PG lit review.pdf?utm_content=bufferce8e7&utm_medium=social&utm_source=twitter
PG lit review.pdf?utm_content=bufferce8e7&utm_medium=social&utm_source=twitter
PG lit review.pdf?utm_content=bufferce8e7&utm_medium=social&utm_source=twitter
- No tags were found...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
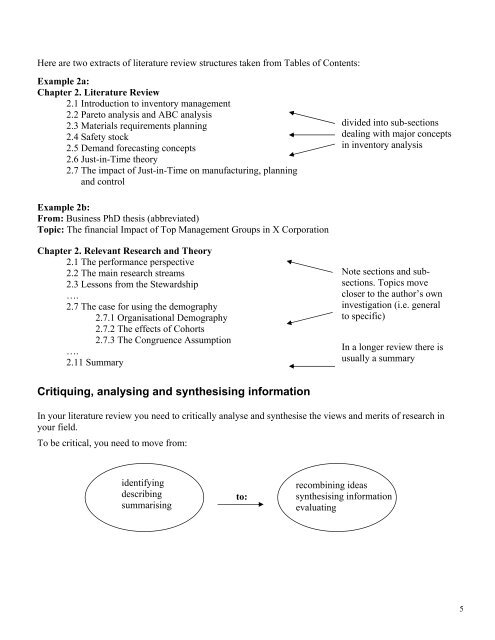
Here are two extracts of <strong>lit</strong>erature <strong>review</strong> structures taken from Tables of Contents:Example 2a:Chapter 2. Literature Review2.1 Introduction to inventory management2.2 Pareto analysis and ABC analysis2.3 Materials requirements planning2.4 Safety stock2.5 Demand forecasting concepts2.6 Just-in-Time theory2.7 The impact of Just-in-Time on manufacturing, planningand controldivided into sub-sectionsdealing with major conceptsin inventory analysisExample 2b:From: Business PhD thesis (abbreviated)Topic: The financial Impact of Top Management Groups in X CorporationChapter 2. Relevant Research and Theory2.1 The performance perspective2.2 The main research streams2.3 Lessons from the Stewardship….2.7 The case for using the demography2.7.1 Organisational Demography2.7.2 The effects of Cohorts2.7.3 The Congruence Assumption….2.11 SummaryNote sections and subsections.Topics movecloser to the author’s owninvestigation (i.e. generalto specific)In a longer <strong>review</strong> there isusually a summaryCritiquing, analysing and synthesising informationIn your <strong>lit</strong>erature <strong>review</strong> you need to critically analyse and synthesise the views and merits of research inyour field.To be critical, you need to move from:identifyingdescribingsummarisingto:recombining ideassynthesising informationevaluating5