Introduction to Solid State theory, DFT and the APW-method - WIEN 2k
Introduction to Solid State theory, DFT and the APW-method - WIEN 2k
Introduction to Solid State theory, DFT and the APW-method - WIEN 2k
- No tags were found...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
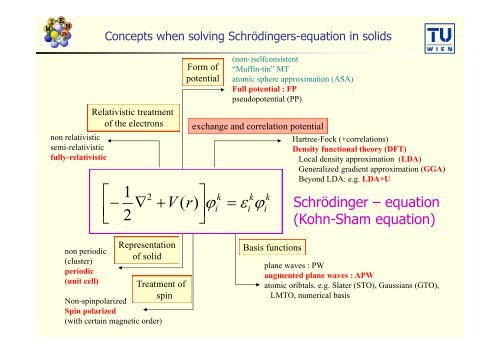
non relativisticsemi-relativisticfully-relativisticConcepts when solving Schrödingers-equation in solidsRelativistic treatmen<strong>to</strong>f <strong>the</strong> electrons1 2Form ofpotential(non-)selfconsistent“Muffin-tin” MTa<strong>to</strong>mic sphere approximation (ASA)Full potential : FPpseudopotential (PP)exchange <strong>and</strong> correlation potential k k k V( r)i ii 2 Hartree-Fock (+correlations)Density functional <strong><strong>the</strong>ory</strong> (<strong>DFT</strong>)Local density approximation (LDA)Generalized gradient approximation (GGA)Beyond LDA: e.g. LDA+USchrödinger – equation(Kohn-Sham equation)non periodic(cluster)periodic(unit cell)Representationof solidTreatment ofspinNon-spinpolarizedSpin polarized(with certain magnetic order)Basis functionsplane waves : PWaugmented plane waves : <strong>APW</strong>a<strong>to</strong>mic oribtals. e.g. Slater (STO), Gaussians (GTO),LMTO, numerical basis