2 LIMITS
2 LIMITS
2 LIMITS
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
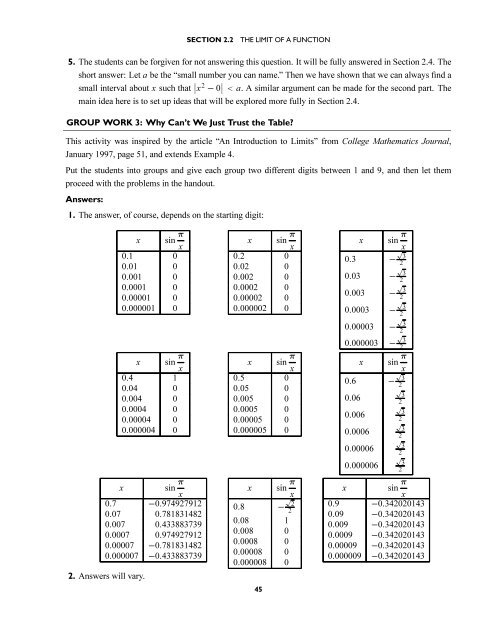
SECTION 2.2THE LIMIT OF A FUNCTION5. The students can be forgiven for not answering this question. It will be fully answered in Section 2.4. Theshort answer: Let a be the “small number you can name.” Then we have shown that we can always find asmallintervalaboutx such that ∣ ∣x 2 − 0 ∣ < a. A similar argument can be made for the second part. Themain idea here is to set up ideas that will be explored more fully in Section 2.4.GROUP WORK 3: Why Can’t We Just Trust the Table?This activity was inspired by the article “An Introduction to Limits” from College Mathematics Journal,January 1997, page 51, and extends Example 4.Put the students into groups and give each group two different digits between 1 and 9, and then let themproceed with the problems in the handout.Answers:1. The answer, of course, depends on the starting digit:x sin π x0.1 00.01 00.001 00.0001 00.00001 00.000001 0x sin π x0.4 10.04 00.004 00.0004 00.00004 00.000004 0x sin π x0.7 −0.9749279120.07 0.7818314820.007 0.4338837390.0007 0.9749279120.00007 −0.7818314820.000007 −0.4338837392. Answers will vary.x sin π x0.2 00.02 00.002 00.0002 00.00002 00.000002 0x sin π x0.5 00.05 00.005 00.0005 00.00005 00.000005 0x0.8 −sin π x√220.08 10.008 00.0008 00.00008 00.000008 045x0.3 −0.03 −0.003 −0.0003 −0.00003 −0.000003 −x0.6 −0.060.0060.00060.000060.000006sin π x√32√32√32√32√32√32sin π x√32√32√32√32√32√32x sin π x0.9 −0.3420201430.09 −0.3420201430.009 −0.3420201430.0009 −0.3420201430.00009 −0.3420201430.000009 −0.342020143