The-Eureka-Phenomenon-by-Isaac-Asimov
The-Eureka-Phenomenon-by-Isaac-Asimov
The-Eureka-Phenomenon-by-Isaac-Asimov
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
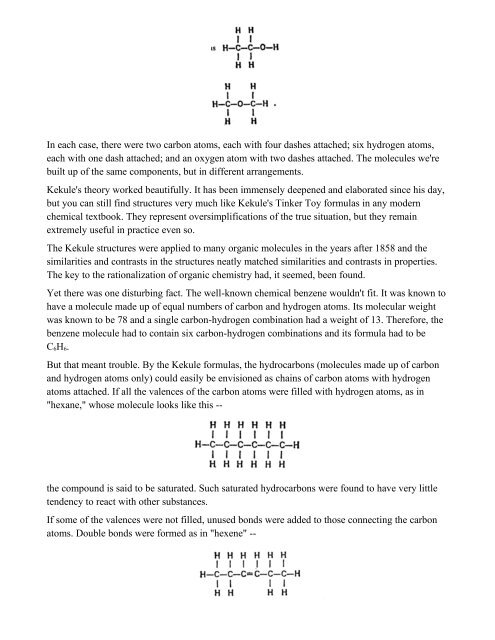
In each case, there were two carbon atoms, each with four dashes attached; six hydrogen atoms,<br />
each with one dash attached; and an oxygen atom with two dashes attached. <strong>The</strong> molecules we're<br />
built up of the same components, but in different arrangements.<br />
Kekule's theory worked beautifully. It has been immensely deepened and elaborated since his day,<br />
but you can still find structures very much like Kekule's Tinker Toy formulas in any modern<br />
chemical textbook. <strong>The</strong>y represent oversimplifications of the true situation, but they remain<br />
extremely useful in practice even so.<br />
<strong>The</strong> Kekule structures were applied to many organic molecules in the years after 1858 and the<br />
similarities and contrasts in the structures neatly matched similarities and contrasts in properties.<br />
<strong>The</strong> key to the rationalization of organic chemistry had, it seemed, been found.<br />
Yet there was one disturbing fact. <strong>The</strong> well-known chemical benzene wouldn't fit. It was known to<br />
have a molecule made up of equal numbers of carbon and hydrogen atoms. Its molecular weight<br />
was known to be 78 and a single carbon-hydrogen combination had a weight of 13. <strong>The</strong>refore, the<br />
benzene molecule had to contain six carbon-hydrogen combinations and its formula had to be<br />
C6H6.<br />
But that meant trouble. By the Kekule formulas, the hydrocarbons (molecules made up of carbon<br />
and hydrogen atoms only) could easily be envisioned as chains of carbon atoms with hydrogen<br />
atoms attached. If all the valences of the carbon atoms were filled with hydrogen atoms, as in<br />
"hexane," whose molecule looks like this --<br />
the compound is said to be saturated. Such saturated hydrocarbons were found to have very little<br />
tendency to react with other substances.<br />
If some of the valences were not filled, unused bonds were added to those connecting the carbon<br />
atoms. Double bonds were formed as in "hexene" --