • C80 • C20 • C40 • C60 • C80 • C0010 20 30 40 50 60 70Leaching time [min]Fig. 8. (a) Extraction <strong>of</strong> Ca by <strong>sulphuric</strong> <strong>acid</strong> for a 10 g charge under various temperatures. (b) Extraction <strong>of</strong> Ca by <strong>sulphuric</strong> <strong>acid</strong> for a 20 gcharge under various temperatures. (c) Extraction <strong>of</strong> Ca by <strong>sulphuric</strong> <strong>acid</strong> for a 30 g charge under various temperatures.pressure <strong>leaching</strong> (Havlik et al., 2004) under similarconditions shows that the <strong>leaching</strong> under normalconditions results in the lower extraction <strong>of</strong> zinc, evenpH1.81.61.41.21.00.80.620 • C40 • C0.460 • C80 • C0.25 10 15 20 25 30 35grams <strong>of</strong> charge [g]Fig. 9. pH vs. charge amount dependence for various temperatures.though there is the tendency for the further dissolution<strong>of</strong> zinc. In high temperature/pressure <strong>leaching</strong> the<strong>leaching</strong> ceases after a short time at a fixed value. Themaximum value is, at best, at a=84%.Furthermore, in regard to iron, the study showsthat the maximum value <strong>of</strong> iron dissolved undernormal <strong>leaching</strong> conditions is about 10%, in contrastto high temperature/pressure <strong>leaching</strong> in which, atthe worst, more than 20% is achieved. In hightemperature/pressure <strong>leaching</strong> at best around 1% <strong>of</strong>dissolved iron is achieved. Under normal <strong>leaching</strong>conditions, regarding both temperature and pressure,the minimum value for the iron dissolution is about2%.The quantity <strong>of</strong> dissolved calcium is rather high.With a <strong>sulphuric</strong> <strong>acid</strong> concentration <strong>of</strong> 0.4 mold dm 3 ,only in one case the white precipitate <strong>of</strong> calciumsulphate is formed. However, this only applies fortemperatures <strong>of</strong> 100 and 150 8C (concerning high
T. Havlik et al. / Hydrometallurgy 77 (2005) 41–50 49aMetal extraction [%]80604020Zn extraction; a/d = 1.2Fe extraction; a/d = 1.2bMetal extraction [%]80604020Zn extraction; a/d = 0.4Fe extraction; a/d = 0.4020 40 60 80Temperature [ • C]020 40 60 80Temperature [ • C]Fig. 10. (a) Dependency <strong>of</strong> metal extraction vs. <strong>leaching</strong> temperature at a/d=1.2. (b) Dependency <strong>of</strong> metal extraction vs. <strong>leaching</strong> temperature ata/d=0.4.temperature/pressure <strong>leaching</strong>). This is the reason thatonly a small amount <strong>of</strong> calcium remains in the solution.Fig. 10a to b show the dependencies <strong>of</strong> metalextraction on the <strong>leaching</strong> temperature for the highestand lowest <strong>dust</strong> charge, each in relation to theamount <strong>of</strong> <strong>acid</strong> available for the <strong>leaching</strong>. For thelowest charge amount <strong>of</strong> a/d=1.2, the zinc extractionis higher having the tendency to increase at a highertemperature. Yet, when using the lowest chargeamount, also the quantity <strong>of</strong> the dissolved iron ishigher compared to a/d=0.4. The comparison <strong>with</strong>the experiment at 100 8C, presented in work (Havliket al., 2004), reveals that this, under normal temperature/pressureconditions, is the optimum temperaturefor the maximal zinc extraction. However, theamount <strong>of</strong> extracted iron is several times higher at100 8C than at 80 8C. It seems that higher values <strong>of</strong>selectivity are obtained by lower temperature and,perhaps, a/d ratios.4. ConclusionAccording to the results obtained in this work, thehydrometallurgical recovery <strong>of</strong> zinc from <strong>EAF</strong> <strong>dust</strong> isfeasible <strong>with</strong> a relatively high recovery yield, whileiron mostly stays in solid phase. A similar conclusioncan be drawn in the case <strong>of</strong> high temperature/pressure<strong>leaching</strong> under equivalent experimental conditions.Comparing the results <strong>of</strong> this work <strong>with</strong> thoseobtained by high temperature/pressure <strong>leaching</strong> manifestthat, concerning the zinc extraction, the last ismore effective. Yet, this does not relate to iron.Additionally, calcium permanently remains in thesolution. Although in high temperature/pressure<strong>leaching</strong> calcium is dissolved first, it later precipitatesas calcium sulphate. This does only relate to temperaturesup to 150 8C and pressures up to 4.1 bar. Evenin higher temperatures/pressures <strong>leaching</strong> calciumpermanently remains in the solution. This behaviourresults from using a low concentration <strong>of</strong> <strong>sulphuric</strong><strong>acid</strong>. This also causes in fact a decrease in the zincyield, yet the amount <strong>of</strong> dissolved iron is low. In sucha way, it can be possible to set up the conditions for anoptimum zinc yield into the solution <strong>with</strong> a minimisediron dissolution. However, the problem persists thatthe chemical and mineralogical composition <strong>of</strong> eachsteelmaking <strong>dust</strong> is individual and that for each onethe conditions <strong>of</strong> processing have to be studied.AcknowledgementThe authors wish to express their gratitude toSlovak grant agency VEGA (Grant 1/9379/02) forfinancial support.ReferencesBarrett, E.C., Nenniger, E.H., Dziewinski, J., 1992. A hydrometallurgicalprocess to treat carbon steel electric arc furnace<strong>dust</strong>. Hydrometallurgy (30), 59–68.